Linux内核中List链表的实现,对于想进阶的程序员来说,无疑是一个很好的学习机会。内核实现了一个功能十分强大的链表,而且是开源的,用在其他需要的地方岂不是很省事。
一、看List实现前,先补充typeof的知识,方便阅读。
typeof(int *) p1, p2; /* Declares two int pointers p1, p2 */ int *p1, *p2; typeof(int) * p3, p4;/* Declares int pointer p3 and int p4 */ int * p3, p4;extern int foo(); typeof(foo()) var;
typeof(foo())var; 等效于typeof(int) var; 也就等效于 int var; 同时foo()函数也不会被执行。
typeof构造的主要应用是用在宏定义中,可以使用typeof关键字来引用宏参数的类型。
二、如何自己在非Linux环境下使用双向List。
将这段代码移植到一般的C程序,那么基本上要实现这么几个功能。1、初始化List头。 2、向List中添加一个节点到首节点后 3、向List中添加一个节点到首节点前 4、从List中删除一个节点 5、从List中取出一个节点,但节点在List中不删除。 6、遍历List Linux内核中的List功能做得那么完善,需要的时候再看看。7、判断链表是否为空。


#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #ifndef ARCH_HAS_PREFETCH #define ARCH_HAS_PREFETCH static void prefetch(const void *x) {;} #endif struct list_head { struct list_head *next, *prev; }; #define list_entry(ptr, type, member) container_of(ptr, type, member) #define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t)& ((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER) #define container_of(ptr, type, member) (type*)((char *)ptr - offsetof(type,member)) #define list_for_each(pos, head) \ for (pos = (head)->next; prefetch(pos->next), pos != (head); \ pos = pos->next) #define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) } //prev和next都指向自己 //prev和next都指向自己 static void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list) { list->next = list; list->prev = list; } //new在编译器里被认作关键字 原代码是new 被改为l_new //l_new 是要被插入的节点 //prev 是插入点前面的一个节点 //next 是插入点后面的一个节点 static void __list_add(struct list_head *l_new, struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next) { next->prev = l_new; l_new->next = next; l_new->prev = prev; prev->next = l_new; } //这个函数对上面简化 新加入的节点在head和head->next之间 也就是head之后 static void list_add(struct list_head *l_new, struct list_head *head) { __list_add(l_new, head, head->next); } //这个函数对上面简化 新加入的节点在head->prev和head之间 也就是head之前 static void list_add_tail(struct list_head *l_new, struct list_head *head) { __list_add(l_new, head->prev, head); } //删除一个双向列表中的一个节点 删除节点在prev和next之间 static void __list_del(struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next) { next->prev = prev; prev->next = next; } //从列表中删除entry节点,这个函数是对上面函数的简化 //entry->next = LIST_POISON1; //entry->prev = LIST_POISON2; static void list_del(struct list_head *entry) { __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next); entry->next = NULL; //这两个指针可以不处理,如果从list中del掉了一个节点, entry->prev = NULL; //接下来 这个节点就要被删除 } //跟上面函数功能一样,将entry中队列里删除后,初始化entry为队列头 static void list_del_init(struct list_head *entry) { __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next); INIT_LIST_HEAD(entry); } //判断list是不是最后一个节点 //head节点是队列的第一个节点 //return list->next == head 或者 return head->prev == list一样 static int list_is_last(const struct list_head *list, const struct list_head *head) { return list->next == head; } //列表是不是为空 //head节点 是队列的头节点 static int list_empty(const struct list_head *head) { return head->next == head; } //建立一个数据结构 typedef struct Student { int id; //学号 char name[16]; //姓名 struct list_head list; }Student; void main(void) { int i=0; char c_tmp[16]={0}; Student* p; struct list_head *n,*pos; Student stdudent_head; //用作列表头 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&stdudent_head.list); //初始化列表头 if(list_empty(&stdudent_head.list)) //如果是空,返回1 { printf("Now List is Empty!\n"); } for(i=0;i<5;i++) { p = (Student* )malloc(sizeof(Student)); p->id = i+1; memset(c_tmp,0,16); sprintf((char*)c_tmp,"MYNAME-%d",i+1); strcpy((char*)(p->name),(char*)c_tmp); list_add_tail(&p->list,&stdudent_head.list); //依次添加5个节点到队列中 } list_for_each(pos, &stdudent_head.list) { p = list_entry(pos,Student,list); printf("----------------------------\n"); printf("id = %d\n",p->id); printf("name = %s\n",p->name); printf("----------------------------\n"); } printf("test end-------------!\n"); system("pause"); }
将上面代码在VS2010下编译,得到结果如下:
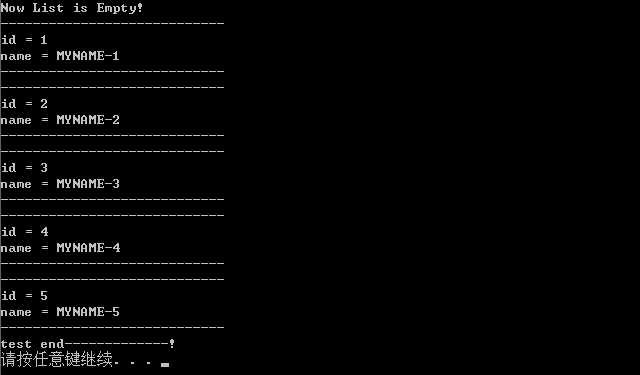
算是基本移植完成。
自己写了之后,会发现,几个宏的实现部分,在VS2010下编译很成问题。上面的container_of宏做了修改,原因参看下面的参考文档。
参考文档:
http://blog.csdn.net/eastmoon502136/article/details/8082009 这篇文档写得更好,值得一看。
http://www.cnblogs.com/wang_yb/archive/2013/04/16/3023892.html 这篇文档里有container_of很好的解释。
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-23069658-id-4745433.html 深入解析container_of宏和offsetof宏。
http://bbs.chinaunix.net/thread-3769132-1-1.html 在Windows平台下,container_of宏编译不过的问题。
附录Linux内核中的list.h文件,方便以后需要查阅:


