
As 4K replaces HD in our homes, manufacturers are unveiling some interesting marketing jargon, like “Ultra HD upscaling” (UHD). But upscaling isn’t some unique feature—it just allows 4K TVs to work with lower resolution video formats, like 1080p and 720p.
随着4K取代我们家庭中的高清,制造商推出了一些有趣的营销术语,例如“超高清升级”(UHD)。 但是升级并不是某些独特功能,它仅允许4K电视使用分辨率较低的视频格式,例如1080p和720p。
所有电视都有升级 (All TVs Have Upscaling)
Upscaling means low-resolution content will fill your entire TV screen. Without it, a low-resolution video takes up less than half of the screen space. This is a typical feature on all TVs. Even 1080p TVs had it—they could upscale 720p content and display it in full-screen mode on a 1080p screen.
升级意味着低分辨率内容将填满整个电视屏幕。 没有它,低分辨率视频将占据不到一半的屏幕空间。 这是所有电视上的典型功能。 即使是1080p电视也可以,它们可以升级720p内容,并在1080p屏幕上以全屏模式显示。
UHD upscaling is what makes your 4K TV work like any other. It can take lower-resolution content and display it on the entire 4K screen.
超高清升级是使您的4K电视像其他任何电视一样工作的原因。 它可以获取较低分辨率的内容并将其显示在整个4K屏幕上。
Upscaled 1080p content on a 4K screen often looks better than 1080p content on a normal 1080p screen. But upscaling isn’t magic—you won’t get the sharp image you would from true, native 4K content. Here’s how it works.
在4K屏幕上放大的1080p内容通常看起来比在普通1080p屏幕上的1080p内容更好。 但是升级并不是魔术,您将无法从真实的原始4K内容中获得清晰的图像。 运作方式如下。
在物理和视觉层面都存在分辨率 (Resolution Exists at a Physical and Visual Level)
Before getting into upscaling, we need to understand the concept of image resolution. At a glance, it’s a relatively simple concept. An image or video with a high resolution looks “better” than an image or video with a low resolution.
在进行升级之前,我们需要了解图像分辨率的概念。 乍一看,这是一个相对简单的概念。 具有高分辨率的图像或视频看起来比具有低分辨率的图像或视频“更好”。
However, we tend to forget some key aspects, namely, the difference between physical resolution and optical resolution. These aspects work together to create a good image, and they’re the basis for understanding upscaling. We’re also going to cover pixel density—but don’t worry—we’ll keep things short and sweet.
但是,我们往往会忘记一些关键方面,即物理分辨率和光学分辨率之间的差异。 这些方面共同创造出良好的形象,它们是了解升级的基础。 我们还将介绍像素密度-但不用担心-我们将使事情简短有趣。
Physical Resolution: On a TV spec sheet, the physical resolution is simply referred to as “resolution.” It’s the number of pixels on a display. A 4K TV has more pixels than a 1080p TV, and a 4K image is four times the size of a 1080p image. All 4K displays, regardless of their size, contain the same number of pixels. While TVs with a high physical resolution can use their extra pixels to offer additional detail, it doesn’t always work out that way. Physical resolution is at the mercy of optical resolution.
物理分辨率:在电视规格表上,物理分辨率简称为“分辨率”。 它是显示器上的像素数。 4K电视的像素比1080p电视的像素多,而4K图像的大小是1080p图像的四倍。 所有4K显示器,无论尺寸大小,均包含相同数量的像素。 虽然物理分辨率较高的电视可以使用其额外的像素来提供更多的细节,但并非总是如此。 物理分辨率受光学分辨率的支配。
Optical Resolution: This is why your old disposable camera photos look better than your pretentious friend’s fancy digital camera photos. When a photo looks sharp and has a clear dynamic range, it has a high optical resolution. TVs sometimes squander their high physical resolution by displaying video with a crappy optical resolution. This leads to blurry images and contrast. Sometimes, this is a result of upscaling, but we’ll get back to that in a minute.
