
On Linux, fd is an easier alternative to the find command. It has a simplified syntax, uses sensible defaults, and has built-in common-sense behavior. Let’s take it through its paces.
在Linux上, fd是find命令的更简单替代方案。 它具有简化的语法,使用合理的默认值,并且具有内置的常识行为。 让我们通过它的步伐。
fd vs find:有什么区别? (fd versus find: What’s the Difference?)
The fd command isn’t meant to replace the traditional find command, which has been on Linux, well, forever. Instead, fd tries to satisfy the majority of common uses of find in a more straightforward way—and, it’s often eight or nine times faster than find. You can see some of its benchmarks on the project’s GitHub repository page.
fd命令并不能代替Linux上的传统find命令,这是永远的。 取而代之的是, fd试图以更直接的方式满足find的大多数常见用法-并且通常比find快八或九倍。 您可以在项目的GitHub存储库页面上查看其一些基准测试。
fd has a colorized output, similar to that of some ls modes. It’s recursive, but doesn’t search hidden directories by default. It knows about Git and will also automatically ignore any patterns in your “.gitignore” file.
fd具有彩色输出,类似于某些ls模式的输出。 它是递归的,但默认情况下不会搜索隐藏目录。 它了解Git ,还将自动忽略“ .gitignore”文件中的任何模式。
fd is case insensitive by default. However, if your search pattern contains an uppercase letter, fd operates in a case sensitive mode. Of course, you can override the defaults, but, in many cases, they work in your favor.
fd默认情况下不区分大小写。 但是,如果您的搜索模式包含大写字母,则fd在区分大小写的模式下运行。 当然,您可以覆盖默认值,但是在许多情况下,默认值对您有利。
安装fd (Installing fd)
Since Ubuntu 19.04 (Disco Dingo,) you can install fd directly by calling the officially maintained package with apt-get. If you’re running an older version of Ubuntu, check the installation instructions on the Git hub page.
从Ubuntu 19.04(Disco Dingo)开始,您可以通过使用apt-get调用正式维护的软件包直接安装fd 。 如果您正在运行旧版本的Ubuntu,请查看Git中心页面上的安装说明。
Type the following:
输入以下内容:
sudo apt-get install fd-find

In Ubuntu, the command is fdfind to avoid a name clash with another existing utility. If you want it to be fd, you can set up an alias:
在Ubuntu中,命令fdfind以避免与另一个现有实用程序发生名称冲突。 如果希望将其设为fd ,则可以设置别名:
alias fd=fdfind

To make the alias persistent so it will remain available after reboots, put it in your “.bashrc” or “.bash_aliases” file.
要使别名保持不变,以便在重新启动后仍然可用,请将其放在“ .bashrc”或“ .bash_aliases”文件中。
To install fd on Fedora, type this command:
要在Fedora上安装fd ,请键入以下命令:
sudo dfn install fd-find

On Manjaro, type the following:
在Manjaro上,键入以下内容:
sudo pacman -Syu fd

fd与fdfind (fd versus fdfind)
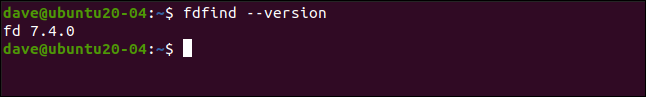
To avoid confusion, we’ve left the command with its default name, fdfind, on our Ubuntu test PC. fd and fdfind are exactly the same command, as you’ll see in the following example (if you ask fdfind to show its version, it calls itself “fd”):
为避免混淆,我们在Ubuntu测试PC上保留了命令的默认名称fdfind 。 fd和fdfind是完全相同的命令,如以下示例所示(如果要求fdfind显示其版本, fdfind其为“ fd”):
fdfind --version
We’ll call the command “fed,” but in the examples, we’ll use the Ubuntu “fdfind.” On other Linux distributions, you can type “fd” instead of “fdfind” to save a few keystrokes.
我们将命令称为“ fed”,但在示例中,我们将使用Ubuntu“ fdfind”。 在其他Linux发行版中,可以键入“ fd”而不是“ fdfind”来保存一些击键。
使用fd进行简单搜索 (Simple Searches with fd)
If you use fd with no command-line options, it behaves a little like ls, except it lists files in subdirectories by default.
如果使用不带命令行选项的fd ,则其行为类似于ls ,除了默认情况下会在子目录中列出文件。
Type the following:
输入以下内容:
fdfind

