目录
C++使用auto推导lambda表达式的类型与function是否等价?
前言:
算法学习记录不是算法介绍,本文记录的是从零开始的学习过程(见到的例题,代码的理解……),所有内容按学习顺序更新,而且不保证正确,如有错误,请帮助指出。
学习工具:蓝桥OJ,LeetCode
背景知识:
你已经学过递归函数的使用。
正文:
什么是DFS(更新中):
全称“Deep First Search”,深度优先搜索。是一种搜索算法。
将解决一个问题的每一个步骤画成树型结构,DFS会按照深度顺序向下搜索,寻找每一个可能的答案,递归解决问题。
DFS模板:
int check(参数)
{
if(满足条件)
return 1;
return 0;
}
bool pd(参数){
相应操作
}
void dfs(int step)
{
判断边界pd()
{
不在边界内,即回溯
}
尝试每一种可能
{
满足check条件
标记
继续下一步dfs(step+1)
恢复初始状态(回溯的时候要用到)
}
}BFS模板:
int check(参数)
{
if(满足条件)
return 1;
return 0;
}
bool pd(参数){
相应操作
}
void bfs()
{
1. 把根节点放入队列尾端
2. 每次从队列中取出一个节点
3. Check 判断是不是答案,如果是结束算法 return;
4. 把当前取出的节点扩展,如果扩展后的节点经Pd()后符合要求,就放入队列,不符合就不放。
5. 转到步骤2,循环执行
}
如果所有节点被扩展完了,没有找到答案就无解。一个名为dfs的函数被反复递归调用,当前状态(解空间中的一个点)作参数
vis是一个数组,记录当前搜索到的结点的状态,通过vis[i]真还是假确定是否要向下继续搜索
这个模型很抽象,例题集可以帮助理解。
回溯法:
回溯算法 = 树的深度优先搜索 + 剪枝函数
回溯的关键不在于递归,而在于“状态”。在回溯算法向前的每一步,你都会去设置某个状态,而当向前走走不通的时候回退,此时需要把之前设置的状态撤销掉。
dfs 只是找某个或某些满足条件的东西,找到就返回,找不到拉倒,与”状态“关系不大。
剪枝:
将搜索过程当中一些不必要的部分直接剔除掉,因为搜索过程构成了一棵树,剔除掉不必要的部分,就像是在树上将树枝剪掉,故名剪枝。
剪枝是回溯法的一种重要优化手段,方法往往先写一个暴力搜索,然后找到某些特殊的数学关系,或者逻辑关系,通过它们的约束让搜索树尽可能小,从而达到降低时间复杂度的目的。
一般来说,剪枝的复杂度难以计算。
记忆化:
将搜索过程中会重复计算且结果相同的部分保存下来,作为一个状态,下次访问到这个状态时直接将子搜索结果返回。
通常使用数组或map进行记忆化,下标一般和dfs参数表对应。

用求斐波那契数列举个例子:
没记忆:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long ;
const ll p = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 1e9,N = 1e3 + 3;
ll f(int n){
if(n <= 2)return 1;
return (f(n - 1) + f(n - 2)) % p;
}
int main()
{
int n; cin >> n;
for(int i = 1;i <= n; ++ i)cout << f(i) << endl;
return 0;
}有记忆:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long ;
const ll p = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 1e9,N = 1e3 + 3;
ll dp[N];
ll f(int n){
if(n <= 2)return 1;
if(dp[n] != -1)return dp[n];
return dp[n] = (f(n - 1) + f(n - 2)) % p;
}
int main()
{
memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));
int n; cin >> n;
for(int i = 1;i <= n; ++ i)cout << f(i) << endl;
return 0;
}让程序求出五十项,可以发现2.943秒和32.18秒差距是很大的。

时间复杂度分析:
时间复杂度分析的本质是解空间的大小,因此在DFS中用解空间的大小作来估算时间复杂度。
一般来说,所有可能解的个数 :n! (n <= 10)
例题集(时间顺序):
