ros2 高级组件其二之大型项目中的 launch
1 前言和资料
早在ROS2高效学习第四章 – ros2 topic 编程之收发 string 并使用 ros2 launch 其一中,我们就为大家引入了 ros2 python 版的 launch 文件,并承诺会单开一篇博客为大家单独讲解 ros2 launch 的高级用法。本文我们将用三个例子,为大家依次介绍在大型项目中常用的几种 ros2 launch 文件用法(如下),这些用法都在三个例子的代码注释中,在本文搜索 Tips 可以快速找到他们。
(1)launch 文件包含
(2)launch 的 event handler机制
(3)使用 yaml 文件配置节点参数的方法
(4)为整个 launch 文件指定命名空间的方法
(5)计算图源名称重映射的方法
(6)launch 中启动 rviz 的方法
(7)launch 中获取环境变量的方法
(8)launch 文件申明可传入参数的方法
(9)launch 文件中调用命令行方法
本文的参考资料如下:
(1)ROS2高效学习第四章 – ros2 topic 编程之收发 string 并使用 ros2 launch 其一
(2)ros1 launch 写法:ROS高效进阶第一章 – ROS高级组件之 launch 文件
(3)Using-Substitutions
(4)Using-Event-Handlers
(5)Using-ROS2-Launch-For-Large-Projects
2 正文
2.1 启动 turtlesim,生成一个 turtle ,设置背景色
(1)创建 launch_example 软件包和相关文件
cd ~/colcon_ws/src
ros2 pkg create --build-type ament_python --license Apache-2.0 launch_example
cd launch_example
touch launch_example/main_simple_launch.py launch_example/substitution_launch.py
(2)编写 substitution_launch.py
from launch_ros.actions import Node
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import DeclareLaunchArgument, ExecuteProcess, TimerAction
from launch.conditions import IfCondition
from launch.substitutions import LaunchConfiguration, PythonExpression
# 导入logging模块来获取logger,这是launch原生支持的日志模块
import launch.logging
def generate_launch_description():
logger = launch.logging.get_logger('main_substitution_launch_debugger')
# 当由 main_launch.py 启动时,这句会打印两次
# 当由本文件启动时,这句只打印一次,知道就好
logger.info('main_substitution_launch.py is started.')
# 创建命名空间的配置变量
# 创建是否使用指定红色值的配置变量
# 创建新的红色背景值的配置变量
turtlesim_ns = LaunchConfiguration('turtlesim_ns')
use_provided_red = LaunchConfiguration('use_provided_red')
new_background_r = LaunchConfiguration('new_background_r')
# Tips:launch 文件申明可传入参数的方法
# 声明命名空间配置, 是否使用指定红色值, 新的红色背景值的启动参数, 分别对应三个配置变量
# 使用 DeclareLaunchArgument 申明的启动参数, 允许从外部为这些参数提供值。
# 在这个例子中, 这三个参数将从 main_launch.py 中传入
turtlesim_ns_launch_arg = DeclareLaunchArgument(
'turtlesim_ns',
default_value=''
)
use_provided_red_launch_arg = DeclareLaunchArgument(
'use_provided_red',
default_value='False'
)
new_background_r_launch_arg = DeclareLaunchArgument(
'new_background_r',
default_value='200'
)
# 实例化一个Node, 用于启动 turtlesim 节点
turtlesim_node = Node(
package='turtlesim',
namespace=turtlesim_ns,
executable='turtlesim_node',
name='sim'
)
# Tips:launch 文件中调用命令行方法
# 实例化一个ExecuteProcess, 用于在3秒后生成一个乌龟
spawn_turtle = ExecuteProcess(
cmd=[[
'ros2 service call ',
turtlesim_ns,
'/spawn ',
'turtlesim/srv/Spawn ',
'"{x: 2, y: 2, theta: 0.2}"'
]],
shell=True
)
# 实例化三个ExecuteProcess, 用于启动3秒后改变背景颜色为护眼绿
change_background_r = ExecuteProcess(
cmd=[[
'ros2 param set ',
turtlesim_ns,
'/sim background_r 199'
]], # 这个逗号是必须的,不能删除
shell=True
)
change_background_g = ExecuteProcess(
cmd=[[
'ros2 param set ',
turtlesim_ns,
'/sim background_g 237'
]],
shell=True
)
change_background_b = ExecuteProcess(
cmd=[[
'ros2 param set ',
turtlesim_ns,
'/sim background_b 204'
]],
shell=True
)
# 实例化一个条件ExecuteProcess, 如果外部 main_launch.py 传入的新的红色背景值为240且使用指定红色值,则改变背景颜色为240
change_background_r_conditioned = ExecuteProcess(
condition=IfCondition(
PythonExpression([
new_background_r,
' == 240',
' and ',
use_provided_red
])
),
cmd=[[
'ros2 param set ',
turtlesim_ns,
'/sim background_r ',
new_background_r
]],
shell=True
)
# 前面都是定义各种变量和实例化各种对象,这里是返回最终的LaunchDescription对象
# 如果launch文件比较复杂,就推荐这种方式,便于修改和抽象,而不是直接把内容在LaunchDescription中展开
return LaunchDescription([
# 先申明三个启动参数
turtlesim_ns_launch_arg,
use_provided_red_launch_arg,
new_background_r_launch_arg,
# 启动 turtlesim 节点,预留五秒等待时间,不然后面的执行将报错
# 五秒是粗略估计,并不准确,完美的解决方案是 event handler
turtlesim_node,
# 5秒后,调用spawn服务,生成一个乌龟,并把背景色改为护眼绿
TimerAction(
period=5.0,
actions=[spawn_turtle,
change_background_r,
change_background_g,
change_background_b],
),
# 8秒后,如果main_launch.py传入的参数符合条件,则改变背景颜色的red值
TimerAction(
period=8.0,
actions=[change_background_r_conditioned],
)
])
(3)编写 main_simple_launch.py
from launch_ros.substitutions import FindPackageShare
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import IncludeLaunchDescription
from launch.launch_description_sources import PythonLaunchDescriptionSource
from launch.substitutions import PathJoinSubstitution, TextSubstitution
def generate_launch_description():
# 定义一个字典,包含背景颜色的红色值
colors = {
'background_r': '240'
}
# Tips:launch 文件包含
# 通过引用launch_example 包内的 launch 文件夹下的 substitution_launch.py 来启动
return LaunchDescription([
IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource([
PathJoinSubstitution([
FindPackageShare('launch_example'),
'launch_example',
'substitution_launch.py'
])
]),
# 创建一个字典,使用.items()获取字典的键值对组成的元组列表,向 substitution_launch.py 传递三个参数
# TextSubstitution 是ROS 2 launch文件中的一个功能,它允许在launch过程中动态生成字符串
# TextSubstitution 支持从环境变量中读取值,也支持将多个字符串拼接起来
launch_arguments={
'turtlesim_ns': 'turtlesim',
'use_provided_red': 'True',
'new_background_r': TextSubstitution(text=str(colors['background_r']))
}.items()
)
])
(4)补充 setup.py
import os
from glob import glob
from setuptools import find_packages, setup
...
data_files=[
...
