
运行级别 linux
When a Linux system boots, it enters its default runlevel and runs the startup scripts associated with that runlevel. You can also switch between runlevels – for example, there’s a runlevel designed for recovery and maintenance operations.
当Linux系统引导时,它将进入其默认运行级别并运行与该运行级别关联的启动脚本。 您还可以在运行级别之间切换–例如,有一个用于恢复和维护操作的运行级别。
Traditionally, Linux used System V-style init scripts – while new init systems will eventually obsolete traditional runlevels, they haven’t yet. For example, Ubuntu’s Upstart system still uses traditional System V-style scripts.
传统上,Linux使用System V风格的初始化脚本-尽管新的初始化系统最终将淘汰传统的运行级别,但它们还没有。 例如,Ubuntu的Upstart系统仍然使用传统的System V样式脚本。
什么是运行级别? (What’s a Runlevel?)
When a Linux system boots, it launches the init processes. init is responsible for launching the other processes on the system. For example, when you start your Linux computer, the kernel starts init, and init executes the startup scripts to initialize your hardware, bring up networking, start your graphical desktop.
当Linux系统启动时,它会启动init进程。 init负责启动系统上的其他进程。 例如,当您启动Linux计算机时,内核将启动init,并且init执行启动脚本以初始化硬件,启动网络,启动图形桌面。
However, there isn’t just one single set of startup scripts init executes. There are multiple run levels with their own startup scripts – for example, one runlevel may bring up networking and launch the graphical desktop, while another runlevel may leave networking disabled and skip the graphical desktop. This means you can drop from “graphical desktop mode” to “text console mode without networking” with a single command, without manually starting and stopping different services.
但是,不仅只有一组启动脚本可以执行init。 具有自己的启动脚本的多个运行级别–例如,一个运行级别可以启动联网并启动图形桌面,而另一个运行级别则可以禁用联网并跳过图形桌面。 这意味着您可以使用单个命令从“图形桌面模式”切换到“无网络的文本控制台模式”,而无需手动启动和停止其他服务。
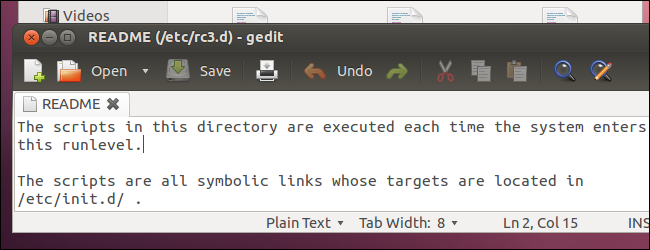
More specifically, init runs the scripts located in a specific directory that corresponds to the runlevel. For example, when you enter runlevel 3 on Ubuntu, init runs the scripts located in the /etc/rc3.d directory.
更具体地说,init运行位于与运行级别相对应的特定目录中的脚本。 例如,当您在Ubuntu上输入运行级别3时,init将运行/etc/rc3.d目录中的脚本。
At least, this is how it works with a traditional System V init system – Linux distributions are beginning to replace the old System V init system. While Ubuntu’s Upstart currently maintains compatibility with SysV init scripts, this is likely to change in the future.
至少,这就是它与传统的System V init系统一起工作的方式-Linux发行版开始取代旧的System V init系统。 尽管Ubuntu的Upstart目前保持与SysV初始化脚本的兼容性,但将来可能会改变。
运行级别 (The Runlevels)
Some runlevels are standard between Linux distributions, while some runlevels vary from distribution to distribution.
有些运行级别是Linux发行版之间的标准配置,而有些运行级别则因发行版本而异。
The following runlevels are standard:
以下运行级别是标准的:
0 – Halt (Shuts down the system.)
0 – 停止 (关闭系统。)
1 – Single User Mode (The system boots into superuser mode without starting daemons or networking. Ideal for booting into a recovery or diagnostics environment.)
1 – 单用户模式 (系统引导至超级用户模式,而无需启动守护程序或网络。非常适合引导至恢复或诊断环境。)
6 – Reboot
6 – 重新启动
Runlevels 2-5 vary depending on distribution. For example, on Ubuntu and Debian, runlevels 2-5 are the same and provide a full multi-user mode with networking and graphical login. On Fedora and Red Hat, runlevel 2 provides multi-user mode without networking (console login only), runlevel 3 provides multi-user mode with networking (console login only), runlevel 4 is unused, and runlevel 5 provides multi-user mode with networking and graphical login.