1.LeetCode 46:全排列
从全排列开始理解回溯算法:
以数组 【 1,3,5】的全排列为例:
人算:按照顺序枚举写出所有结果
如何交给计算机算?:
回忆学习递归函数的时候,构建一个递归函数强调要先找到递归条件关系式
(参见浙大版《C语言程序设计(第4版)》)
于是先寻找递归条件关系式
发现以1开头的全排列【1,3,5】【1,5,3】是【1】+【3,5】的全排列(递归条件关系式)
”使用编程的方法得到全排列,就是在这样的一个树形结构中完成遍历,从树的根结点到叶子结点形成的路径就是其中一个全排列。“
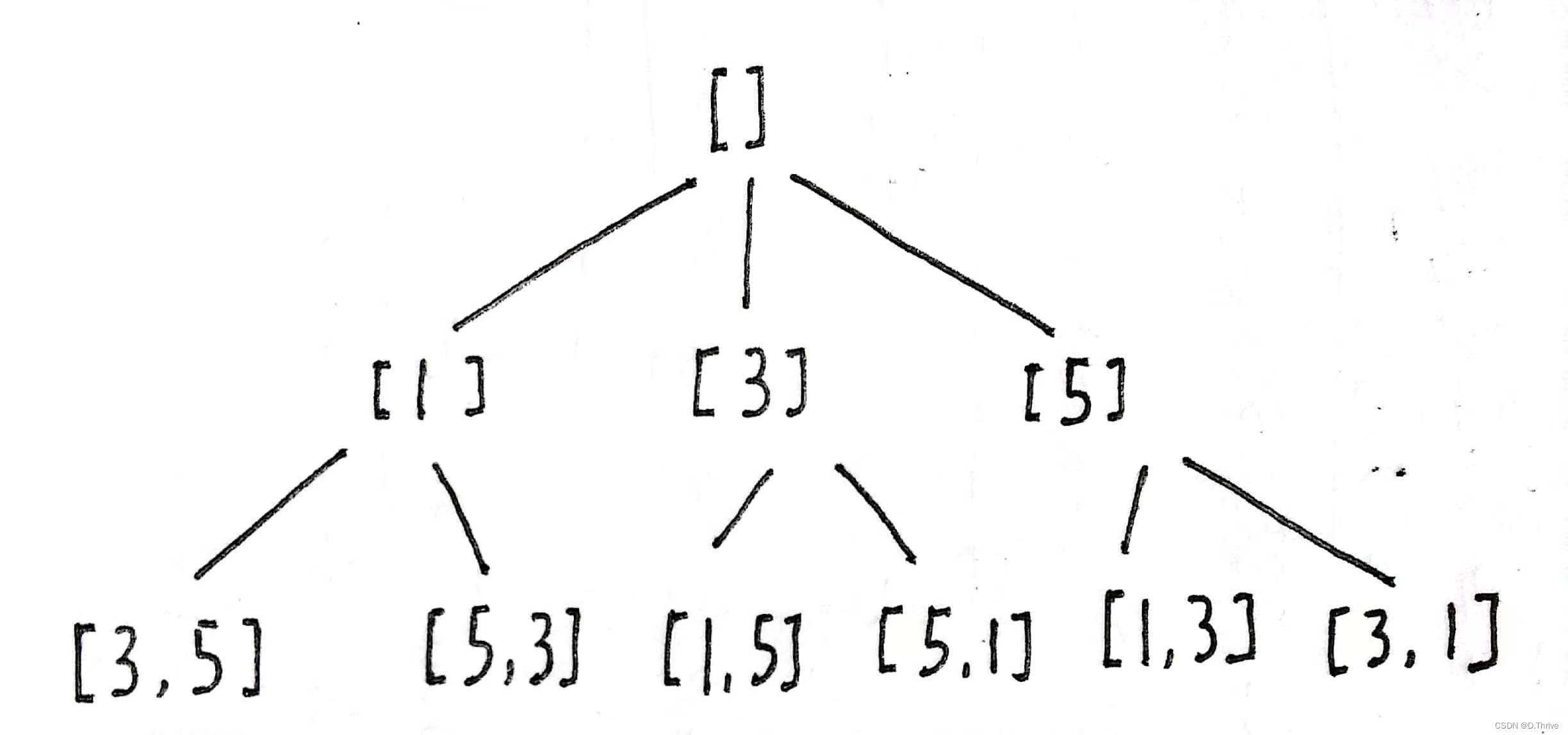
然后得到代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<bool> visited(22, false);
vector<vector<int> > res;
vector<int> ans;
function<void(int,int)> dfs = [&] (int tar, int cnt){
if (cnt == n - 1){
ans.push_back(tar);
res.push_back(ans);
ans.pop_back();
return;
}
ans.push_back(tar);
visited[tar + 11] = true;
for (auto x : nums) {
if (visited[x + 11] == false)
dfs (x, cnt + 1);
}
ans.pop_back();
visited[tar + 11] = false;
};
for (auto x : nums) {
dfs (x,0);
}
return res;
}
};2.蓝桥OJ 3511:飞机降落
N架飞机,每个飞机的降落所需时间都不一样,每个飞机能等的时间也不一样,
因此不能简单贪心算法解决,
可以发现:N <= 10 ,10!= 3628800
因此可以选用dfs搜索算法完全解决此题。
找到了一份比较好懂的答案分析下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 创建飞机结构体变量
struct plane
{
int t, d, l;
};
bool vis[15]; // true表示飞机降落,false表示飞机未降落
bool flag; // 标记是否全部安全降落
vector<plane> p(15);
// 深搜
void dfs(int m, int cnt, int last) // last表示此前所有飞机降落所需的单位时间
{
if (cnt == m)
{
flag = true;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
if (!vis[i] && p[i].t + p[i].d >= last)
//只有来的时刻+盘旋时间 > last 的飞机才可以安全降落
{
vis[i] = true;
dfs(m, cnt + 1, max(last, p[i].t) + p[i].l);//向下搜索:并根据当前情况改变last
vis[i] = false; //向下搜索至最深处后未满足条件,返回到当前岔口,修改vis数组
}
}
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
int N;
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
cin >> p[i].t >> p[i].d >> p[i].l;
flag = false;
dfs(N, 0, 0);
if (flag)
cout << "YES" << endl;
else
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
return 0;
}这题中的dfs:
有点类似枚举:将所有可能的情况列出
也有点类似贪心:每次满足小条件并不断积累,得出最终答案
搜索从p[0]-p[N-1]分别作为会降落的第一架飞机,确定第一架飞机后,再在p[0]-[N-1]中分别确定要降落的第二架飞机,这个过程中不断尝试,得出能满足条件的顺序。
下图可以帮助理解:

函数的三个参数:“m”、“cnt”、“last”
分别表示:要确定的飞机数、现在搜完的飞机数、此前花费了的时间
技巧:
1.使用结构体与向量组合,类似结构体数组,免去了开三个数组的麻烦。
2.使用全局变量vis[],flag,这样dfs和主函数可以公用,免去了传递参数入函数
这里的 last 和 m,也可以作为全局变量,这样dfs函数可以只用一个参数,即 dfs(int cnt);