The output appears in different colors for different file types and directories.
对于不同的文件类型和目录,输出以不同的颜色显示。

To see files of a specific type, use the -e
要查看特定类型的文件,请使用-e
For example, you could type the following:
例如,您可以键入以下内容:
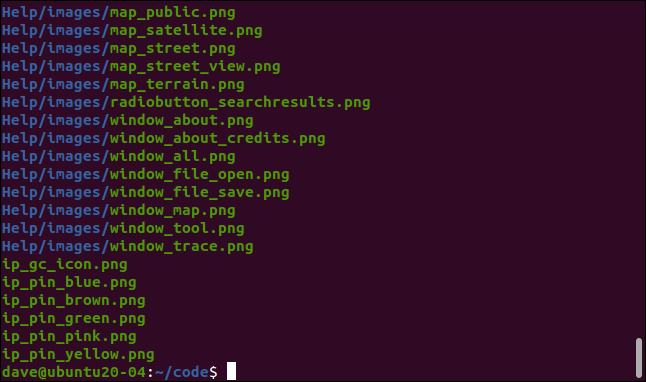
fdfind -e png

Now, the only files listed are PNG image files.
现在,列出的唯一文件是PNG图像文件。
To look for a single file, type its name on the command line, like so:
要查找单个文件,请在命令行上键入其名称,如下所示:
fdfind index.page
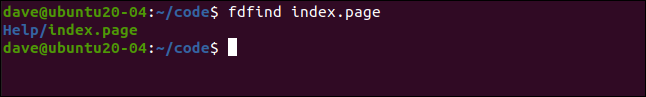
The file is found and happens to be in a subdirectory. We didn’t have to tell fd to search recursively.
找到该文件,并且恰好在子目录中。 我们不必告诉fd进行递归搜索。
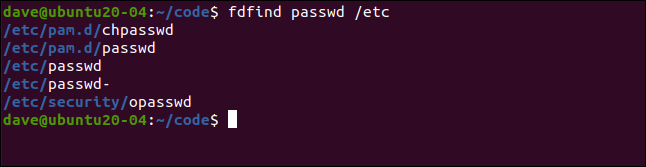
To have the search start in a particular directory, include a file path on the command line. The following command will start a search in the “/etc” directory, and look for files that include “passwd” in the file name:
要在特定目录中开始搜索,请在命令行上包含文件路径。 以下命令将在“ / etc”目录中开始搜索,并查找文件名中包含“ passwd”的文件:
fdfind passwd /etc
Here, we’re searching for all C source code files that contain “coord” in the file name:
在这里,我们正在搜索文件名中包含“ coord”的所有C源代码文件:
fdfind -e c coord
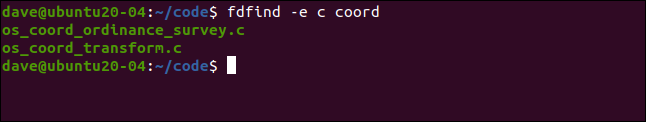
Two matching files were found.
找到两个匹配的文件。
fd和Git (fd and Git)
Git is an extremely popular source code version control system. If you use Git on your computer, you probably use “.gitignore” files to tell Git which files it should concern itself with, and which it can ignore. By default, fd respects the settings in your “.gitignore” files.
Git是一种非常流行的源代码版本控制系统。 如果您在计算机上使用Git,则可能使用“ .gitignore”文件来告诉Git它应该关注的文件以及可以忽略的文件。 默认情况下, fd遵循“ .gitignore”文件中的设置。
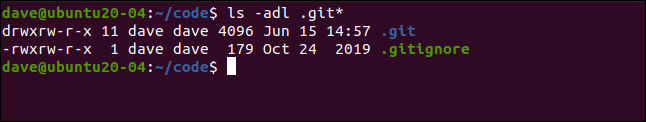
In this directory, we’ve got a Git repository and “.gitignore” file. We type the following:
在此目录中,我们有一个Git存储库和“ .gitignore”文件。 我们输入以下内容:
ls -adl .git*
Let’s ask fd to list any files that contain “coord” in the file name. We’ll then repeat the search and use the -I (no ignore) option. This tells fd to ignore the settings in the “.gitignore” file and report every matching file.
