Linux environments you install from the Store (like Ubuntu and openSUSE) keep their files in a hidden folder. You can access this folder to back up and view files. You can also access your Windows files from the Bash shell.
从商店安装Linux环境(例如Ubuntu和openSUSE)将其文件保存在隐藏的文件夹中。 您可以访问此文件夹以备份和查看文件。 您还可以从Bash Shell访问Windows文件。
Update: Starting with Windows 10’s May 2019 Update, there’s now an official, safe way to access your Linux files from Windows applications.
更新:从Windows 10的2019年5月更新开始,现在有一种官方,安全的方法可以从Windows应用程序访问Linux文件。
不要使用Windows工具修改Linux文件 (Don’t Modify Linux Files With Windows Tools)
Microsoft strongly warns against adding or modifying Linux files with Windows software. This could cause metadata problems or file corruption, and may force you to uninstall and reinstall your Linux distribution to fix it. However, you can still view and back up your Linux files using Windows software, and that won’t cause any problems.
Microsoft强烈警告不要使用Windows软件添加或修改Linux文件。 这可能会导致元数据问题或文件损坏,并可能迫使您卸载并重新安装Linux发行版以对其进行修复。 但是,您仍然可以使用Windows软件查看和备份Linux文件,这不会引起任何问题。
In other words, treat the Linux folder as if it were read-only from within Windows. Don’t use any Windows tool, including graphical apps or command line tools, to modify them. Don’t create new files within these folders using Windows tools, either.
换句话说,将Linux文件夹视为Windows文件夹中的只读文件夹。 请勿使用任何Windows工具(包括图形应用程序或命令行工具)对其进行修改。 也不要使用Windows工具在这些文件夹中创建新文件。
If you do want to work with a file from both the Linux and Windows environments, you should create it in your Windows file system. For example, if you have a folder at C:\project in Windows, you could also access it at /mnt/c/project in the Linux environment. Because it’s stored on the Windows file system and is accessed under /mnt/c, it’s safe to modify the file with either Windows or Linux tools.
如果确实要使用Linux和Windows环境中的文件,则应在Windows文件系统中创建该文件。 例如,如果您在Windows中的C:\ project下有一个文件夹,那么您也可以在Linux环境中的/ mnt / c / project上访问它。 因为它存储在Windows文件系统上,并且可以在/ mnt / c下访问,所以可以安全地使用Windows或Linux工具来修改文件。
Windows在其中存储Linux文件的位置 (Where Windows Stores the Linux Files)
Your Linux file system is stored in a hidden folder for a reason, as Microsoft doesn’t want you tampering with it. But, if you need to view or back up some files, you’ll find them stored in a hidden folder. To access it, open File Explorer and plug the following address into the address bar:
您Linux文件系统存储在一个隐藏的文件夹中是有原因的,因为Microsoft不想您对其进行篡改。 但是,如果您需要查看或备份某些文件,则会发现它们存储在隐藏文件夹中。 要访问它,请打开文件资源管理器,然后将以下地址插入地址栏:
%userprofile%\AppData\Local\Packages
(This takes you to C:\Users\NAME\AppData\Local\Packages . You can also show hidden folders in File Explorer and navigate here manually, if you prefer.