3.使用max函数,简练地模拟出了两种满足条件情况的不同处理办法:
如果当前last < p[i].t :飞机到之前降落跑道就空了,那么这次操作后总用时就是p[i].t + p[i].l
如果当前last > p[i].t :飞机到的时候降落跑道被占用,飞机需要先盘旋,那么这次操作后总用时:last + p[i]
3.LeetCode 200 :岛屿个数
这种方法又称 Flood Fill ,实现方法有 DFS 和 BFS
每次找到一个陆地“1”,就将所有与这个相连的“1”全部变“0”,让这个岛消失,同时答案加1。
class Solution {
int m,n;
int dx[4] = {-1,0,1,0},dy[4] = {0,-1,0,1};
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
int ans = 0;
m = grid.size(),n = grid[0].size();
for(int i = 0;i < m;i ++) {
for(int j = 0;j < n;j ++) {
if(grid[i][j] == '1') {
dfs(grid,i,j);
ans ++;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<char>>&grid,int x,int y) {
grid[x][y] = '0';
for(int i = 0;i < 4;i ++){
int nx = x + dx[i],ny = y + dy[i];
if(nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n&& grid[nx][ny] == '1') {
dfs(grid,nx,ny);
}
}
}
};4.蓝桥OJ 3513:岛屿个数
这道题是,LeetCode 200的加强版,区别在于这题要求不统计“湖心岛”。
可以发现,通过调用两个不同的DFS,可以解决这个较复杂的问题:
DFS_Sea能调用DFS_Island,而DFS_Island不能调用DFS_Sea
这就是说,每次回答只会搜一次海,这次搜索会将四面八方的海全部标记
再搜陆地,即使遇到了没被标记过的海,也无法进入DFS_Sea,这样,湖心岛也就不会被搜了。
可以发现,DFS的使用很灵活,在这个算法中,vis[]数组的功能可以直接通过data[]实现
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int deltaOfIsland[4][2] = {{-1, 0},{1, 0},{0, -1},{0, 1}};//四面
int deltaOfSea[8][2] = {{-1, -1},{-1, 0},{-1, 1},{0, 1},{1, 1},{1, 0},{1, -1},{0, -1}};//八方
int ans = 0;
void DFS_Island(vector<vector<char>>& data, int r, int c, int m, int n){
data[r][c] = 'N';
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i){
int newR = r + deltaOfIsland[i][0];
int newC = c + deltaOfIsland[i][1];
if(newR >= 0 && newR < m && newC >= 0 && newC < n){
if(data[newR][newC] == '1')
DFS_Island(data, newR, newC, m, n);
}
}
}
void DFS_Sea(vector<vector<char>>& data, int r, int c, int m, int n){
data[r][c] = 'N';
for(int i = 0; i < 8; ++i){
int newR = r + deltaOfSea[i][0];
int newC = c + deltaOfSea[i][1];
if(newR >= 0 && newR < m && newC >= 0 && newC < n){
if(data[newR][newC] == '1'){
DFS_Island(data, newR, newC, m, n);
++ans;
}
else if(data[newR][newC] == '0'){
DFS_Sea(data, newR, newC, m, n);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