(os.path.join('share', package_name, 'launch_example'), glob(os.path.join('launch_example', '*_launch.py'))),
(os.path.join('share', package_name, 'config'), glob(os.path.join('config', '*.yaml'))),
(os.path.join('share', package_name, 'config'), glob(os.path.join('config', '*.rviz')))
],
(5)编译并运行
~/colcon_ws
colcon build --packages-select launch_example
source install/local_setup.bash
ros2 launch launch_example main_simple_launch.py
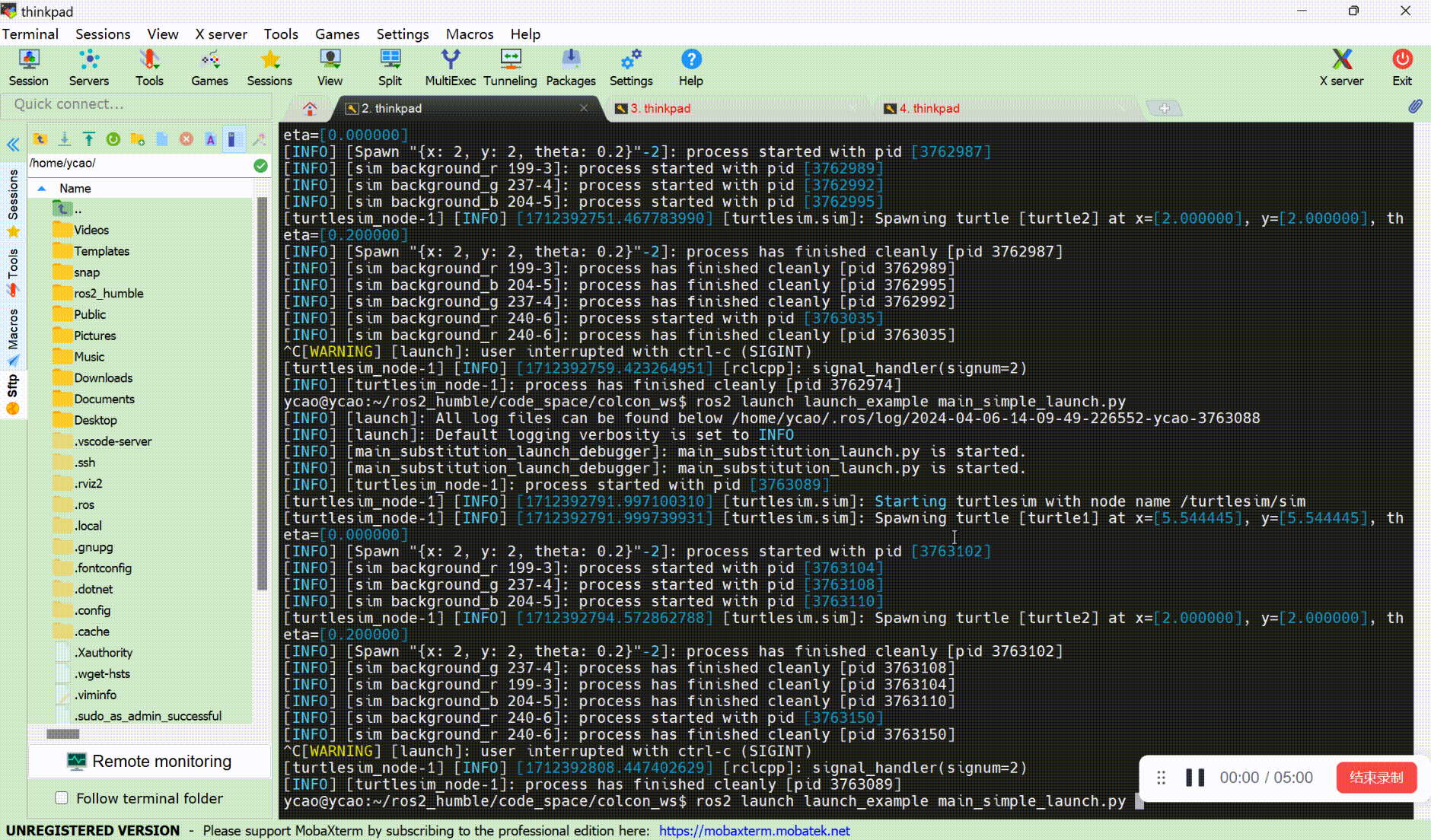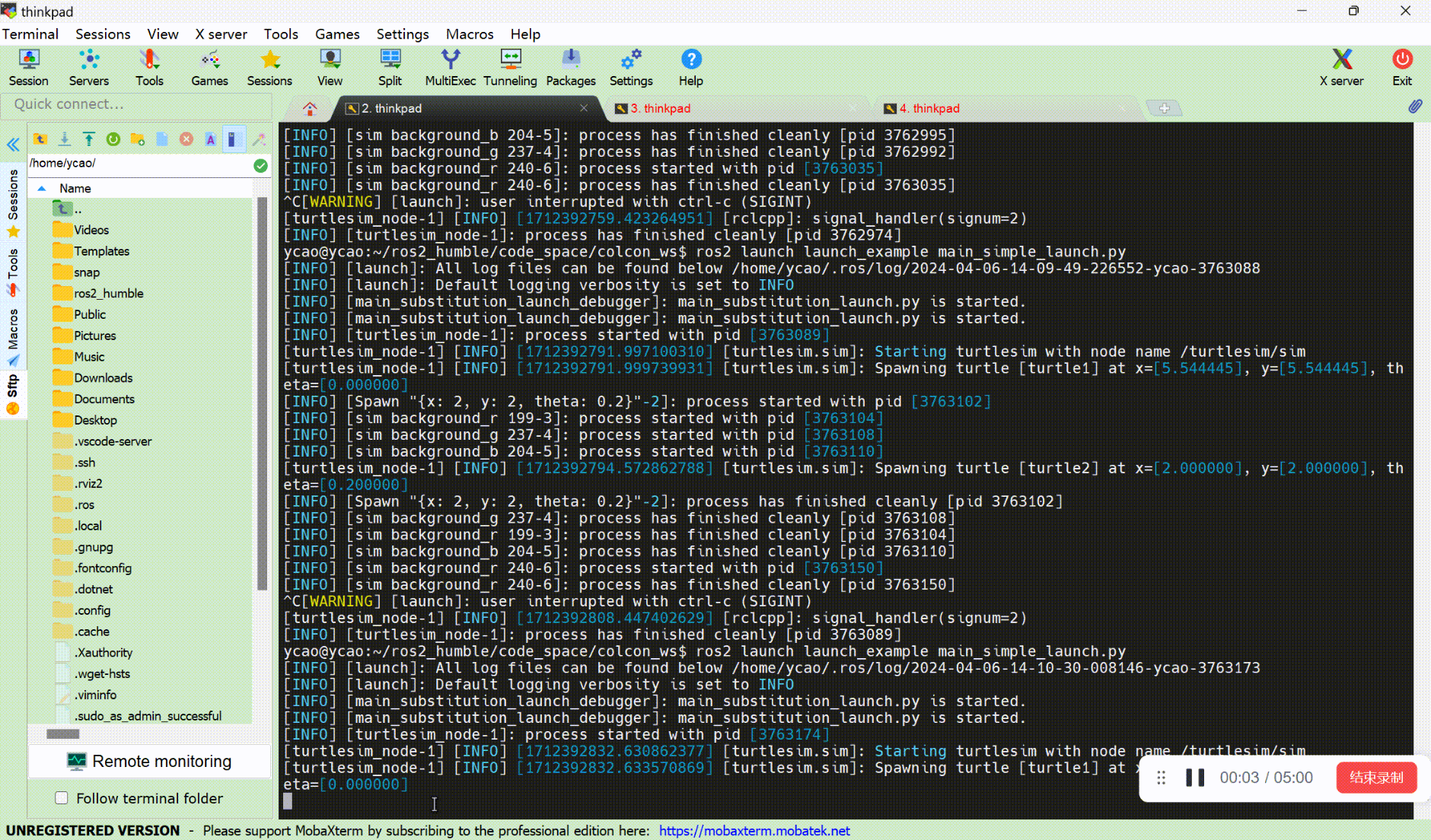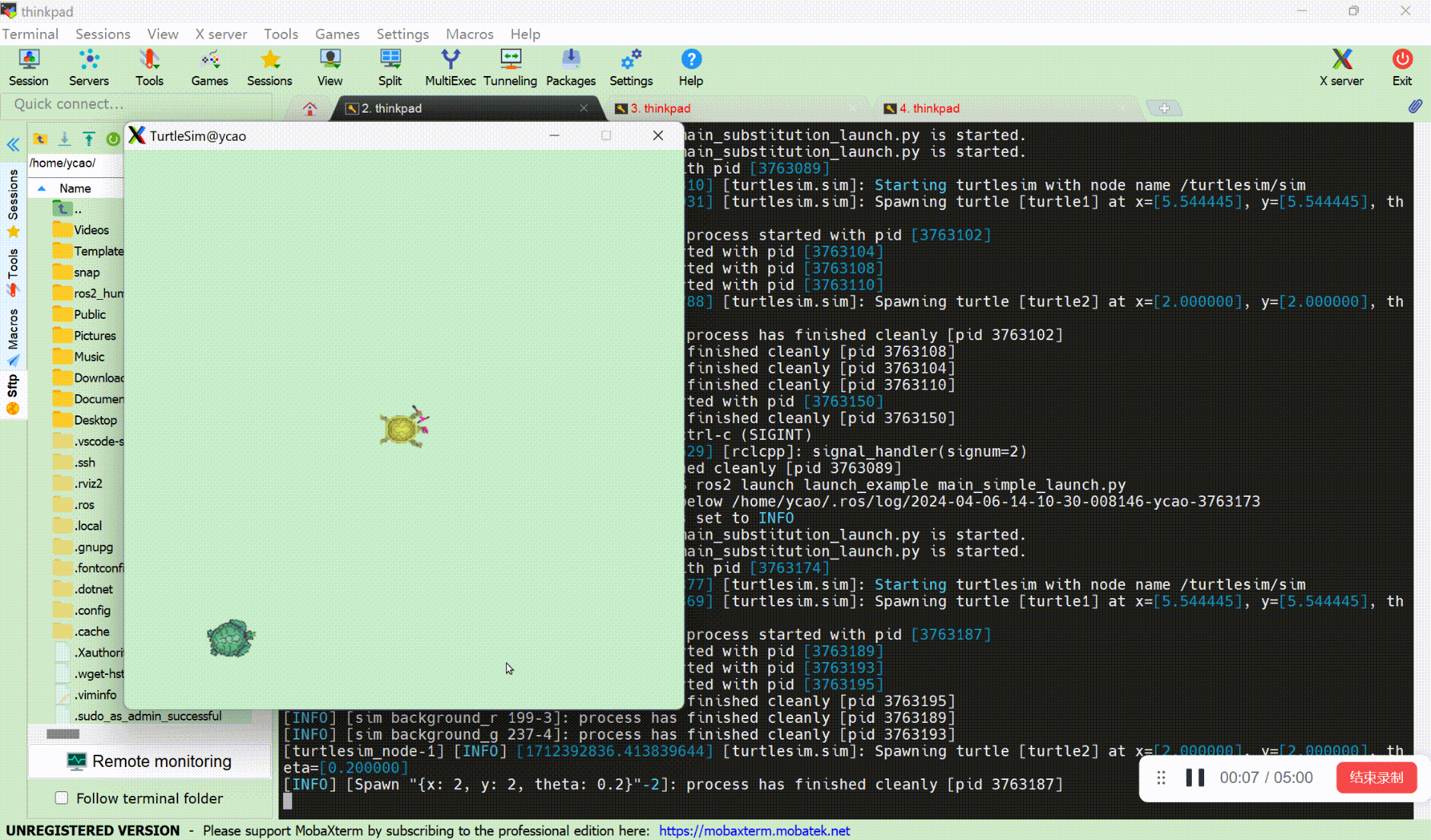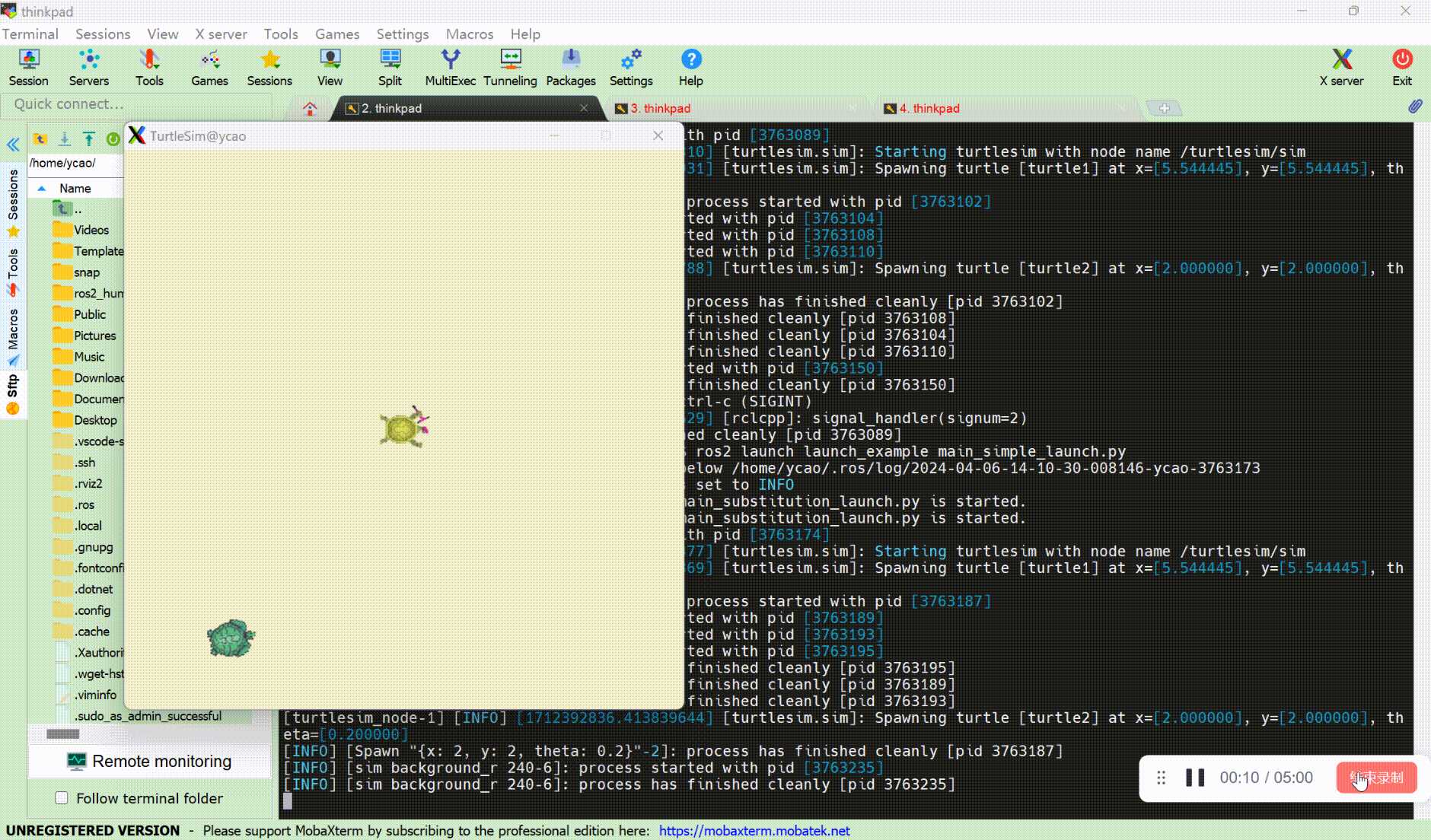
2.2 使用 event handler 重写上节的样例
(1)event handler 引入:上节的样例,我们使用 TimerAction 控制各个动作的先后顺序,但这么做会导致程序运行效果并不稳定,而且可能浪费启动时间,更好的方式是使用事件处理器 event handler 。
ROS2 launch 的事件处理器(event handler)是一种允许用户自定义对特定事件的响应行为的机制。当进程状态发生变化时(例如,节点启动、节点关闭、进程死亡等),这些变化会触发自定义的响应行为。使用事件处理器,launch 系统具备了高度的灵活性和可扩展性,使得开发者可以根据不同的运行时情况和需求,定制处理流程和逻辑。这对于构建稳健、可靠的 ROS2 应用程序至关重要。
(2)在 launch_example 中创建新的样例文件
cd ~/colcon_ws/src/launch_example
touch launch_example/event_handler_launch.py
(3)编写 event_handler_launch.py
from launch_ros.actions import Node
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import (DeclareLaunchArgument, EmitEvent, ExecuteProcess,
LogInfo, RegisterEventHandler, TimerAction)
from launch.conditions import IfCondition
from launch.event_handlers import (OnExecutionComplete, OnProcessExit,
OnProcessIO, OnProcessStart, OnShutdown)
from launch.events import Shutdown
from launch.substitutions import (EnvironmentVariable, FindExecutable,
LaunchConfiguration, LocalSubstitution,
