进程的概念:
程序(任务)的执行过程,具有动态性;
持有资源(共享内容,共享文件)和线程,是系统进行资源分配和调度的基本单位。
线程的概念:
线程是系统中最小的执行单元。 同一进程中有多个线程。 线程共享进程的资源。
线程之间的关系(交互):互斥、同步。
java提供了两种多线程实现方式:
1、继承java.lang包下的Thread类,覆写Thread的run()方法
2、实现java.lang.Runnable接口,同样在run()方法中实现运行在线程上的代码
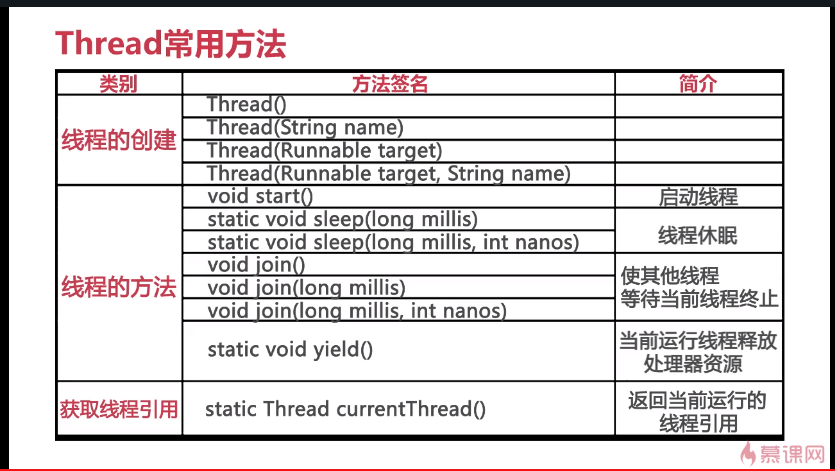
一个简单的例子:
package com.study.thread;
public class Actor extends Thread {
public void run(){
System.out.println(getName()+"是一个演员!");
int count = 0;
boolean keepRunning = true;
while(keepRunning){
System.out.println(getName()+"登台演出:"+ (++count));
if(count == 100){
keepRunning = false;
}
if(count%10== 0){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
System.out.println(getName()+"的演出结束了!");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Thread actor = new Actor();
actor.setName("Mr. Thread");
actor.start();
Thread actressThread = new Thread(new Actress(),"Ms. Runnable");
actressThread.start();
}
}
class Actress implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"是一个演员!");
int count = 0;
boolean keepRunning = true;
while(keepRunning){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"登台演出:"+ (++count));
if(count == 100){
keepRunning = false;
}
if(count%10== 0){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"的演出结束了!");
}
}





















 246
246











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