1 #ifndef _LINUX_LIST_H 2 #define _LINUX_LIST_H 3 4 #include <linux/stddef.h> 5 #include <linux/poison.h> 6 7 #ifndef ARCH_HAS_PREFETCH 8 #define ARCH_HAS_PREFETCH 9 static inline void prefetch(const void *x) {;} 10 #endif 11 12 /* 13 * Simple doubly linked list implementation. 14 * 15 * Some of the internal functions ("__xxx") are useful when 16 * manipulating whole lists rather than single entries, as 17 * sometimes we already know the next/prev entries and we can 18 * generate better code by using them directly rather than 19 * using the generic single-entry routines. 20 */ 21 22 struct list_head { 23 struct list_head *next, *prev; 24 }; 25 26 #define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) } 27 28 #define LIST_HEAD(name) \ 29 struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) 30 31 static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list) 32 { 33 list->next = list; 34 list->prev = list; 35 } 36 37 /* 38 * Insert a new entry between two known consecutive entries. 39 * 40 * This is only for internal list manipulation where we know 41 * the prev/next entries already! 42 */ 43 static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new, 44 struct list_head *prev, 45 struct list_head *next) 46 { 47 next->prev = new; 48 new->next = next; 49 new->prev = prev; 50 prev->next = new; 51 } 52 53 /** 54 * list_add - add a new entry 55 * @new: new entry to be added 56 * @head: list head to add it after 57 * 58 * Insert a new entry after the specified head. 59 * This is good for implementing stacks. 60 */ 61 static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head) 62 { 63 __list_add(new, head, head->next); 64 } 65 66 /** 67 * list_add_tail - add a new entry 68 * @new: new entry to be added 69 * @head: list head to add it before 70 * 71 * Insert a new entry before the specified head. 72 * This is useful for implementing queues. 73 */ 74 static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head) 75 { 76 __list_add(new, head->prev, head); 77 } 78 79 /* 80 * Delete a list entry by making the prev/next entries 81 * point to each other. 82 * 83 * This is only for internal list manipulation where we know 84 * the prev/next entries already! 85 */ 86 static inline void __list_del(struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next) 87 { 88 next->prev = prev; 89 prev->next = next; 90 } 91 92 /** 93 * list_del - deletes entry from list. 94 * @entry: the element to delete from the list. 95 * Note: list_empty() on entry does not return true after this, the entry is 96 * in an undefined state. 97 */ 98 static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry) 99 { 100 __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next); 101 entry->next = LIST_POISON1; 102 entry->prev = LIST_POISON2; 103 } 104 105 /** 106 * list_replace - replace old entry by new one 107 * @old : the element to be replaced 108 * @new : the new element to insert 109 * 110 * If @old was empty, it will be overwritten. 111 */ 112 static inline void list_replace(struct list_head *old, 113 struct list_head *new) 114 { 115 new->next = old->next; 116 new->next->prev = new; 117 new->prev = old->prev; 118 new->prev->next = new; 119 } 120 121 static inline void list_replace_init(struct list_head *old, 122 struct list_head *new) 123 { 124 list_replace(old, new); 125 INIT_LIST_HEAD(old); 126 } 127 128 /** 129 * list_del_init - deletes entry from list and reinitialize it. 130 * @entry: the element to delete from the list. 131 */ 132 static inline void list_del_init(struct list_head *entry) 133 { 134 __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next); 135 INIT_LIST_HEAD(entry); 136 } 137 138 /** 139 * list_move - delete from one list and add as another's head 140 * @list: the entry to move 141 * @head: the head that will precede our entry 142 */ 143 static inline void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head) 144 { 145 __list_del(list->prev, list->next); 146 list_add(list, head); 147 } 148 149 /** 150 * list_move_tail - delete from one list and add as another's tail 151 * @list: the entry to move 152 * @head: the head that will follow our entry 153 */ 154 static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list, 155 struct list_head *head) 156 { 157 __list_del(list->prev, list->next); 158 list_add_tail(list, head); 159 } 160 161 /** 162 * list_is_last - tests whether @list is the last entry in list @head 163 * @list: the entry to test 164 * @head: the head of the list 165 */ 166 static inline int