vector< vector<vector<char>> > datas;
for(int i = 0; i < t; ++i){
int m, n;
cin >> m >> n;
vector<vector<char>> data(m + 2, vector<char>(n + 2, '0')); //扩展一圈0
for(int r = 1; r < m + 1; ++r){
for(int c = 1; c < n + 1; ++c){
cin >> data[r][c];
}
}
datas.push_back(data);
}
for(int i = 0; i < t; ++i){
vector<vector<char>> data = datas[i];
int m = data.size();
int n = data[0].size();
DFS_Sea(data, 0, 0, m, n);
cout << ans << endl;
ans = 0;
}
return 0;
}5.LeetCode 2477:到达首都的最小油耗
class Solution {
public:
long long minimumFuelCost(vector<vector<int>>& roads, int seats) {
long long ans = 0;
int n = roads.size() + 1;
vector<vector<int> > G(n);
for (auto x : roads) {
G[x[0]].push_back(x[1]);
G[x[1]].push_back(x[0]);
}
function<int(int,int)> DFS = [&] (int u, int p){
int res = 1;
for (auto v : G[u]) {
if (v != p) {
int x = DFS(v,u);
ans += (x + seats - 1) / seats;
res += x;
}
}
return res;
};
DFS(0,-1);
return ans;
}
};6.蓝桥OJ 2942:数字王国之军训排队(剪枝)
不剪枝:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 15;
int a[N],n;
vector<int>v[N];
bool dfs(int cnt,int dep)
{
if(dep == n + 1)
{
//检查当前方案的合法性
for(int i = 1;i <= cnt;i ++)
{
for(int j = 0;j < v[i].size();++j)
{
for(int k = j+1 ;k < v[i].size();++k)
{
if(v[i][k] % v[i][j] == 0) return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
//枚举每个人所属的队伍
for(int i = 1;i <= cnt; ++i)
{
v[i].push_back(a[dep]);
if(dfs(cnt,dep + 1))return true;
//恢复现场
v[i].pop_back();
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++)cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++)
{
if(dfs(i,1))
{
cout << i << '\n';
break;
}
}
return 0;
}剪枝:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 15;
int a[N],n;
vector<int>v[N];
bool dfs(int cnt,int dep)
{
if(dep == n + 1)
{
return true;
}
//枚举每个人所属的队伍
for(int i = 1;i <= cnt;i ++)
{
bool tag = true;
for(const auto &j : v[i])
{
if(a[dep] % j == 0)
{
tag = false;
break;
}
}
if(!tag)continue;
v[i].push_back(a[dep]);
if(dfs(cnt,dep + 1))return true;
//恢复现场
v[i].pop_back();
}
return false;
}
int main(){
