一、什么是事务?
将多个操作当做一个原子操作来进行。(原子不可分割)
二、什么是ThreadLocal?
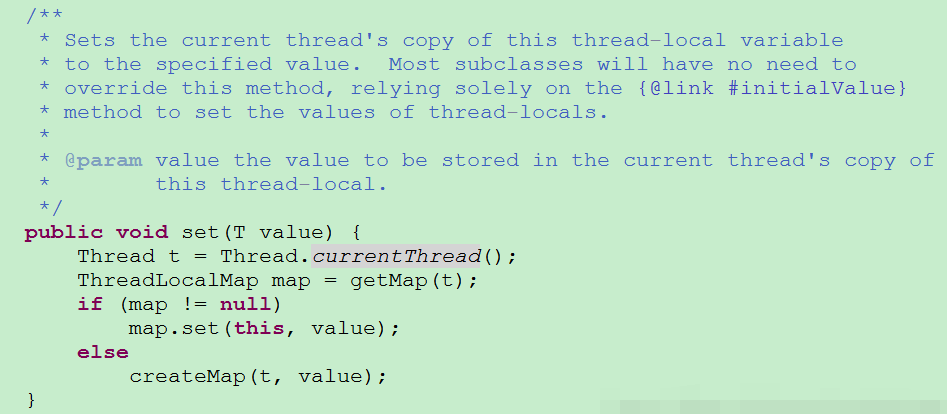
由以上API文档可以看出:
ThreadLocal主要用于解决线程安全问题,该类的对象一般以全局static形式存在,以便在全局范围内的资源共享,线程是安全的。ThreadLocal并不是本地线程,而是一个线程变量,它只是用来维护本地变量。针对每个线程提供自己的变量版本,避免了多线程的冲突问题,每个线程只需要维护自己的版本就好,彼此独立,不影响到对方。下图可以看到,向ThreadLocal里面存东西就是创建了一个Map,一个线程对应一个Map集合,然后ThreadLocal把这个Map挂到当前的线程底下,一个key值对应一个value,这样Map就只属于当前线程。
在线程消失之后,其线程局部实例的所有副本都会被垃圾回收(除非存在对这些副本的其他引用)。
上面我们知道了变量副本的存放在了map中,当我们不在调用set,此时不在将引用指向该‘map’,而本线程退出时会执行资源回收操作,将申请的资源进行回收,其实就是将引用设置为null。这时已经不在有任何引用指向该map,故而会被垃圾回收。
对比ThreadLocal和Synchronized同步机制:
相同点:都能解决多线程处理中对同一变量的访问冲突问题(即线程安全问题)。
不同点:
1、适用情况不同
在Synchronized同步机制中,使用同步保证同一时间只有一个线程访问,多个线程不能同时访问共享资源,否则出错。而ThreadLocal隔离了相关资源,并在同一个线程中可以共享这个资源,不同线程彼此独立,修改不会影响对方。
2、实现效果不同
对于多线程资源共享问题,同步机制采用了“以时间换空间”的方式,而ThreadLocal采用了“以空间换时间”的方式。前者仅提供一份变量,让不同线程排队访问,后者为每个线程都提供了一个变量的副本,因此各个线程内部访问互不受影响。
三、jdbc如何控制事务?
(1)jdbc在默认情况下自动提交事务,即一条sql语句执行后,立即提交事务。
(2)如果多个操作(即有多条sql语句要执行)要当做一个整理来执行,比如:在转账业务中需要执行两个sql,一个用来对账号进行扣除余额的操作(-1000),另一个用来对另一个账号进行加余额操作(+1000),显然,两个操作要么同时成功,要么同时失败。
(3)三个方法
//当flag为false,表示禁止自动提交
connection.setAutoCommit(booleanfalg);
//提交事务
connection.commit();
//回滚事务
connection.rollback();四、事务的封装(实例)
比如要“转账”操作,从资金账户(t_account表中的某条记录)扣掉200元,然后股票账户(t_stock表中的某条记录)增加价值200的股票。一般的编程逻辑是,先扣钱,紧接着再将和扣除的钱等价的股票数增加到指定股票账户。问题是,按照这种先后执行顺序,万一在扣钱后系统异常或者突然断电等极端情况下,可能会出现钱扣了但股票没买的情况,如何避免?需要将“转账”和“入账”这两个事务封装在一起,保证同时要么都执行,要么都不执行。示例如下:
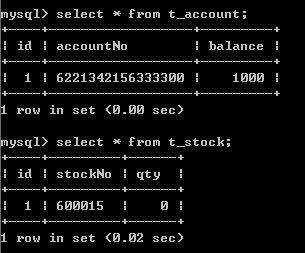
先创建两张数据表,资金账户和股票账户,"6221342156333300"账号中有1000元,股票账户中股票号为”600015“的数量为0;用到SQL语句:
create table t_account(
id int primary key auto_increment,
accountNo varchar(16),
balance int
) ENGINE=InnoDB;
insert into t_account(accountNo,balance) values('6221342156333300',1000);
create table t_stock(
id int primary key auto_increment,
stockNo varchar(6),
qty int
) ENGINE=InnoDB;
insert into t_stock(stockNo,qty)values('600015',0);
1.新建实体
/**
* @Description:资金账户
*
*/
public class Account {
private int id;
private String accountNo;
private int balance;
//省略get()和set()
}
/**
* @Description:股票账户
*
*/
public class Stock {
private int id;
private String stockNo;
private int qty;
//省略get()和set()
}
public interface AccountDao {
public Account findByAccountNo(String accountNo) throws Exception;
public void modify(Account a) throws Exception;
}public interface StockDao {
public Stock findByStockNo(String stockNo) throws Exception;
public void modify(Stock s) throws Exception;
}
public class AccountDAOImpl implements AccountDao {
@Override
public Account findByAccountNo(String accountNo) throws Exception {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement stat = null;
ResultSet rst = null;
Account a = null;
try {
conn = DBUtil.getConnection2();
stat = conn
.prepareStatement("select * from t_account where accountNo=?");
stat.setString(1, accountNo);
rst = stat.executeQuery();
if (rst.next()) {
a = new Account();
a.setAccountNo(accountNo);
a.setBalance(rst.getInt("balance"));
a.setId(rst.getInt("id"));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw e;
} finally {
}
return a;
}
@Override
public void modify(Account a) throws Exception {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement stat = null;
try {
conn = DBUtil.getConnection2();
stat = conn.prepareStatement("update t_account set balance=? "
+ "where accountNo=?");
stat.setInt(1, a.getBalance());
stat.setString(2, a.getAccountNo());
stat.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw e;
} finally {
}
}
}
public class StockDaoImpl implements StockDao {
@Override
public Stock findByStockNo(String stockNo) throws Exception {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement stat = null;
ResultSet rst = null;
Stock s = null;
try {
conn = DBUtil.getConnection2();
stat = conn
.prepareStatement("select * from t_stock where stockNo=?");
stat.setString(1, stockNo);
rst = stat.executeQuery();
if (rst.next()) {
s = new Stock();
s.setStockNo(stockNo);
s.setQty(rst.getInt("qty"));
s.setId(rst.getInt("id"));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw e;
} finally {
}
return s;
}
@Override