list_is_last(const struct list_head *list, 167 const struct list_head *head) 168 { 169 return list->next == head; 170 } 171 172 /** 173 * list_empty - tests whether a list is empty 174 * @head: the list to test. 175 */ 176 static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head) 177 { 178 return head->next == head; 179 } 180 181 /** 182 * list_empty_careful - tests whether a list is empty and not being modified 183 * @head: the list to test 184 * 185 * Description: 186 * tests whether a list is empty _and_ checks that no other CPU might be 187 * in the process of modifying either member (next or prev) 188 * 189 * NOTE: using list_empty_careful() without synchronization 190 * can only be safe if the only activity that can happen 191 * to the list entry is list_del_init(). Eg. it cannot be used 192 * if another CPU could re-list_add() it. 193 */ 194 static inline int list_empty_careful(const struct list_head *head) 195 { 196 struct list_head *next = head->next; 197 return (next == head) && (next == head->prev); 198 } 199 200 /** 201 * list_is_singular - tests whether a list has just one entry. 202 * @head: the list to test. 203 */ 204 static inline int list_is_singular(const struct list_head *head) 205 { 206 return !list_empty(head) && (head->next == head->prev); 207 } 208 209 static inline void __list_cut_position(struct list_head *list, 210 struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry) 211 { 212 struct list_head *new_first = entry->next; 213 list->next = head->next; 214 list->next->prev = list; 215 list->prev = entry; 216 entry->next = list; 217 head->next = new_first; 218 new_first->prev = head; 219 } 220 221 /** 222 * list_cut_position - cut a list into two 223 * @list: a new list to add all removed entries 224 * @head: a list with entries 225 * @entry: an entry within head, could be the head itself 226 * and if so we won't cut the list 227 * 228 * This helper moves the initial part of @head, up to and 229 * including @entry, from @head to @list. You should 230 * pass on @entry an element you know is on @head. @list 231 * should be an empty list or a list you do not care about 232 * losing its data. 233 * 234 */ 235 static inline void list_cut_position(struct list_head *list, 236 struct list_head *head, struct list_head *entry) 237 { 238 if (list_empty(head)) 239 return; 240 if (list_is_singular(head) && 241 (head->next != entry && head != entry)) 242 return; 243 if (entry == head) 244 INIT_LIST_HEAD(list); 245 else 246 __list_cut_position(list, head, entry); 247 } 248 249 static inline void __list_splice(const struct list_head *list, 250 struct list_head *prev, 251 struct list_head *next) 252 { 253 struct list_head *first = list->next; 254 struct list_head *last = list->prev; 255 256 first->prev = prev; 257 prev->next = first; 258 259 last->next = next; 260 next->prev = last; 261 } 262 263 /** 264 * list_splice - join two lists, this is designed for stacks 265 * @list: the new list to add. 266 * @head: the place to add it in the first list. 267 */ 268 static inline void list_splice(const struct list_head *list, 269 struct list_head *head) 270 { 271 if (!list_empty(list)) 272 __list_splice(list, head, head->next); 273 } 274 275 /** 276 * list_splice_tail - join two lists, each list being a queue 277 * @list: the new list to add. 278 * @head: the place to add it in the first list. 279 */ 280 static inline void list_splice_tail(struct list_head *list, 281 struct list_head *head) 282 { 283 if (!list_empty(list)) 284 __list_splice(list, head->prev, head); 285 } 286 287 /** 288 * list_splice_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list. 289 * @list: the new list to add. 290 * @head: the place to add it in the first list. 291 * 292 * The list at @list is reinitialised 293 */ 294 static inline void list_splice_init(struct list_head *list, 295 struct list_head *head) 296 { 297 if (!list_empty(list)) { 298 __list_splice(list, head, head->next); 299 INIT_LIST_HEAD(list); 300 } 301 } 302 303 /** 304 * list_splice_tail_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list 305 * @list: the new list to add. 306 * @head: the place to add it in the first list. 307 * 308 * Each of the lists is a queue. 309 * The list at @list is reinitialised 310 */ 311 static inline void list_splice_tail_init(struct list_head *list, 312 struct list_head *head) 313 { 314 if (!list_empty(list)) { 315 __list_splice(list, head->prev, head); 316 INIT_LIST_HEAD(list); 317 } 318 } 319 320 /** 321 * list_entry - get the struct for this entry 322 * @ptr: the &struct list_head pointer. 