PythonExpression)
def generate_launch_description():
turtlesim_ns = LaunchConfiguration('turtlesim_ns')
use_provided_red = LaunchConfiguration('use_provided_red')
new_background_r = LaunchConfiguration('new_background_r')
turtlesim_ns_launch_arg = DeclareLaunchArgument(
'turtlesim_ns',
default_value=''
)
use_provided_red_launch_arg = DeclareLaunchArgument(
'use_provided_red',
default_value='False'
)
new_background_r_launch_arg = DeclareLaunchArgument(
'new_background_r',
default_value='200'
)
turtlesim_node = Node(
package='turtlesim',
namespace=turtlesim_ns,
executable='turtlesim_node',
name='sim'
)
spawn_turtle = ExecuteProcess(
cmd=[[
FindExecutable(name='ros2'),
' service call ',
turtlesim_ns,
'/spawn ',
'turtlesim/srv/Spawn ',
'"{x: 2, y: 2, theta: 0.2}"'
]],
shell=True
)
change_background_r = ExecuteProcess(
cmd=[[
FindExecutable(name='ros2'),
' param set ',
turtlesim_ns,
'/sim background_r ',
'120'
]],
shell=True
)
change_background_g = ExecuteProcess(
cmd=[[
FindExecutable(name='ros2'),
' param set ',
turtlesim_ns,
'/sim background_g ',
'237'
]],
shell=True
)
change_background_b = ExecuteProcess(
cmd=[[
FindExecutable(name='ros2'),
' param set ',
turtlesim_ns,
'/sim background_b ',
'204'
]],
shell=True
)
change_background_r_conditioned = ExecuteProcess(
condition=IfCondition(
PythonExpression([
new_background_r,
' == 240',
' and ',
use_provided_red
])
),
cmd=[[
FindExecutable(name='ros2'),
' param set ',
turtlesim_ns,
'/sim background_r ',
new_background_r
]],
shell=True
)