(这会将您带到C:\Users\NAME\AppData\Local\Packages 。您也可以在文件资源管理器中显示隐藏的文件夹,并根据需要手动导航到此处。
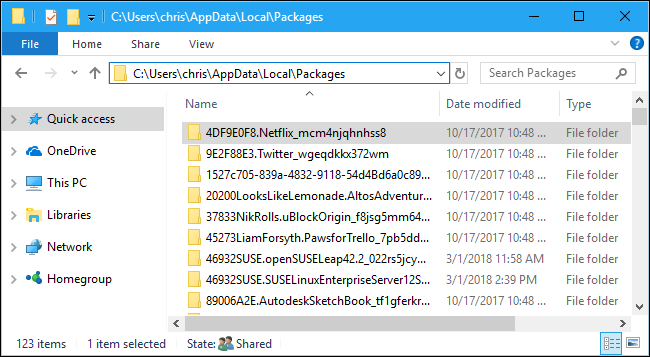
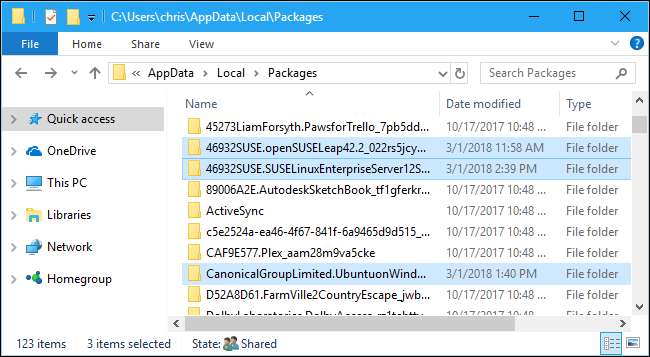
In this folder, double-click the folder for the Linux distribution whose files you want to view:
在此文件夹中,双击您要查看其文件的Linux发行版的文件夹:
Ubuntu: CanonicalGroupLimited.UbuntuonWindows_79rhkp1fndgsc
Ubuntu :CanonicalGroupLimited.UbuntuonWindows_79rhkp1fndgsc
openSUSE Leap 42: 46932SUSE.openSUSELeap42.2_022rs5jcyhyac
openSUSE Leap 42 :46932SUSE.openSUSELeap42.2_022rs5jcyhyac
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12: 46932SUSE.SUSELinuxEnterpriseServer12SP2_022rs5jcyhyac
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 :46932SUSE.SUSELinuxEnterpriseServer12SP2_022rs5jcyhyac
The names of these folders may change slightly in the future. Just look for a folder named after the Linux distribution.
这些文件夹的名称将来可能会稍有变化。 只需查找以Linux发行版命名的文件夹。
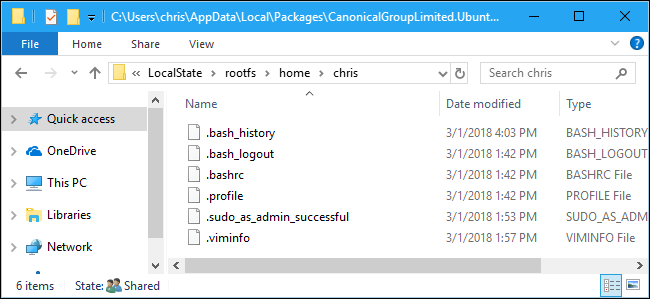
In the Linux distribution’s folder, double-click the “LocalState” folder, and then double-click the “rootfs” folder to see its files.
在Linux发行版的文件夹中,双击“ LocalState”文件夹,然后双击“ rootfs”文件夹以查看其文件。
In other words, the files are stored at:
换句话说,文件存储在:
C:\Users\NAME\AppData\Local\Packages\DISTRO_FOLDER\LocalState\rootfs
Note: In older versions of Windows 10, these files were stored under C:\Users\Name\AppData\Local\lxss. This changed starting with the Fall Creators Update.
注意:在Windows 10的旧版本中,这些文件存储在C:\ Users \ Name \ AppData \ Local \ lxss下。 从Fall Creators Update开始,情况发生了变化。
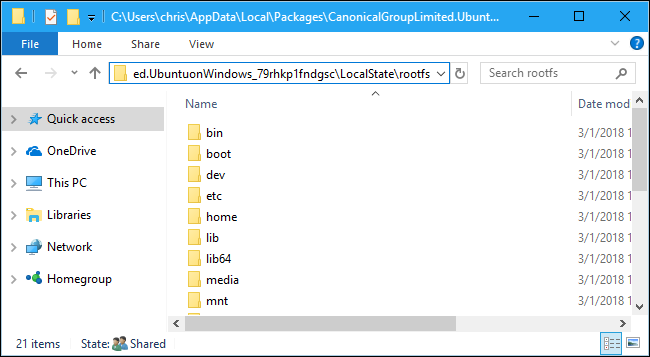
To view the files stored in your home folder, double-click the “home” folder, and then double-click your UNIX username.