323 * @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in. 324 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 325 */ 326 #define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \ 327 container_of(ptr, type, member) 328 329 /** 330 * list_first_entry - get the first element from a list 331 * @ptr: the list head to take the element from. 332 * @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in. 333 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 334 * 335 * Note, that list is expected to be not empty. 336 */ 337 #define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) \ 338 list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member) 339 340 /** 341 * list_for_each - iterate over a list 342 * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor. 343 * @head: the head for your list. 344 */ 345 #define list_for_each(pos, head) \ 346 for (pos = (head)->next; prefetch(pos->next), pos != (head); \ 347 pos = pos->next) 348 349 /** 350 * __list_for_each - iterate over a list 351 * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor. 352 * @head: the head for your list. 353 * 354 * This variant differs from list_for_each() in that it's the 355 * simplest possible list iteration code, no prefetching is done. 356 * Use this for code that knows the list to be very short (empty 357 * or 1 entry) most of the time. 358 */ 359 #define __list_for_each(pos, head) \ 360 for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next) 361 362 /** 363 * list_for_each_prev - iterate over a list backwards 364 * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor. 365 * @head: the head for your list. 366 */ 367 #define list_for_each_prev(pos, head) \ 368 for (pos = (head)->prev; prefetch(pos->prev), pos != (head); \ 369 pos = pos->prev) 370 371 /** 372 * list_for_each_safe - iterate over a list safe against removal of list entry 373 * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor. 374 * @n: another &struct list_head to use as temporary storage 375 * @head: the head for your list. 376 */ 377 #define list_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) \ 378 for (pos = (head)->next, n = pos->next; pos != (head); \ 379 pos = n, n = pos->next) 380 381 /** 382 * list_for_each_prev_safe - iterate over a list backwards safe against removal of list entry 383 * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor. 384 * @n: another &struct list_head to use as temporary storage 385 * @head: the head for your list. 386 */ 387 #define list_for_each_prev_safe(pos, n, head) \ 388 for (pos = (head)->prev, n = pos->prev; \ 389 prefetch(pos->prev), pos != (head); \ 390 pos = n, n = pos->prev) 391 392 /** 393 * list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type 394 * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 395 * @head: the head for your list. 396 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 397 */ 398 #define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \ 399 for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member); \ 400 prefetch(pos->member.next), &pos->member != (head); \ 401 pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member)) 402 403 /** 404 * list_for_each_entry_reverse - iterate backwards over list of given type. 405 * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 406 * @head: the head for your list. 407 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 408 */ 409 #define list_for_each_entry_reverse(pos, head, member) \ 410 for (pos = list_entry((head)->prev, typeof(*pos), member); \ 411 prefetch(pos->member.prev), &pos->member != (head); \ 412 pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member)) 413 414 /** 415 * list_prepare_entry - prepare a pos entry for use in list_for_each_entry_continue() 416 * @pos: the type * to use as a start point 417 * @head: the head of the list 418 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 419 * 420 * Prepares a pos entry for use as a start point in list_for_each_entry_continue(). 421 */ 422 #define list_prepare_entry(pos, head, member) \ 423 ((pos) ? : list_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member)) 424 425 /** 426 * list_for_each_entry_continue - continue iteration over list of given type 427 * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 428 * @head: the head for your list. 429 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 430 * 431 * Continue to iterate over list of given type, continuing after 432 * the current position. 