# 该launch文件的功能同 main_launch.py + substitution_launch.py
# 上面的代码注释同 substitution_launch.py,我们重点解释下面的 event handler
########################################################################
# Tips: launch 的 event handler机制
# ROS2 launch 的事件处理器(event handler)是一种机制,它允许用户自定义对特定事件的响应行为。
# 当进程状态发生变化时(例如,节点启动、节点关闭、进程死亡等),这些变化会触发自定义的响应行为。
# 使用事件处理器,launch 系统具备了高度的灵活性和可扩展性,使得开发者可以根据不同的运行时情况和需求,定制处理流程和逻辑。
# 这对于构建稳健、可靠的 ROS 2 应用程序至关重要。
return LaunchDescription([
turtlesim_ns_launch_arg,
use_provided_red_launch_arg,
new_background_r_launch_arg,
turtlesim_node,
# RegisterEventHandler 用于注册一个事件处理器,这里注册了五个事件处理器
RegisterEventHandler(
# event_handlers 的 OnProcessStart 用于处理进程启动事件,当进程启动时触发响应行为
OnProcessStart(
# target_action 指定了事件处理器要监听的目标动作,这里是拉起 turtlesim_node
target_action=turtlesim_node,
# on_start 是一个列表,用来定义进程启动后的响应行为
# 这里的行为是打印一条日志,然后执行 spawn_turtle
on_start=[
LogInfo(msg='Turtlesim started, spawning turtle'),
spawn_turtle
]
)
),
RegisterEventHandler(
# event_handlers 的 OnProcessIO 用于处理进程输入输出事件,当进程有输入/输出(如标准输出)时触发响应行为
OnProcessIO(
# 这里要监听的事件是 spawn_turtle 的标准输出
target_action=spawn_turtle,
# on_stdout 是一个函数,这里用 lambda表达式打印 spawn_turtle 的标准输出
# lambda表达式是一个匿名函数,用于简单的函数定义,其中 event 是函数参数,返回值是LogInfo对象
# event.text是spawn_turtle的标准输出,event.text.decode()将字节流解码为字符串
on_stdout=lambda event: LogInfo(
msg='Spawn request says "{}"'.format(
event.text.decode().strip())
)
)
),
RegisterEventHandler(
# event_handlers 的 OnExecutionComplete 用于处理动作执行完成事件,当动作执行完成时触发响应行为
OnExecutionComplete(
# 这里的目标动作仍是 spawn_turtle
target_action=spawn_turtle,
# on_completion 是一个列表,用来定义动作执行完成后的响应行为
# 这里的行为是打印一条日志,然后执行将背景色改为护眼绿,然后根据参数有条件的将背景色的red值改为240
on_completion=[