public void modify(Stock s) throws Exception {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement stat = null;
try {
conn = DBUtil.getConnection2();
conn.setAutoCommit(false);// 禁止自动提交事务
stat = conn.prepareStatement("update t_stock set qty=? "
+ "where stockNo=?");
stat.setInt(1, s.getQty());
stat.setString(2, s.getStockNo());
stat.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw e;
} finally {
}
}
}
4.设计工具类,利用ThreadLocal确保后续转账的“进账”和“出账”使用的是同一个Connection。
public class DBUtil {
private static String driver = ConfigUtil.getValue("driver");
private static String url = ConfigUtil.getValue("url");
private static String dbUser = ConfigUtil.getValue("dbUser");
private static String dbPwd = ConfigUtil.getValue("dbPwd");
private static ThreadLocal<Connection> connectionHoders = new ThreadLocal<Connection>();
public static synchronized Connection getConnection2() throws Exception {
// 先从线程局部变量(看成一个容器)中取
Connection conn = connectionHoders.get();
if (conn == null) {
conn = getConnection();
// 以当前线程对象作为key,以conn作为value放到一个HashMap里面
connectionHoders.set(conn);
}
return conn;
}
public static void close2() {
// 以当前线程对象作为key,从HashMap中取对应的value
Connection conn = connectionHoders.get();
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
connectionHoders.set(null);// 清空容器
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
Class.forName(driver);
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, dbUser, dbPwd);
}
public static void close(Connection conn) {
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}5.这里使用了配置文件和配置工具类
db.properties:
#mysql
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
dbUser=root
dbPwd=111111
#Oracle
AccountDao=dao.impl.AccountDAOImpl
/**
* @Description:读取db.properties文件
*
*/
public class ConfigUtil {
public static Properties props = new Properties();
static {
InputStream ips = ConfigUtil.class.getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("util/db.properties");
try {
props.load(ips);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("读取db.properties失败");
}
}
public static String getValue(String key) {
return props.getProperty(key);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(getValue("driver"));
}
}
6.新建事务管理器,统一操作事务。
/**
* @Description:事务管理器
*
*/
public class TransactionManager {
// 开始一个事务
public static void begin() throws Exception {
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnection2();
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
}
// 提交一个事务
public static void commit() throws Exception {
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnection2();
conn.commit();
// 必须关闭连接
DBUtil.close2();
}
// 回滚一个事务
public static void rollback() throws Exception {
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnection2();
conn.rollback();
// 必须关闭连接
DBUtil.close2();
}
}
7.完成业务类,并设置异常测试。
/**
* @Description:业务类
*
*/
public class AccountService {
public void buyStock(String accountNo, String stockNo, int amount)
throws Exception {
//开始事务
TransactionManager.begin();
try {
AccountDao accountDao = new AccountDAOImpl();
// 根据资金账户找到要操作的记录
Account a = accountDao.findByAccountNo(accountNo);
// 减去相应金额
a.setBalance(a.getBalance() - amount);
// 修改
accountDao.modify(a);
if (1 == 1) {
throw new Exception("系统出现异常");
}
// 修改股票账户
StockDao stockDao = new StockDaoImpl();
Stock s = stockDao.findByStockNo(stockNo);
s.setQty(s.getQty() + amount / 10);
stockDao.modify(s);
TransactionManager.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
TransactionManager.rollback();
}
}
}
8.使用单元测试测试7中的服务。
public class AccountServiceTest {
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
AccountService service = new AccountService();
service.buyStock("6221342156333300", "600015", 10);
}
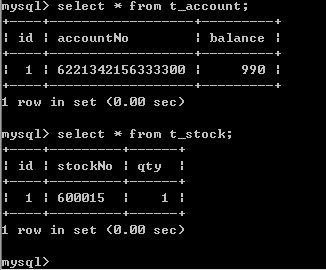
}运行效果图:
就算出现异常,也不会只执行异常前面的“扣钱”操作而不执行异常后面的“增股票”操作,而是两者都不执行。
若将7中
if (1 == 1)if (1 == 2)购买股票成功,扣钱和增股票同时进行!
源代码:
http://download.csdn.net/detail/daijin888888/9473339
转载请注明出处:
http://blog.csdn.net/daijin888888/article/details/50988053























 232
232

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