要查看存储在主文件夹中的文件,请双击“主”文件夹,然后双击您的UNIX用户名。
Remember, don’t modify any of these files or add files to these folders from File Explorer!
请记住,不要修改这些文件中的任何一个,也不要从文件资源管理器中将文件添加到这些文件夹中!
Windows系统驱动器在Linux中的显示位置 (Where Your Windows System Drive Appears in Linux)
The Windows Subsystem for Linux makes your full Windows system drive available so you can work with the same files in both environments. However, the Bash environment doesn’t just dump you in your C:\ drive. Instead, it places you in your UNIX account’s home directory within the Linux environment’s file system.
适用于Linux的Windows子系统使您可以使用完整的Windows系统驱动器,因此您可以在两种环境中使用相同的文件。 但是,Bash环境不仅会将您转储到C:\驱动器中。 相反,它将您放置在Linux环境文件系统中UNIX帐户的主目录中。
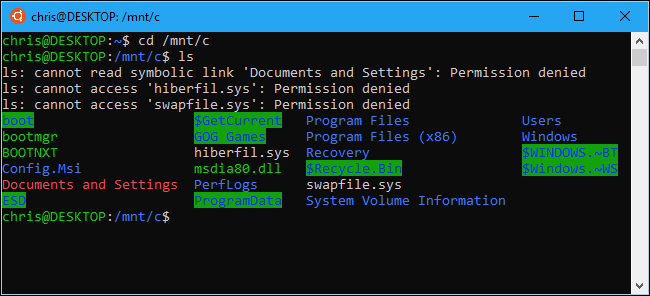
Your Windows system drive and other connected drives are exposed in the /mnt/ directory there, where other drives are traditionally made available in the Linux directory structure. Specifically, you’ll find the C: drive at the following location in the Bash environment:
Windows系统驱动器和其他连接的驱动器位于/ mnt /目录中,而其他驱动器通常在Linux目录结构中可用。 具体来说,您将在Bash环境中的以下位置找到C:驱动器:
/mnt/c
To change to this directory with the cd command, just type:
要使用cd命令更改到此目录,只需键入:
cd /mnt/c
If you have a D: drive, you’ll find it located at /mnt/d, and so on.
如果您有D:驱动器,则会在/ mnt / d中找到它,依此类推。
For example, to access a file stored at C:\Users\Chris\Downloads\File.txt, you’d use the path /mnt/c/Users/Chris/Downloads/File.txt in the Bash environment. And yes, it’s case-sensitive, so you need “Downloads” and not “downloads.”
例如,要访问存储在C:\ Users \ Chris \ Downloads \ File.txt中的文件,可以在Bash环境中使用路径/mnt/c/Users/Chris/Downloads/File.txt。 是的,它区分大小写,因此您需要“下载”而不是“下载”。
You can also mount external drives and network locations to access more files from within the Linux environment.
您还可以挂载外部驱动器和网络位置,以从Linux环境中访问更多文件。
Note that, when accessing Windows system files, your Bash shell environment has the permissions it was launched with. If you launched it normally from the shortcut, it will have the same file access permissions your Windows user account does.
请注意,在访问Windows系统文件时,您的Bash Shell环境具有启动时所使用的权限。 如果您通常从快捷方式启动它,它将具有与Windows用户帐户相同的文件访问权限。
For example, if you want to access a system folder your user account doesn’t have permission to access, you’d need to right-click the Bash shell shortcut and select “Run as Administrator” to launch the Bash shell with Windows Administrator privileges.
例如,如果您要访问系统文件夹,而您的用户帐户没有访问权限,则需要右键单击Bash shell快捷方式,然后选择“以管理员身份运行”以使用Windows Administrator特权启动Bash Shell。 。
This works just like the Command Prompt, which needs to be launched as Administrator if you need write access to Administrator-only files, or write access to system files. You can’t just use sudo in the Bash environment.
就像命令提示符一样,如果您需要对仅管理员文件的写访问权限或对系统文件的写访问权限,则需要以管理员身份启动命令提示符。 您不能只在Bash环境中使用sudo 。





















 1618
1618











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