LogInfo(msg='Spawn finished'),
change_background_r,
change_background_g,
change_background_b,
TimerAction(
period=2.0,
actions=[change_background_r_conditioned],
)
]
)
),
RegisterEventHandler(
# event_handlers 的 OnProcessExit 用于处理进程退出事件,当进程退出时触发响应行为
OnProcessExit(
# 这里要监听的事件是 turtlesim_node 的退出
target_action=turtlesim_node,
# on_exit 是一个列表,用来定义进程退出后的响应行为
# 这里的行为是打印一条日志,然后发出 Shutdown 系统关闭事件
# Tips: launch 中获取环境变量的方法
on_exit=[
LogInfo(msg=(EnvironmentVariable(name='USER'),
' closed the turtlesim window')),
EmitEvent(event=Shutdown(
reason='Window closed'))
]
)
),
RegisterEventHandler(
# event_handlers 的 OnShutdown 用于处理系统关闭事件,当系统收到关闭请求时触发响应行为
OnShutdown(
# on_shutdown 是一个列表,用来定义系统关闭后的响应行为
# 这里的行为是打印一条日志,日志中包含了系统关闭的原因
on_shutdown=[LogInfo(
msg=['Launch was asked to shutdown: ',
LocalSubstitution('event.reason')]
)]
)
),
])
(4)编译并运行
~/colcon_ws
colcon build --packages-select launch_example
source install/local_setup.bash
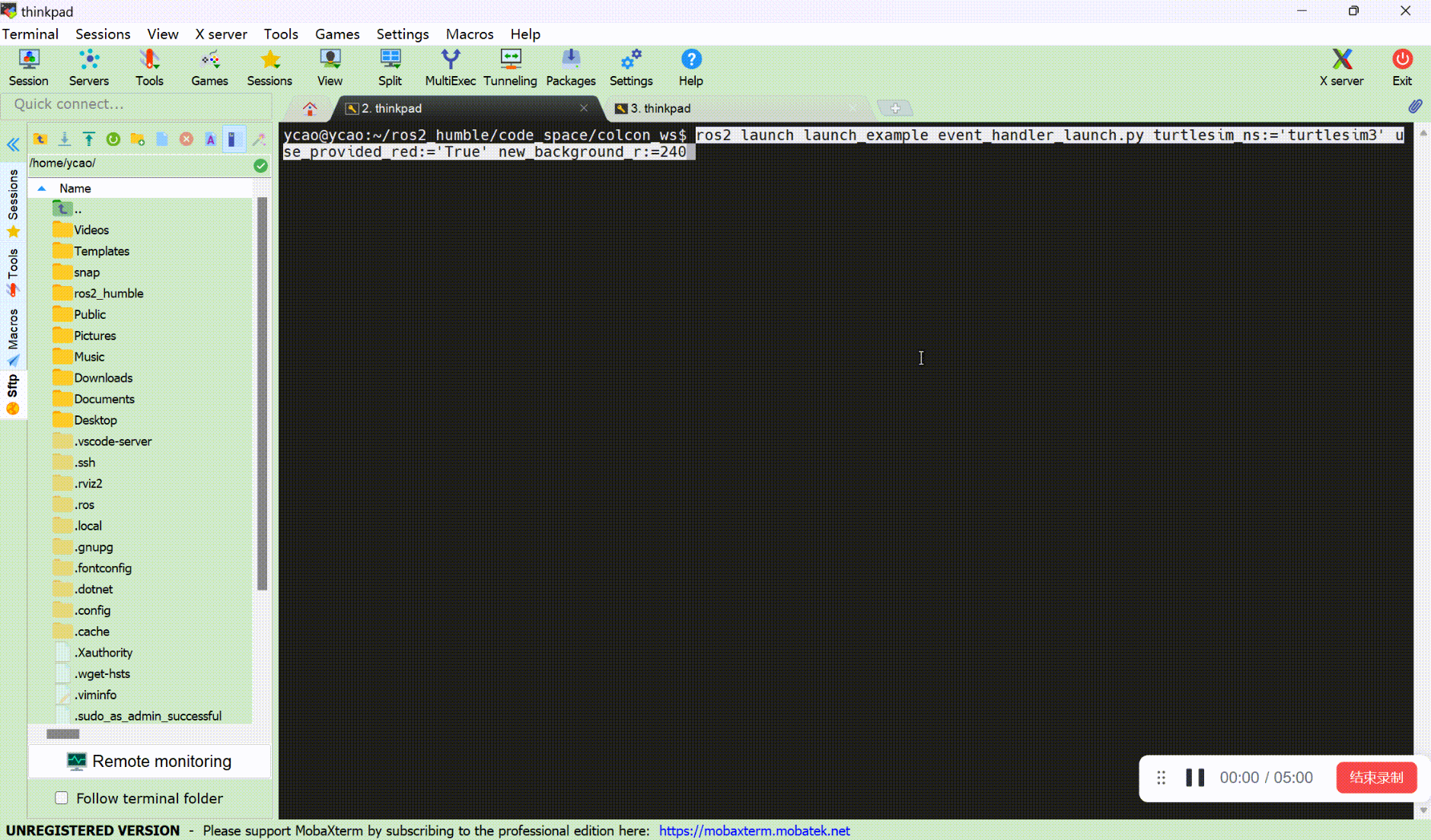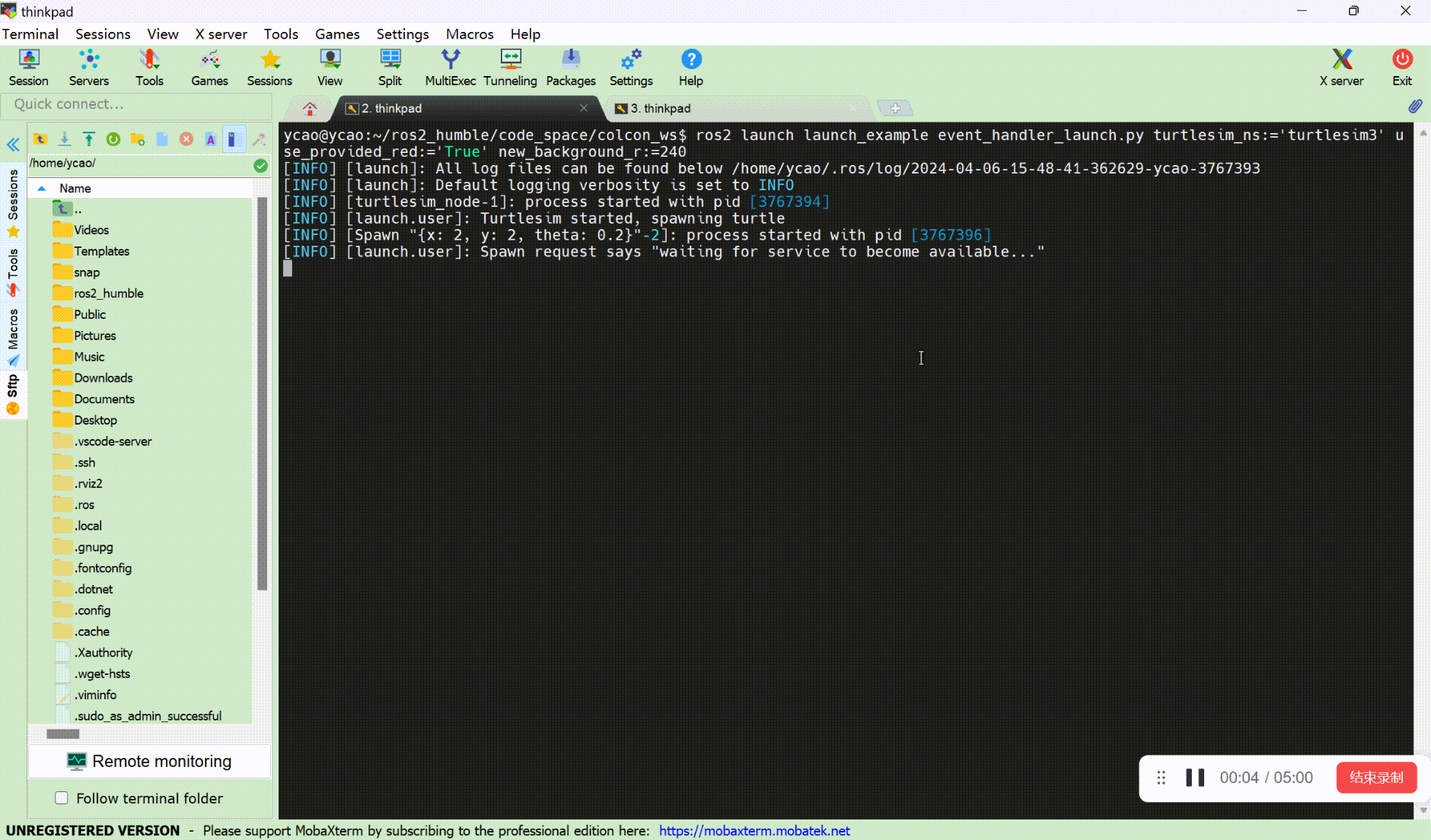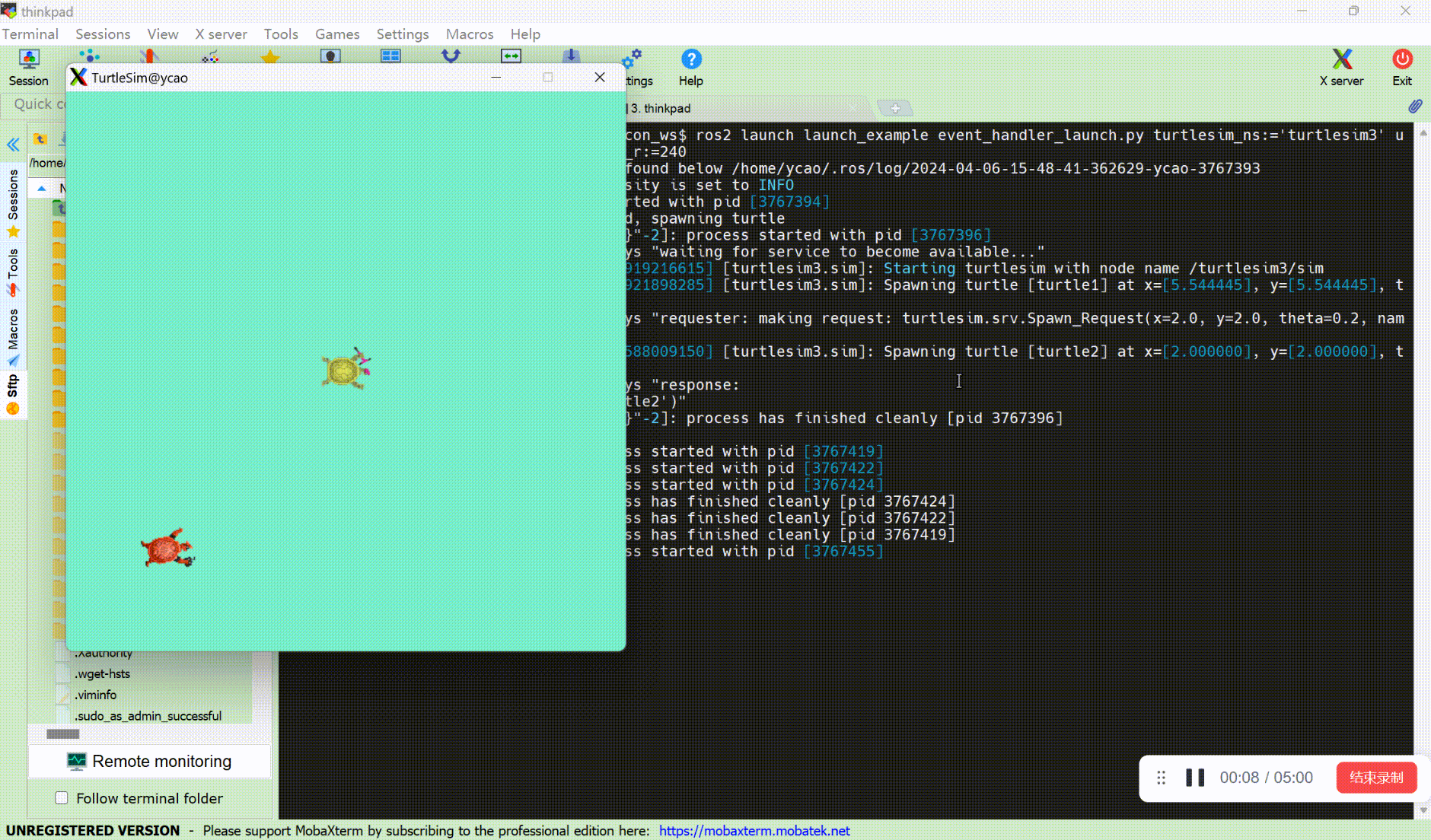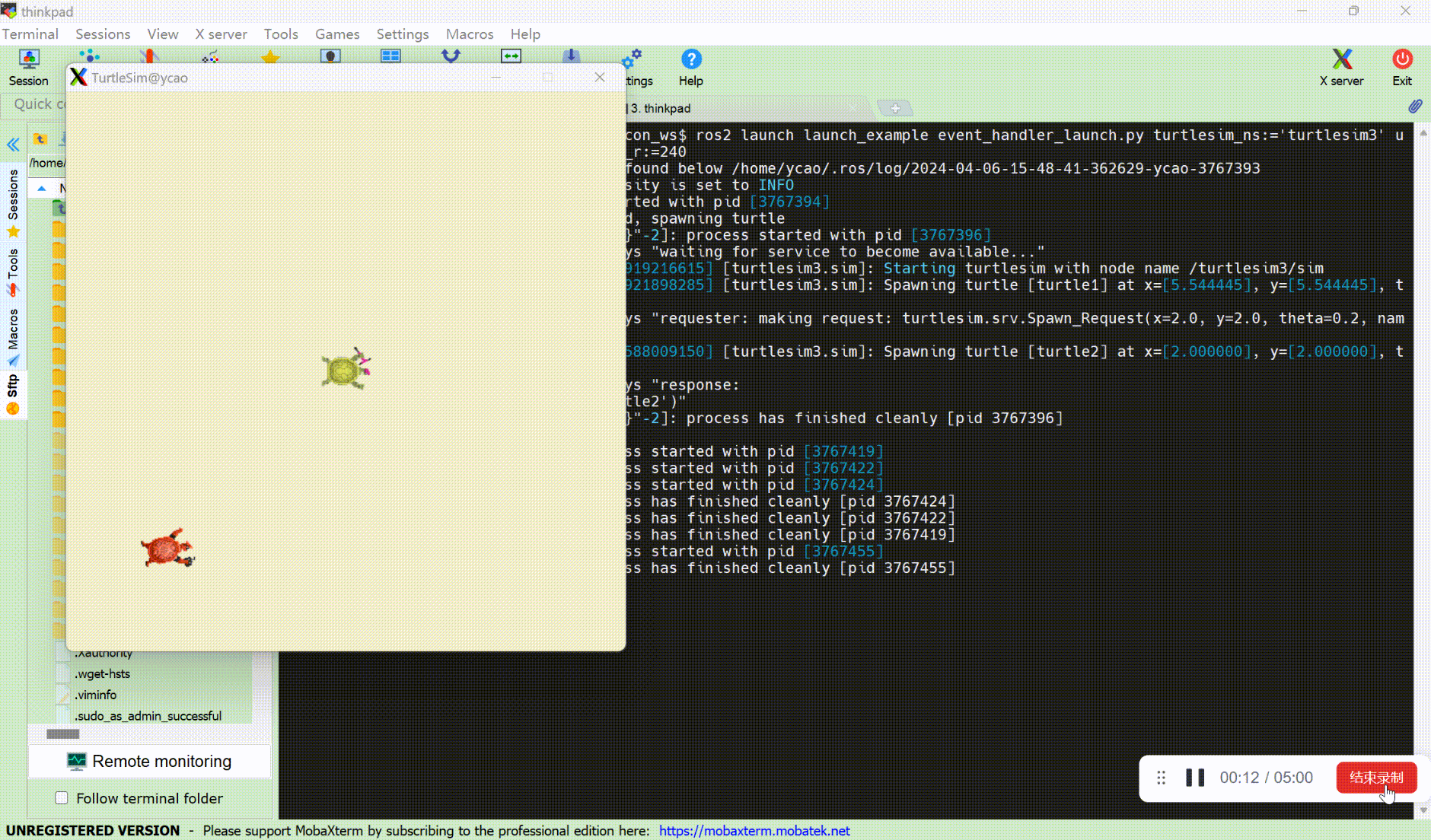
ros2 launch launch_example event_handler_launch.py turtlesim_ns:='turtlesim3' use_provided_red:='True' new_background_r:=240
2.3 turtle_tf_mimic_rviz_launch 样例
(1)样例说明:这个样例依赖 turtle-tf2-py 软件包,先启动一个窗口,里面有两个乌龟,turtle2始终追着turtle1运动(实现这个效果需要 TF 的知识,这里并不深究)。启动第二个窗口,在 mimic 节点的作用下 ,这个窗口的乌龟将与第一个窗口的turtle2同步运动。使用命令行控制第一个窗口的turtle1乌龟做圆周运动,并启动 rviz,监听第一个窗口的两个turtle的TF信息,并可视化显示。
(2)安装 turtle-tf2-py 软件包,并在 launch_example 中创建新的样例文件