让我们让fd列出文件名中包含“ coord”的所有文件。 然后,我们将重复搜索并使用-I (不可忽略)选项。 这告诉fd忽略“ .gitignore”文件中的设置,并报告每个匹配的文件。
To do all of this, we type the following:
为此,我们键入以下内容:
fdfind coord
fdfind coord -I
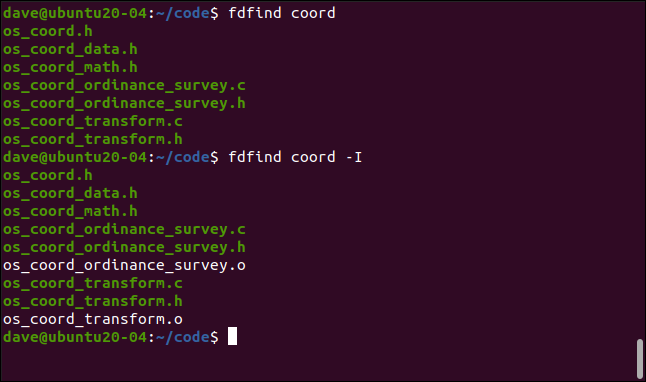
The two extra files in the second set of results are object files. These are created when a file program is compiled. They’re then used by the linker to create the final executable version of the program.
第二组结果中的两个额外文件是目标文件。 这些是在编译文件程序时创建的。 然后,链接器将它们用于创建程序的最终可执行版本。
Object files are typically ignored by source code version control programs. They’re regenerated every time you compile your program, so you don’t have to store copies of them. There’s an entry in the “.gitignore” file that instructs Git to ignore object files, and, by default, fd ignores them, too.
目标文件通常被源代码版本控制程序忽略。 每次编译程序时都会重新生成它们,因此您不必存储它们的副本。 “ .gitignore”文件中有一个条目,指示Git忽略目标文件,默认情况下, fd忽略它们。
The -I (no ignore) option forces fd to return everything it finds, rather than being guided by the “.gitginore” file.
-I (不忽略)选项强制fd返回找到的所有内容,而不是由“ .gitginore”文件引导。
文件类型和区分大小写 (File Types and Case Sensitivity)
You can ask fd to look for directories, files (including those that are executable and empty), and symbolic links. You can do so by using the -t (type) option, followed by one of the letters below:
您可以要求fd查找目录,文件(包括可执行文件和空文件)以及符号链接。 您可以使用-t (类型)选项,然后使用以下字母之一进行操作:
f: File.
f :文件。
d: Directory.
d :目录。
l: Symbolic link.
l :符号链接。
x: Executable file.
x :可执行文件。
e: Empty file.
e :空文件。
The following looks for a directory called images:
以下内容查找名为images的目录:
fdfind -td images
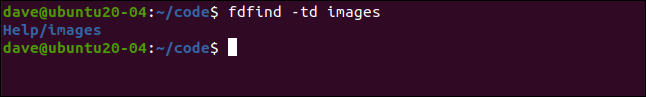
A match is found, one subdirectory lower than the current one.
找到一个匹配项,子目录比当前子目录低。
Let’s see how case sensitivity works with search patterns. We type the following to first search for files that contain “geo” in their file names, and then for those that contain “Geo” in their file names:
让我们看看区分大小写如何与搜索模式一起使用。 我们键入以下内容,首先搜索文件名中包含“ geo”的文件,然后搜索文件名中包含“ Geo”的文件:
fdfind -tf geo
fdfind -tf Geo