光学分辨率:这就是为什么您的旧一次性相机照片看上去比自命不凡的朋友喜欢的数码相机照片更好。 当照片看起来清晰且具有清晰的动态范围时,它具有很高的光学分辨率。 电视有时会通过显示光学分辨率低的视频来浪费其高物理分辨率。 这会导致图像模糊和对比度。 有时,这是升级的结果,但是我们将在一分钟内再次讨论。
Pixel Density: The number of pixels per inch on a display. All 4K displays contain the same amount of pixels, but on smaller 4K displays, the pixels are closer to each other, so they have a high pixel density. A 4K iPhone, for example, has a higher pixel density than a 70-inch 4K TV. We’re mentioning this to reinforce the idea that screen size isn’t the same thing as physical resolution, and that a screen’s pixel density doesn’t define its physical resolution.
像素密度:显示器上每英寸的像素数。 所有4K显示器都包含相同数量的像素,但是在较小的4K显示器上,像素彼此靠近,因此它们具有高像素密度。 例如,4K iPhone比70英寸4K电视具有更高的像素密度。 我们提到这一点是为了加强这样的观念,即屏幕尺寸与物理分辨率不同,并且屏幕的像素密度并未定义其物理分辨率。
Now that we’re all brushed up on the difference between physical and optical resolution, it’s time to get into upscaling.
既然我们都已经了解了物理分辨率和光学分辨率之间的差异,那么该开始进行扩展了。
放大使图像“更大” (Upscaling Makes an Image “Bigger”)
Every TV contains a mess of interpolation algorithms, which are used to upscale low-resolution images. These algorithms effectively add pixels to an image to increase their resolution. But why would you need to increase an image’s resolution?
每台电视都包含一堆插值算法,这些插值算法用于放大低分辨率图像。 这些算法有效地将像素添加到图像以提高其分辨率。 但是,为什么需要增加图像的分辨率?
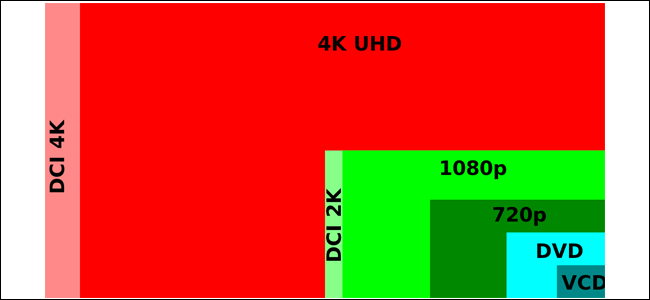
Remember, physical resolution is defined by the number of pixels on a display. It has nothing to do with the actual size of your TV. A 1080p TV screen is comprised of only 2,073,600 pixels, while a 4K screen has 8,294,400. If you show a 1080p video on a 4K TV without upscaling, the video will take up only a quarter of the screen.
请记住,物理分辨率是由显示器上的像素数定义的。 它与电视的实际尺寸无关。 1080p电视屏幕仅包含2,073,600像素,而4K屏幕具有8,294,400像素。 如果您在不升级的情况下在4K电视上显示1080p视频,则视频将仅占据屏幕的四分之一。
For a 1080p image to fit a 4K display, it needs to gain 6 million pixels through the upscaling process (at which point, it will become a 4K image). However, upscaling relies on a process called interpolation, which is really just a glorified guessing game.
对于适合4K显示屏的1080p图像,它需要通过放大过程获得600万像素(此时,它将变成4K图像)。 但是,升级依赖于称为插值的过程,这实际上只是一个美化的猜测游戏。
升级降低光学分辨率 (Upscaling Reduces Optical Resolution)
There are several ways to interpolate an image. The most basic is called “nearest neighbor” interpolation. To perform this process, an algorithm adds a mesh of “blank” pixels to an image, and then guesses which color value each blank pixel should be by looking at its four neighboring pixels.