# 安装 turtle-tf2-py 软件包
sudo apt-get install ros-humble-turtle-tf2-py
cd ~/colcon_ws/src/launch_example
mkdir config
touch config/turtlesim_param.yaml
touch launch_example/main_turtle_tf_mimic_rviz_launch.py launch_example/turtlesim_world_2_launch.py
(3)编辑 main_turtle_tf_mimic_rviz_launch.py
import os
from ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_directory
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import IncludeLaunchDescription
from launch.launch_description_sources import PythonLaunchDescriptionSource
from launch.actions import GroupAction
from launch_ros.actions import PushRosNamespace
from launch_ros.actions import Node
from launch.actions import (DeclareLaunchArgument, EmitEvent, ExecuteProcess,
LogInfo, RegisterEventHandler, TimerAction)
from launch.substitutions import (EnvironmentVariable, FindExecutable,
LaunchConfiguration, LocalSubstitution,
PythonExpression)
from launch.events import Shutdown
from launch.actions import (ExecuteProcess, LogInfo, RegisterEventHandler)
from launch.event_handlers import (OnExecutionComplete, OnProcessExit,
OnProcessIO, OnProcessStart, OnShutdown)
def generate_launch_description():
# 使用 IncludeLaunchDescription 来包含 turtle_tf2_py 包中的 turtle_tf2_demo.launch.py 文件
# 该文件会启动一个窗口,里面有两个乌龟,turtle2始终追着turtle1运动,实现这个效果需要 TF 的知识,这里并不深究
turtlesim_world_1 = IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource([os.path.join(
get_package_share_directory('turtle_tf2_py'), 'launch'),
'/turtle_tf2_demo.launch.py'])
)