In the first command, we used a lowercase search pattern, which caused fd to operate in a case-insensitive way. This means both “Geo” and “geo” are valid matches.
在第一个命令中,我们使用小写搜索模式,这导致fd以不区分大小写的方式运行。 这意味着“地理位置”和“地理位置”都是有效的匹配项。
Our second command contained an uppercase character, which caused fd to operate in a case-sensitive manner. This means only “Geo” is a valid match.
我们的第二个命令包含一个大写字符,这导致fd以区分大小写的方式运行。 这意味着只有“ Geo”是有效的匹配项。
命令执行 (Command Execution)
The fd command allows you to launch another command and execute it on each of the found files.
使用fd命令可以启动另一个命令,并在找到的每个文件上执行该命令。
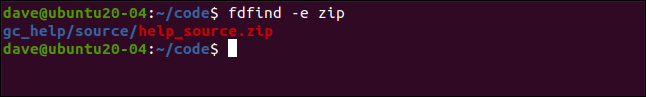
Let’s say we know there’s a Zip file somewhere in our source code directory tree. We can look for it using the following command, which searches for files with the ZIP extension:
假设我们知道在我们的源代码目录树中的某个地方有一个Zip文件。 我们可以使用以下命令来查找它,该命令搜索具有ZIP扩展名的文件:
fdfinf -e zip
With the -x (exec) option, you can pass each found file to another command to be processed by it. For example, we can type the following to call the unzip utility to unzip our ZIP file (the “{}” is a placeholder representing the found file):
使用-x (exec)选项,您可以将找到的每个文件传递给另一个命令,以供其处理。 例如,我们可以键入以下内容来调用unzip实用程序以解压缩我们的ZIP文件(“ {}”是代表找到的文件的占位符):
fdfind -e zip -x unzip {}
This will unzip the file in the current working directory. If we want it to be unzipped in the directory containing the ZIP file, we can use one of the following placeholders:
这会将文件解压缩到当前工作目录中。 如果我们希望将其解压缩到包含ZIP文件的目录中,则可以使用以下占位符之一:
{}: The full file path and name of the found file.
{} :完整的文件路径和找到的文件的名称。
{/}: The file name of the found file.
{/} :找到的文件的文件名。
{//}: The directory containing the found file.
{//} :包含找到的文件的目录。
{/.}: The file name of the found file, without the extension.
{/。} :找到的文件的文件名,不带扩展名。
For our ZIP file to be found and unzipped in the directory that contains it, we can use the unzip -d (directory) option, and pass in the parent directory placeholder ({//}):
为了找到我们的ZIP文件并将其解压缩到包含它的目录中,我们可以使用unzip -d (目录)选项,并传入父目录占位符( {//} ):
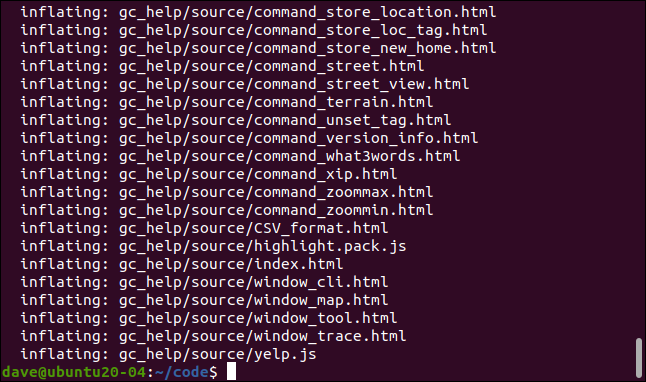
fdfind -e zip -x unzip {} -d {//}

The ZIP file is then located and the unzipped in its parent directory.
然后找到ZIP文件,并将其解压缩到其父目录中。
您要去的地方? (Your Go-to Find?)
Because it covers the most common uses with such simplicity, fd can easily become your go-to “find” command. Whenever you need its more advanced features, you can always return to that seasoned veteran, find.
因为它以这种简单的方式涵盖了最常见的用途,所以fd可以轻松地成为您的“查找”命令。 每当您需要其更高级的功能时,都可以随时返回该经验丰富的资深人士, find 。
翻译自: https://www.howtogeek.com/682244/how-to-use-the-fd-command-on-linux/























 546
546

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