有几种插值图像的方法。 最基本的称为“最近邻”插值。 为了执行此过程,一种算法将“空白”像素的网格添加到图像,然后通过查看其四个相邻像素来猜测每个空白像素应具有的颜色值。
For example, a blank pixel surrounded by white pixels will turn out white; whereas a blank pixel surrounded by white and blue pixels might come out light blue. It’s a straightforward process, but it leaves a lot of digital artifacts, blur, and rugged outlines in an image. In other words, interpolated images have a poor optical resolution.
例如,被白色像素包围的空白像素将变成白色; 而被白色和蓝色像素包围的空白像素可能会变成浅蓝色。 这是一个简单的过程,但是会在图像中留下许多数字假象,模糊和粗糙的轮廓。 换句话说,内插图像具有较差的光学分辨率。

Compare these two images. The one on the left is unedited, and the one on the right is the victim of the nearest neighbor interpolation process. The image on the right looks terrible, even though it’s the same physical resolution as the one on the left. This happens on a small scale every time your 4K TV uses nearest neighbor interpolation to upscale an image.
比较这两个图像。 左侧的一个未编辑,右侧的一个是最近邻插值过程的受害者。 即使其物理分辨率与左侧的分辨率相同,右侧的图像看起来也很糟糕。 每当您的4K电视使用最近邻插值来放大图像时,这种情况都会在小范围内发生。
“Wait a minute,” you might be saying. “My new 4K TV doesn’t look anything like this!” Well, that’s because it doesn’t rely entirely on nearest neighbor interpolation—it uses a mix of methods to upscale images.
您可能会说:“等一下。” “我的新4K电视看起来不像这样!” 嗯,这是因为它不完全依赖于最近邻插值-它使用多种方法来放大图像。
升级尝试也无法解决光学分辨率 (Upscaling Tries to Tackle Optical Resolution, Too)
Okay, so nearest neighbor interpolation is flawed. It’s a brute-force method for increasing an image’s resolution that doesn’t take optical resolution into account. That’s why TVs use two other forms of interpolation alongside nearest neighbor interpolation. These are called bicubic (smoothing) interpolation and bilinear (sharpening) interpolation.
好的,所以最近邻居插值有缺陷。 这是一种提高图像分辨率的蛮力方法,没有考虑光学分辨率。 这就是电视在与最近邻插值一起使用其他两种插值形式的原因。 这些称为双三次(平滑)插值和双线性(锐化)插值。

With bicubic (smoothing) interpolation, each pixel added to an image looks to its 16 neighboring pixels to take on a color. This results in an image that’s decidedly “soft.” On the other hand, bilinear (sharpening) interpolation only looks to its nearest two neighbors and produces a “sharp” image. By mixing these methods—and applying some filters for contrast and color—your TV can generate an image that has no noticeable loss in optical quality.
通过双三次(平滑)插值,添加到图像中的每个像素都将使其16个相邻像素看起来像彩色。 这样得出的图像肯定是“柔和的”。 另一方面,双线性(锐化)插值仅查找其最近的两个邻居,并生成“锐化”图像。 通过混合使用这些方法(并为对比度和颜色应用一些滤镜),您的电视所生成的图像不会出现明显的光学质量损失。
Of course, interpolation is still a guessing game. Even with proper interpolation, some video can take on “ghosting” after being upscaled—especially if your cheap TV sucks at upscaling. These artifacts also become more apparent when super-low-quality images (720p and lower) are upscaled to 4K resolution, or when images are upscaled on insanely large TVs with a low pixel density.