# 启动第二个窗口,其背景色通过加载全局参数文件配置成护眼绿
# 在下面的 mimic_node 的作用下 ,这个窗口的乌龟将与第一个窗口的turtle2同步运动
turtlesim_world_2 = IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource([os.path.join(
get_package_share_directory('launch_example'), 'launch_example'),
'/turtlesim_world_2_launch.py'])
)
# Tips: 为整个 launch 文件指定命名空间的方法
# 为了防止两个窗口的节点名字冲突,这里使用 PushRosNamespace 来给第二个窗口的节点加上一个命名空间名turtlesim2
# PushRosNamespace可以在不修改launch文件的情况下,给节点加上命名空间,避免重名,非常高效
turtlesim_world_2_with_namespace = GroupAction(
actions=[
PushRosNamespace('turtlesim2'),
turtlesim_world_2,
]
)
# Tips: 计算图源名称重映射的方法
# mimic_node 会订阅第一个窗口的turtle2乌龟的位置信息,然后控制第二个窗口的乌龟做同步运动
# 关注这里的remappings用法
mimic_node = Node(
package='turtlesim',
executable='mimic',
name='mimic',
remappings=[
('/input/pose', '/turtle2/pose'),
('/output/cmd_vel', '/turtlesim2/turtle1/cmd_vel'),
]
)
# Tips: launch 中启动 rviz 的方法
# 针对第一个窗口,启动rviz,监听两个turtle的TF信息,并可视化显示
turtlesim_world_1_rviz_config = os.path.join(
get_package_share_directory('launch_example'),
'config',
'turtle.rviz'
)
turtlesim_world_1_rviz_node = Node(
package='rviz2',
executable='rviz2',
name='rviz2',
arguments=['-d', turtlesim_world_1_rviz_config]
)
# 由于第一个窗口的turtle2乌龟会追着turtle1乌龟运动,而第二个窗口的turtle1乌龟会与第一个窗口的turtle2同步运动
# 因此需要给第一个窗口的turtle1乌龟添加额外的运动控制命令,不然都不动了
# 这里是让第一个窗口的turtle1乌龟做圆周运动
draw_cycle = ExecuteProcess(
cmd=[
'ros2', 'topic', 'pub', '-r', '1',
'/turtle1/cmd_vel', 'geometry_msgs/msg/Twist',
'{linear: {x: 2.0, y: 0.0, z: 0.0}, angular: {x: 0.0, y: 0.0, z: -1.8}}'
],
output='screen'
)
return LaunchDescription([
turtlesim_world_1,
turtlesim_world_2_with_namespace,
mimic_node,