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++)cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++)
{
if(dfs(i,1))
{
cout << i << '\n';
break;
}
}
return 0;
}7.蓝桥OJ 3008:特殊三角形(剪枝)
原先,枚举至最深出,再判断该方案的合法性
剪枝,每次深入一层时都会判断,若不合法就直接中止这条搜索枝条。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int M=1e6+5;
int cnt[M],prefix[M]; //cnt记录边的乘积为i的三角形个数
int t;
void dfs(int dep,int st,int mul,int sum){ //dep最大是3(枚举三条边的长度)
//剪枝 //st确保边的三元组是递增的
if(mul>1e6) return;
if(dep==4){
cnt[mul]++;
return; //剪枝2
}
int maxn=pow(1e6/mul,1.0/(4-dep))+5; //剪枝3,确定边的最大值
for(int i=st+1;i<(dep==3 ? sum :maxn);i++){ //枚举边,剪枝4两边之和大于第三边
dfs(dep+1,i,mul*i,sum+i);
}
}
int main(){
dfs(1,1,1,0);
for(int i=1;i<=1e6;i++){ //乘积前缀和
prefix[i]=prefix[i-1]+cnt[i];
}
cin>>t;
for(int i=1;i<=t;i++){
int l,r;
cin>>l>>r;
cout<<prefix[r]-prefix[l-1]<<endl;
}
return 0;
}8.蓝桥OJ 3935:仙境诅咒
这题是又一个典型的DFS,通过匿名函数,和函数指针,更灵活地解决问题。
// 等价于对于任意两个距离小于等于 D 的人都连一条边
// 求起点所在连通块的大小
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using LL = long long;
using ld = long double;
using Pair = std::pair<ld, ld>;
void solve(const int &Case) {
int n;
std::cin >> n;
std::vector<Pair> a(n);
for (auto &[x, y]: a)std::cin >> x >> y;
int D;
std::cin >> D;
std::vector<int> vis(n);
auto norm = [&](const auto &x, const auto &y) { // 距离的平方
return (x.first - y.first) * (x.first - y.first) + (x.second - y.second) * (x.second - y.second);
};
std::function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int x) {
vis[x] = 1; // 标记当前人已经搜索过,以后不用再搜索
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (vis[i])continue; // 如果下一个人已经被搜索过,则不会再去搜
if (norm(a[i], a[x]) <= D * D)dfs(i);
}
};
dfs(0);
for (const auto &x: vis)std::cout << x << '\n';
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(nullptr);
std::cout.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
// std::cin >> T;
for (int Case = 1; Case <= T; Case++)solve(Case);
return 0;
}注意:
一.for(auto &[x,y] : a)在C++11中不能使用,可以看到本地编译器警示:
二.这份代码中的norm 函数与 dfs 函数的定义都使用了lambda表达式,
但在等号左边一个用了auto 另一个用了 function,为什么要这样写?有个问题:
C++使用auto推导lambda表达式的类型与function是否等价?