运行级别2-5取决于发行版。 例如,在Ubuntu和Debian上,运行级别2-5相同,并提供具有网络和图形登录功能的完整多用户模式。 在Fedora和Red Hat上,运行级别2提供了无网络的多用户模式(仅控制台登录),运行级别3提供了具有网络的多用户模式(仅控制台登录),运行级别4未使用,运行级别5提供了多用户模式。网络和图形登录。
切换到其他运行级别 (Switching to a Different Runlevel)
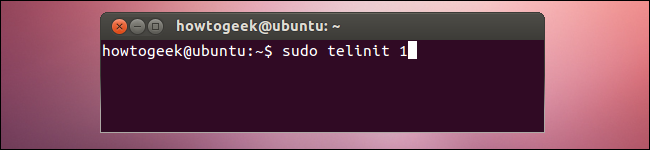
To switch to a different runlevel while the system is already running, use the following command:
要在系统已经运行时切换到另一个运行级别,请使用以下命令:
sudo telinit #
sudo telinit#
Replace # with the number of the runlevel you want to switch to. Omit sudo and run the command as root if you’re running a distribution that doesn’t use sudo.
将#替换为要切换到的运行级别的编号。 如果运行的发行版不使用sudo,请忽略sudo并以root身份运行命令。
直接引导到特定的运行级别 (Booting Directly to a Specific Runlevel)
You can select a runlevel to boot into from the boot loader – Grub, for example. At the start of the boot process, press a key to access Grub, select your boot entry, and press e to edit it.
您可以从启动加载程序(例如Grub)中选择要运行的运行级别。 在启动过程开始时,按一个键以访问Grub,选择您的启动项,然后按e进行编辑。
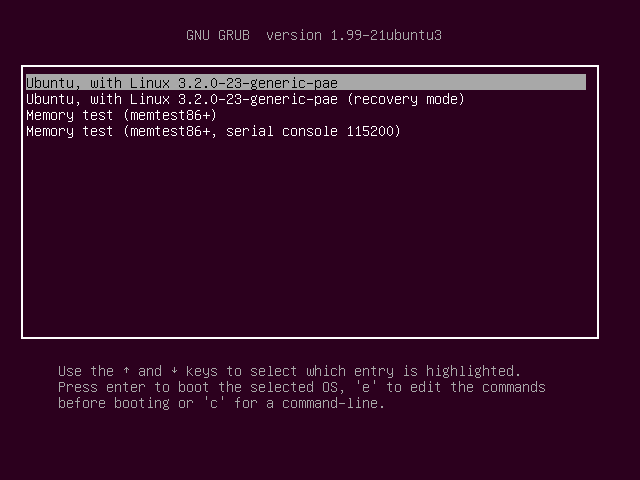
You can add single to the end of the linux line to enter the single-user runlevel (runlevel 1). (Press Ctrl+x to boot after.) This is the same as the recovery mode option in Grub.
您可以在Linux行的末尾添加single来输入单用户运行级别(运行级别1)。 (按Ctrl + x之后启动。)这与Grub中的恢复模式选项相同。
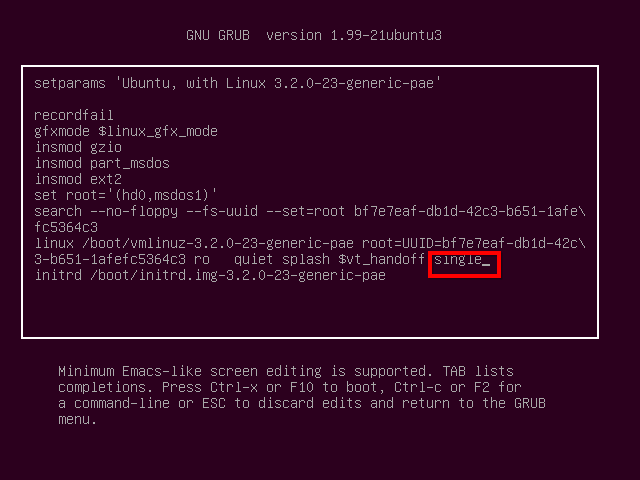
Traditionally, you could specify a number as a kernel parameter and you’d boot to that runlevel – for example, using 3 instead of single to boot to runlevel 3. However, this doesn’t appear to work on the latest versions of Ubuntu – Upstart doesn’t seem to allow it. Similarly, how you change the default runlevel will depend on your distribution.
传统上,您可以将数字指定为内核参数,然后引导至该运行级别–例如,使用3而不是单个引导至运行级别3。但是,这似乎不适用于最新版本的Ubuntu –新贵似乎不允许这样做。 同样,如何更改默认运行级别将取决于您的分发。
While Ubuntu’s Upstart daemon still emulates the SystemV init system, much of this information will change in the future. For example, Upstart is event-based – it can stop and start services when events occur (for example, a service could start when a hardware device is connected to the system and stop when the device is removed.) Fedora also has its own successor to init, systemd.
尽管Ubuntu的Upstart守护程序仍在模拟SystemV初始化系统,但将来很多信息会改变。 例如,Upstart是基于事件的–它可以在事件发生时停止和启动服务(例如,服务可以在硬件设备连接到系统时启动,而在设备被移除时停止。)Fedora也有自己的后继者。初始化,systemd。
翻译自: https://www.howtogeek.com/119340/htg-explains-what-runlevels-are-on-linux-and-how-to-use-them/
运行级别 linux





















 927
927











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