433 */ 434 #define list_for_each_entry_continue(pos, head, member) \ 435 for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \ 436 prefetch(pos->member.next), &pos->member != (head); \ 437 pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member)) 438 439 /** 440 * list_for_each_entry_continue_reverse - iterate backwards from the given point 441 * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 442 * @head: the head for your list. 443 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 444 * 445 * Start to iterate over list of given type backwards, continuing after 446 * the current position. 447 */ 448 #define list_for_each_entry_continue_reverse(pos, head, member) \ 449 for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member); \ 450 prefetch(pos->member.prev), &pos->member != (head); \ 451 pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member)) 452 453 /** 454 * list_for_each_entry_from - iterate over list of given type from the current point 455 * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 456 * @head: the head for your list. 457 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 458 * 459 * Iterate over list of given type, continuing from current position. 460 */ 461 #define list_for_each_entry_from(pos, head, member) \ 462 for (; prefetch(pos->member.next), &pos->member != (head); \ 463 pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member)) 464 465 /** 466 * list_for_each_entry_safe - iterate over list of given type safe against removal of list entry 467 * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 468 * @n: another type * to use as temporary storage 469 * @head: the head for your list. 470 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 471 */ 472 #define list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, n, head, member) \ 473 for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member), \ 474 n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \ 475 &pos->member != (head); \ 476 pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member)) 477 478 /** 479 * list_for_each_entry_safe_continue 480 * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 481 * @n: another type * to use as temporary storage 482 * @head: the head for your list. 483 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 484 * 485 * Iterate over list of given type, continuing after current point, 486 * safe against removal of list entry. 487 */ 488 #define list_for_each_entry_safe_continue(pos, n, head, member) \ 489 for (pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member), \ 490 n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \ 491 &pos->member != (head); \ 492 pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member)) 493 494 /** 495 * list_for_each_entry_safe_from 496 * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 497 * @n: another type * to use as temporary storage 498 * @head: the head for your list. 499 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 500 * 501 * Iterate over list of given type from current point, safe against 502 * removal of list entry. 503 */ 504 #define list_for_each_entry_safe_from(pos, n, head, member) \ 505 for (n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \ 506 &pos->member != (head); \ 507 pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member)) 508 509 /** 510 * list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse 511 * @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 512 * @n: another type * to use as temporary storage 513 * @head: the head for your list. 514 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct. 515 * 516 * Iterate backwards over list of given type, safe against removal 517 * of list entry. 518 */ 519 #define list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse(pos, n, head, member) \ 520 for (pos = list_entry((head)->prev, typeof(*pos), member), \ 521 n = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member); \ 522 &pos->member != (head); \ 523 pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.prev, typeof(*n), member)) 524 525 /* 526 * Double linked lists with a single pointer list head. 527 * Mostly useful for hash tables where the two pointer list head is 528 * too wasteful. 529 * You lose the ability to access the tail in O(1). 