答案是不等价,
lambda表达式,用于定义匿名函数,这种函数不用写在外边,使用方便
auto是自动变量,可以自动识别类型,使用方便
function是函数指针,类似C中的写法,需要在定义时确定返回类型和参数列表。
1.auto推导出来的lambda如果没必要的话不要转换成function,因为有性能损失。
2.您不能在不返回任何内容的递归函数中使用auto。您必须使用void。这适用于lambda函数。
对这段代码做出修改:

就会这样报错,因为函数dfs是一个不返回任何内容的递归函数。

9.蓝桥OJ 4234:小怂爱水洼
经典网格题移动方法:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,m;
const int M = 105;
int mp[M][M];
int mov[4][2] = {{1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};
int visit1[M][M];
typedef long long ll;
ll sum ;
bool check(int x,int y){
return x>=1&&x<=n&&y>=1&&y<=m;
}
void dfs(int x,int y){
if(mp[x][y] == 0 || visit1[x][y])return ;
visit1[x][y] = 1;
sum+=mp[x][y];
for(int i = 0;i < 4;i ++){
int xx = x + mov[i][0];
int yy = y + mov[i][1];
if(!visit1[xx][yy]&&check(xx,yy)){
dfs(xx,yy);
}
}
}
int main(){
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++){
for(int j = 1;j <= m;j ++){
cin >> mp[i][j];
}
}
ll MAX = INT_MIN;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++){
for(int j = 1;j <= m;j ++){
if(mp[i][j]>0)dfs(i,j);
MAX = max(MAX,sum);
sum = 0;
}
}
cout<<MAX<<endl;
}10.蓝桥OJ 4494:黄金树
这题在二叉树中使用dfs
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using ll = long long ;
using ld = long double;
using namespace std;
void solve(const int &Case) {
int n;cin >> n;
vector<int>a(n + 1);
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++)cin >> a[i];
vector<int>ls (n + 1),rs(n + 1);
//vector<vector<int>> G(n + 1);
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++) {
cin >> ls[i] >> rs[i];
}
int ans = 0;
function<void(int ,int )>dfs = [&](int x,int w) {
if( x == -1)return ;
if( w == 0)ans += a[x];
dfs(ls[x],w + 1);
dfs(rs[x],w-1);
};
dfs(1,0);
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
solve(1);
return 0;
}11.蓝桥OJ 3820:混境之地5(记忆化)
直接跑dfs计算可能会超时,这里考虑设置状态,记忆化处理。
dp[x][y][t]表示从起点到点(x,y),且喷气背包使用了t次的 状态 下是否可以到终点。
没记忆:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const ll p = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 1e9,N = 1e3 + 3;
int n,m,k,sx,sy,fx,fy,h[N][N];
int dx[] = {0,0,1,-1};
int dy[] = {1,-1,0,0};
bool inmp(int x,int y)
{
return 1 <= x && x <= n && 1 <= y && y <= m;
}
//返回值表示能否到达终点(fx,fy),t表示当前使用的喷气背包的次数
bool dfs(int x,int y,int t)
{
if(x == fx && y == fy)return true;
for(int i = 0;i < 4 ;i ++)
{
int nx = x + dx[i],ny = y + dy[i];
if(!inmp(nx,ny))continue;
if(!t)
{
//不用
if(h[x][y] > h[nx][ny] && dfs(nx,ny,0))return true;
if(h[x][y] + k > h[nx][ny] && dfs(nx,ny,1))return true;
}else
{
if(h[x][y] > h[nx][ny] && dfs(nx,ny,1))return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m >> k;
cin >> sx >> sy >> fx >> fy;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++){
for(int j = 1;j <= m;j ++)
{
cin >> h[i][j];
}
}
cout << (dfs(sx,sy,0)?"Yes" : "No") << '\n';