turtlesim_world_1_rviz_node,
# 依次启动这些节点,最后启动draw_cycle
RegisterEventHandler(
OnProcessStart(
target_action=turtlesim_world_1_rviz_node,
on_start=[
LogInfo(msg='Turtlesim started, spawning turtle'),
draw_cycle
]
)
),
RegisterEventHandler(
OnProcessExit(
target_action=turtlesim_world_1_rviz_node,
on_exit=[
LogInfo(msg=(EnvironmentVariable(name='USER'),
' closed the turtlesim window')),
EmitEvent(event=Shutdown(
reason='Window closed'))
]
)
),
RegisterEventHandler(
OnShutdown(
on_shutdown=[LogInfo(
msg=['Launch was asked to shutdown: ',
LocalSubstitution('event.reason')]
)]
)
),
])
(4)编辑 turtlesim_world_2_launch.py
import os
from ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_directory
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch_ros.actions import Node
def generate_launch_description():
# Tips: 使用 yaml 文件配置节点参数的方法
# 加载全局参数文件,设置窗口背景色为护眼绿
turtlesim_world_2_param = os.path.join(
get_package_share_directory('launch_example'),
'config',
'turtlesim_param.yaml'
)
return LaunchDescription([
Node(
package='turtlesim',
executable='turtlesim_node',
name='sim',
parameters=[turtlesim_world_2_param]
)
])
(5)编辑 turtlesim_param.yaml
# 使用通配符匹配所有节点
/**:
# 注意这里是两个下划线"__"
ros__parameters:
background_r: 199
background_g: 237
background_b: 204
(6)编译并运行
~/colcon_ws
colcon build --packages-select launch_example
source install/local_setup.bash
ros2 launch launch_example main_turtle_tf_mimic_rviz_launch.py

3 总结
本文代码托管在本人的 github 上:launch_example




















 1074
1074











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