当然,插值仍然是一个猜谜游戏。 即使采用适当的插值方式,某些视频在放大后也会出现“重影”现象,尤其是如果您的廉价电视在放大时糟透了。 当将超低质量的图像(720p及更低)放大到4K分辨率时,或者在像素密度低的疯狂大型电视上放大图像时,这些伪影也会变得更加明显。

The above image isn’t an example of upscaling from a TV. Instead, it’s an example of the upscaling done for the Buffy The Vampire Slayer HD DVD release (taken from a video essay by Passion of The Nerd). It’s a good (albeit extreme) example of how poor interpolation can ruin an image. No, Nicholas Brendon isn’t wearing some waxy vampire makeup, that’s just what happened to his face during the upscaling process.
上面的图像不是电视升级的示例。 相反,这是Buffy The Vampire Slayer HD DVD版本升级的示例(摘自Passion of The Nerd的视频文章)。 这是一个很好的(尽管极端)的例子,说明插值效果差会破坏图像。 不,尼古拉斯·布伦登(Nicholas Brendon)没有穿着蜡质的吸血鬼妆,这就是在升级过程中脸部发生的一切。
While all TVs offer upscaling, some might have better upscaling algorithms than others, resulting in a better picture.
虽然所有电视都提供升频功能,但某些电视可能具有比其他电视更好的升频算法,从而获得更好的图像。
升级是必要的,而且很少引起注意 (Upscaling Is Necessary and Rarely Noticeable)
Even with all of its faults, upscaling is a good thing. It’s a process that usually goes off without a hitch and enables you to watch a variety of video formats on the same TV. Is it perfect? Of course not. That’s why some film and video game purists prefer to enjoy old art on its intended medium: old-ass TVs. But, as of right now, upscaling isn’t something to get too excited about. Nor is it something to get too upset about.
即使存在所有故障,扩大规模也是一件好事。 这个过程通常顺利进行,使您能够在同一台电视上观看各种视频格式。 完美吗? 当然不是。 这就是为什么一些电影和视频游戏的纯粹主义者更喜欢在其预期的媒介(老式电视)上欣赏老式艺术品的原因。 但是,到目前为止,提升规模并不是一件令人兴奋的事情。 也不要太生气。
It’s worth mentioning that 8K, 10K, and 16K video formats are already supported by some of the hardware we use every day. If upscaling technology can’t catch up with these high-resolution formats, there’s a chance it will result in a much greater loss in quality than what we’re used to.
值得一提的是,我们每天使用的某些硬件已经支持8K,10K和16K视频格式。 如果升级技术无法赶上这些高分辨率格式,则很有可能会导致质量损失比我们以往所承受的损失大得多。
Since manufacturers and streaming services are still dragging their feet toward 4K, though, maybe we shouldn’t worry about 8K just yet.
由于制造商和流媒体服务仍在朝着4K方向发展,也许我们现在不必担心8K。
翻译自: https://www.howtogeek.com/427091/what-is-upscaling-on-a-tv/







 电视升级( Upscaling)是指将低分辨率内容转换以适应更高分辨率屏幕的过程,如4K电视。所有电视都有升级功能,4K电视通过插值算法将较低分辨率的视频内容放大到4K屏幕。虽然升级可以改善图像,但它并不等同于真实4K内容的清晰度。升级过程中,物理分辨率和光学分辨率是关键因素,而插值算法的质量决定了升级效果。尽管存在瑕疵,但升级对于观看多种视频格式在同一大屏幕电视上是必要的,并且通常不会引起显著的视觉问题。
电视升级( Upscaling)是指将低分辨率内容转换以适应更高分辨率屏幕的过程,如4K电视。所有电视都有升级功能,4K电视通过插值算法将较低分辨率的视频内容放大到4K屏幕。虽然升级可以改善图像,但它并不等同于真实4K内容的清晰度。升级过程中,物理分辨率和光学分辨率是关键因素,而插值算法的质量决定了升级效果。尽管存在瑕疵,但升级对于观看多种视频格式在同一大屏幕电视上是必要的,并且通常不会引起显著的视觉问题。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