530 */ 531 532 struct hlist_head { 533 struct hlist_node *first; 534 }; 535 536 struct hlist_node { 537 struct hlist_node *next, **pprev; 538 }; 539 540 #define HLIST_HEAD_INIT { .first = NULL } 541 #define HLIST_HEAD(name) struct hlist_head name = { .first = NULL } 542 #define INIT_HLIST_HEAD(ptr) ((ptr)->first = NULL) 543 static inline void INIT_HLIST_NODE(struct hlist_node *h) 544 { 545 h->next = NULL; 546 h->pprev = NULL; 547 } 548 549 static inline int hlist_unhashed(const struct hlist_node *h) 550 { 551 return !h->pprev; 552 } 553 554 static inline int hlist_empty(const struct hlist_head *h) 555 { 556 return !h->first; 557 } 558 559 static inline void __hlist_del(struct hlist_node *n) 560 { 561 struct hlist_node *next = n->next; 562 struct hlist_node **pprev = n->pprev; 563 *pprev = next; 564 if (next) 565 next->pprev = pprev; 566 } 567 568 static inline void hlist_del(struct hlist_node *n) 569 { 570 __hlist_del(n); 571 n->next = LIST_POISON1; 572 n->pprev = LIST_POISON2; 573 } 574 575 static inline void hlist_del_init(struct hlist_node *n) 576 { 577 if (!hlist_unhashed(n)) { 578 __hlist_del(n); 579 INIT_HLIST_NODE(n); 580 } 581 } 582 583 static inline void hlist_add_head(struct hlist_node *n, struct hlist_head *h) 584 { 585 struct hlist_node *first = h->first; 586 n->next = first; 587 if (first) 588 first->pprev = &n->next; 589 h->first = n; 590 n->pprev = &h->first; 591 } 592 593 /* next must be != NULL */ 594 static inline void hlist_add_before(struct hlist_node *n, 595 struct hlist_node *next) 596 { 597 n->pprev = next->pprev; 598 n->next = next; 599 next->pprev = &n->next; 600 *(n->pprev) = n; 601 } 602 603 static inline void hlist_add_after(struct hlist_node *n, 604 struct hlist_node *next) 605 { 606 next->next = n->next; 607 n->next = next; 608 next->pprev = &n->next; 609 610 if(next->next) 611 next->next->pprev = &next->next; 612 } 613 614 #define hlist_entry(ptr, type, member) container_of(ptr,type,member) 615 616 #define hlist_for_each(pos, head) \ 617 for (pos = (head)->first; pos && ({ prefetch(pos->next); 1; }); \ 618 pos = pos->next) 619 620 #define hlist_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) \ 621 for (pos = (head)->first; pos && ({ n = pos->next; 1; }); \ 622 pos = n) 623 624 /** 625 * hlist_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type 626 * @tpos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 627 * @pos: the &struct hlist_node to use as a loop cursor. 628 * @head: the head for your list. 629 * @member: the name of the hlist_node within the struct. 630 */ 631 #define hlist_for_each_entry(tpos, pos, head, member) \ 632 for (pos = (head)->first; \ 633 pos && ({ prefetch(pos->next); 1;}) && \ 634 ({ tpos = hlist_entry(pos, typeof(*tpos), member); 1;}); \ 635 pos = pos->next) 636 637 /** 638 * hlist_for_each_entry_continue - iterate over a hlist continuing after current point 639 * @tpos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 640 * @pos: the &struct hlist_node to use as a loop cursor. 641 * @member: the name of the hlist_node within the struct. 642 */ 643 #define hlist_for_each_entry_continue(tpos, pos, member) \ 644 for (pos = (pos)->next; \ 645 pos && ({ prefetch(pos->next); 1;}) && \ 646 ({ tpos = hlist_entry(pos, typeof(*tpos), member); 1;}); \ 647 pos = pos->next) 648 649 /** 650 * hlist_for_each_entry_from - iterate over a hlist continuing from current point 651 * @tpos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 652 * @pos: the &struct hlist_node to use as a loop cursor. 653 * @member: the name of the hlist_node within the struct. 654 */ 655 #define hlist_for_each_entry_from(tpos, pos, member) \ 656 for (; pos && ({ prefetch(pos->next); 1;}) && \ 657 ({ tpos = hlist_entry(pos, typeof(*tpos), member); 1;}); \ 658 pos = pos->next) 659 660 /** 661 * hlist_for_each_entry_safe - iterate over list of given type safe against removal of list entry 662 * @tpos: the type * to use as a loop cursor. 663 * @pos: the &struct hlist_node to use as a loop cursor. 664 * @n: another &struct hlist_node to use as temporary storage 665 * @head: the head for your list. 666 * @member: the name of the hlist_node within the struct. 667 */ 668 #define hlist_for_each_entry_safe(tpos, pos, n, head, member) \ 669 for (pos = (head)->first; \ 670 pos && ({ n = pos->next; 1; }) && \ 671 ({ tpos = hlist_entry(pos, typeof(*tpos), member); 1;}); \ 672 pos = n) 673 674 #endif





















 691
691











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