return 0;
}有记忆:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
const ll p = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 1e9,N = 1e3 + 3;
int n,m,k,sx,sy,fx,fy,h[N][N];
int dx[] = {0,0,1,-1};
int dy[] = {1,-1,0,0};
int dp[N][N][2];
bool inmp(int x,int y)
{
return 1 <= x && x <= n && 1 <= y && y <= m;
}
//返回值表示能否到达终点(fx,fy),t表示当前使用的喷气背包的次数
bool dfs(int x,int y,int t)
{
if(x == fx && y == fy)return true;
if(dp[x][y][t] != -1)return dp[x][y][t];
for(int i = 0;i < 4 ;i ++)
{
int nx = x + dx[i],ny = y + dy[i];
if(!inmp(nx,ny))continue;
if(!t)
{
//不用
if(h[x][y] > h[nx][ny] && dfs(nx,ny,0))return true;
if(h[x][y] + k > h[nx][ny] && dfs(nx,ny,1))return true;
}else
{
if(h[x][y] > h[nx][ny] && dfs(nx,ny,1))return true;
}
}
return dp[x][y][t] = false;
}
int main()
{
memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));
cin >> n >> m >> k;
cin >> sx >> sy >> fx >> fy;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++){
for(int j = 1;j <= m;j ++)
{
cin >> h[i][j];
}
}
cout << (dfs(sx,sy,0)?"Yes" : "No") << '\n';
return 0;
}代码运行结果对比:

有记忆化处理的代码明显节省了内存占用。效率提高。
12.蓝桥OJ 216:地宫取宝 (记忆化)
这个地图很大,直接写搜索会超时,必须使用记忆化处理
我们记录这个最大值为mx,手中宝贝个数为cnt,
于是设置状态:dp[x][y][mx][cnt]表示走到(x,y),手中cnt个宝,且最大值为mx的方案
注意:开dp数组时要估算大小,这个四维数组占用空间约1e6,已经接近上限。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long ;
const ll p = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 1e9 ,N = 55;
int n,m,k,c[N][N];
int dx[] = {0,1};
int dy[] = {1,0};
int dp[N][N][15][15];
bool inmp(int x,int y)
{
return 1 <= x && x <= n && 1 <= y && y <= m;
}
ll dfs(int x,int y,int mx, int cnt)
{
if( x == n && y == m )return (ll)(cnt == k);
if(dp[x][y][mx][cnt] != -1)return dp[x][y][mx][cnt];
ll res = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < 2;i ++)
{
int nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i];
if(!inmp(nx,ny))continue;
//拿上这个宝贝
if(c[nx][ny] > mx && cnt < k)res = (res + dfs(nx,ny,c[nx][ny],cnt + 1)) % p;
//不拿这个宝贝
res = (res + dfs(nx,ny,mx,cnt)) % p;
}
return dp[x][y][mx][cnt] = res;
}
int main()
{
memset(dp,-1,sizeof dp);
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++){
for(int j = 1;j <= m;j ++)
{
cin >> c[i][j];
c[i][j] ++; //整体加1不影响结果,这样对mx可以设置初值为0,避免数组越界到-1
}
}
cout << (dfs(1,1,0,0) + dfs(1,1,c[1][1],1)) % p;
return 0;
}总结:
编写DFS程序就是在写递归函数,结合递归函数特征进行归纳:
1.递归出口:
递归函数要有递归出口,不同的题需要归纳出不同的递归中止条件
2.状态变量
表示了在求解一个问题时侯所处的阶段,前面所提到的 vis[]、cnt、dep、m、n等等都是状态变量,作为dfs函数的参数,表示递归至哪一层的状态。这个状态由题目的限制而调整。
3.回溯法
回溯就是DFS的一部分,DFS需要回退才能找到答案。
”「回溯算法」强调了「深度优先遍历」思想的用途“
用一个不断变化的状态变量,在尝试各种可能时搜索需要的结果。
4.优化:
记忆化就像是去设置一个表示状态变量的状态变量
剪枝就像是在每一层递归添加判断,根据变化后的状态不断决定是否向下。
5.DFS函数返回值:
不返回、返回bool数组、返回int数组……根据题目对回答的要求调整






















 1549
1549











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








