还是先上效果图:
在学习新内容之前,我们先来弄清楚两个问题:
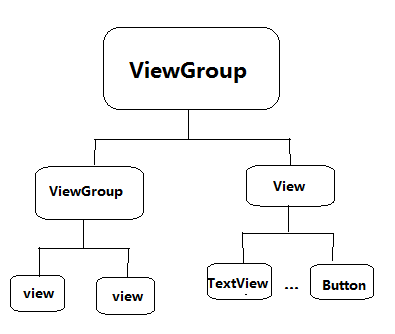
1 . 什么是ViewGroup?ViewGroup是一种容器。它包含零个或以上的View及子View。
这里写图片描述(图片来自网上)
ViewGroup内部可以用来存放多个View控件,并且根据自身的测量模式,来测量View子控件,并且决定View子控件的位置。这在下面会逐步讲解它是怎么测量及决定子控件大小和位置的。
继承ViewGroup,并重写它们的构造方法
/**
* 作者:chengxiangtong on 2016/11/10 14:00
* 邮箱:528440900@qq.com
*/
public class CustomerViewGroup extends ViewGroup {
int paddingleft = 0;
int paddingtop = 0;
int paddingright = 0;
int paddingbottom = 0;
public CustomerViewGroup(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public CustomerViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public CustomerViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
//ViewGroup它是一个容器,它是用来存放和管理子控件的,并且子控件的测量方式是根据它的测量模式来进行的,
// 所以我们必须重写它的onMeasure(),在该方法中进行对子View的大小进行测量 @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); paddingleft = getPaddingLeft(); paddingtop = getPaddingTop(); paddingright = getPaddingRight(); paddingbottom = getPaddingBottom(); int childcount = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < childcount; i++) { View view = getChildAt(i); measureChild(view, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); } int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); int mHeight = 0; int mWidth = 0; int mMaxWidth = 0; if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { for (int i = 0; i < childcount; i++) { View view = getChildAt(i); mWidth += view.getMeasuredWidth(); mHeight += view.getMeasuredHeight(); } setMeasuredDimension(mWidth + paddingleft + paddingright, mHeight + paddingtop + paddingbottom); } else if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { for (int i = 0; i < childcount; i++) { View view = getChildAt(i); mMaxWidth = Math.max(mMaxWidth, view.getMeasuredWidth());// mHeight += view.getMeasuredHeight(); } setMeasuredDimension(mMaxWidth+ paddingleft + paddingright, heightSize+ paddingtop + paddingbottom); } else if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { for (int i = 0; i < childcount; i++) { View view = getChildAt(i);// mWidth += view.getMeasuredWidth(); mHeight += view.getMeasuredHeight(); } setMeasuredDimension(widthSize+ paddingleft + paddingright, mHeight+ paddingtop + paddingbottom); } } @Override protected void onLayout(boolean b, int i, int i1, int i2, int i3) { int childcount = getChildCount(); int preheight = paddingtop; for (int k = 0; k < childcount; k++) { View view = getChildAt(k); int cheight = view.getMeasuredHeight(); if (view.getVisibility() != View.GONE || view.getVisibility() != View.INVISIBLE) { view.layout(i + paddingleft, preheight, i2 + paddingright, preheight += cheight); } } }}
我们重写了onMeasure(),在方法里面,我们首先先获取ViewGroup中的子View的个数,然后遍历它所有的子Vie
w,得到每一个子View,调用measureChild()放来,来对子View进行测量。刚才提到子View的测量是根据ViewGroup
所提供的测量模式来进行来,所以在measureChild()方法中,把ViewGroup的widthMeasureSpec 和 heightMeasureS
pec和子View一起传进去了,我们可以跟进去看看是不是和我们所说的一样。
measureChild()方法源码:
measureChild()源码方法里面很好理解,它首先得到子View的LayoutParams,然后根据ViewGroup传递进来的宽高属
性值和自身的LayoutParams 的宽高属性值及自身padding属性值分别调用getChildMeasureSpec()方法获取到子View
的测量。由该方法我们也知道ViewGroup中在测量子View的大小时,测量结果分别是由父节点的测量模式和子View本
身的LayoutParams及padding所决定的。
下面我们再来看看getChildMeasureSpec()方法的源码,看看它是怎么获取测量结果的。
getChildMeasureSpec()方法源码:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
该方法:首先是获取父节点(这里是ViewGroup)的测量模式和测量的大小,并根据测量的大小值与子Vie
w自身的padding属性值相比较取最大值得到一个size的值。
然后根据父节点的测量模式分别再来判定子View的LayoutParams属性值,根据LayoutParams的属性值从而获取到子
View测量的大小和模式,知道了ziView的测量模式和大小就能决定子View的大小了。
我们再来分析一下ViewGroup是怎样给子View定位的,首先我们也是必须先重写onLayout()方法,代码如下:
很好理解,给子View定位,首先必须知道有多少个子View才行,所以我们先得到子View的数量,然后遍历获取每个子
View。其实在定位子View的layout()方法中,系统并没有
给出具体的定位方法,而是给了我们最大的限度来自己定义,下面来看下layout源码:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
在上面一段代码中,最关键个就是setFrame(l, t, r, b);这个方法,它主要是来定位子View的四个顶点左右坐标的,然后
关键的定位方法是在onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);这个方法中,跟进去看看
- 1
- 2
系统给了我们最大的自由,让我们自己根据需求去定义了。
而我这里是根据子View的高度让它们竖直顺序的排列下来。
定义一个记录上一个View的高度的变量,每次遍历以后都让它加上当前的View高度,由此就可以竖直依次地排列了每
个子View,从而实现了子View的定义。
接下来我们看看布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <test.com.test.CustomerViewGroup xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" android:background="#999999" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="vertical"> <test.com.test.CompositeViews android:id="@+id/CompositeViews" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" app:centerTextBackground="@android:color/holo_blue_bright" app:leftTextBackground="@android:color/holo_purple" app:rightTextBackground="@android:color/holo_purple"/> <test.com.test.CustomerRunLine android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="10dp" app:c_color="#ef5621" android:paddingBottom="50dp" app:c_h="80dp" app:c_w="4dp" /> <test.com.test.AudioView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> </test.com.test.CustomerViewGroup>
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements CompositeViews.tabBarListener { private CompositeViews mCompositeViews; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.layout); mCompositeViews = (CompositeViews) findViewById(R.id.CompositeViews); mCompositeViews.settabBarOnclcikLisenter(this); } @Override public void mTextViewleftListener() { Toast.makeText(this,"mTextViewleftListener",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); } @Override public void mTextViewrightListener() { Toast.makeText(this,"mTextViewrightListener",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); } }
好的这篇也说完了,赶紧试试吧,文中有联系方式 ,多多交流
,多多交流
github 地址:https://github.com/xiangtongcheng/customerView

























 345
345











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








