题目:
1、滑雪
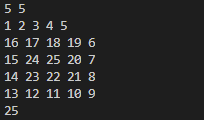
Michael喜欢滑雪这并不奇怪, 因为滑雪的确很刺激。可是为了获得速度,滑的区域必须向下倾斜,而且当你滑到坡底,你不得不再次走上坡或者等待升降机来载你。Michael想知道在一个区域中最长底滑坡。区域由一个二维数组给出。数组的每个数字代表点的高度。下面是一个例子
1 2 3 4 5
16 17 18 19 6
15 24 25 20 7
14 23 22 21 8
13 12 11 10 9
一个人可以从某个点滑向上下左右相邻四个点之一,当且仅当高度减小。在上面的例子中,一条可滑行的滑坡为24-17-16-1。当然25-24-23-…-3-2-1更长。事实上,这是最长的一条。
Input
输入的第一行表示区域的行数R和列数C(1 <= R,C <= 100)。下面是R行,每行有C个整数,代表高度h,0<=h<=10000。
Output
输出最长区域的长度。
Sample Input
5 5
1 2 3 4 5
16 17 18 19 6
15 24 25 20 7
14 23 22 21 8
13 12 11 10 9
Sample Output
25
y_,x_=map(int,input().split(' '))
nums=[]
for i in range(y_):
nums.append(list(map(int,input().split(' '))))
c=[[0 for a in range(x_)] for b in range(x_)]# 用于记录每个位置最多能往下划多少。
def check(y,x):
move=[[-1,0],[+1,0],[0,+1],[0,-1]]
if c[y][x]!=0:
return c[y][x]
count=1
for a,b in move:
ny=y+a
nx=x+b
if 0<=ny<y_ and 0<=nx<x_ and nums[y][x]>nums[ny][nx]:
count=max(count,check(ny,nx)+1)
c[y][x]=count#将结果记录
return c[y][x]#返回当前结果与上一次的最大长度进行比较。
res=0
for y in range(y_):
for x in range(x_):
res=max(res,check(y,x))
print(res)
结果:
题目:
2、八皇后问题是一个以国际象棋为背景的问题:如何能够在 8×8 的国际象棋棋盘上放置八个皇后,使得任何一个皇后都无法直接吃掉其他的皇后?为了达到此目的,任两个皇后都不能处于同一条横行、纵行或斜线上。八皇后问题可以推广为更一般的n皇后摆放问题:这时棋盘的大小变为n×n,而皇后个数也变成n。当且仅当 n = 1 或 n ≥ 4 时问题有解。
Input
无输入。
Output
按给定顺序和格式输出所有八皇后问题的解(见Sample Output)。
Sample Input
Sample Output
No. 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
No. 2
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
No. 3
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
No. 4
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
No. 5
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
No. 6
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
No. 7
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
No. 8
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
No. 9
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
…以下省略
代码:
queen = [None]*8
sum = 0
def check(queen, y): # 只需要检测从第0行到当前已经放置的行数。
for i in range(y):
# 判断是否不要同行的有在同一列的情况 或者 成对角线放置的情况。
if queen[i] == queen[y] or abs(i-y) == abs(queen[i]-queen[y]):
return False
return True
def put(queen, y):
global sum
if y == len(queen): # 如果能够经过检测放到最后一行就是一种新的放置方法。
sum += 1
return sum
for k in range(len(queen)): # k代表列数
queen[y] = k # 寻找在当前行有哪些列可以放置queen,所以把列的值赋给当前行数的queen。
if check(queen, y):
put(queen, y+1)
put(queen, 0)
print(sum)
结果:92






















 4932
4932











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








