一、@Conditional 注解
@Conditional 注解:按照一定的条件进行判断,满足条件向容器中注册 bean
1.1 注解定义:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Conditional {
// 必须满足所有的条件才能被注册到 IoC 容器中
// value 属性值是一个继承自 Condition 接口的子类
Class<? extends Condition>[] value();
}
- @Conditional 注解中只有一个属性 value,该 value 值必须是实现了 Condition 接口的子类
- 该接口可以配置在类上以及方法上
1.2 Condition 接口
再来看一下 Condition 接口:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Condition {
boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata);
}
Condition 接口中只定义了一个 matches 方法,所有的配置在 @Conditional 注解上的类都需要实现该方法。该方法主要用于确定配置了该注解的类或方法是否可以注册到 IoC 容器中,确定条件即为 matches 方法,如果 matches 方法返回 true,表示条件匹配,可以注册到 IoC 容器。
matches 方法有两个参数:
- context:条件上下文,是一个接口
- metadata:被检查的类或方法的元数据,是一个接口
1.3 ConditionContext 接口:
public interface ConditionContext {
// 如果条件匹配,则返回将保存 bean 定义的 BeanDefinitionRegistry。
BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry();
// 获取容器
@Nullable
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory();
// 获取当前应用的环境
Environment getEnvironment();
// 获取当前正在使用的资源加载器
ResourceLoader getResourceLoader();
@Nullable
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}
1.4 AnnotatedTypeMetadata 接口:
public interface AnnotatedTypeMetadata {
// 获取当前类的所有的注解
MergedAnnotations getAnnotations();
// 判断当前类的所有的注解当中是否存在要查找的注释类型
default boolean isAnnotated(String annotationName) {
return getAnnotations().isPresent(annotationName);
}
// 根据注解名称获取注解属性
@Nullable
default Map<String, Object> getAnnotationAttributes(String annotationName) {
return getAnnotationAttributes(annotationName, false);
}
// 获取所有的注解属性
@Nullable
default Map<String, Object> getAnnotationAttributes(String annotationName,
boolean classValuesAsString) {
MergedAnnotation<Annotation> annotation = getAnnotations().get(annotationName,
null, MergedAnnotationSelectors.firstDirectlyDeclared());
if (!annotation.isPresent()) {
return null;
}
return annotation.asAnnotationAttributes(Adapt.values(classValuesAsString, true));
}
// 根据注解名称获取所有的注解属性
@Nullable
default MultiValueMap<String, Object> getAllAnnotationAttributes(String annotationName) {
return getAllAnnotationAttributes(annotationName, false);
}
// 获取所有的注解属性值
@Nullable
default MultiValueMap<String, Object> getAllAnnotationAttributes(
String annotationName, boolean classValuesAsString) {
Adapt[] adaptations = Adapt.values(classValuesAsString, true);
return getAnnotations().stream(annotationName)
.filter(MergedAnnotationPredicates.unique(MergedAnnotation::getMetaTypes))
.map(MergedAnnotation::withNonMergedAttributes)
.collect(MergedAnnotationCollectors.toMultiValueMap(map ->
map.isEmpty() ? null : map, adaptations));
}
}
二、@Conditional 注解配置在方法上
案例:如果系统是 Windows,则给容器中注册 Person 对象bill,如果系统是 Mac OS,则给容器中注册 Person 对象 jobs。
WindowConditon 类:
package org.example.condition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata;
public class WindowsCondition implements Condition {
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
// 获取 IoC 使用的 BeanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
// 获取类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = context.getClassLoader();
// 获取当前环境信息
Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();
// 获取 bean 定义的注册类
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = context.getRegistry();
System.out.println("WindowsCondition................");
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
if(property.contains("Windows")){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
MacCondition 类:
package org.example.condition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata;
public class MacCondition implements Condition {
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();
System.out.println("MacCondition................");
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
if(property.contains("Mac")){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
配置类:
package org.example.config;
import org.example.condition.MacCondition;
import org.example.condition.WindowsCondition;
import org.example.pojo.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("org.example")
public class ConditionTestConfig {
@Conditional(WindowsCondition.class)
@Bean("bill")
public Person person01(){
return new Person("Bill Gates", "62");
}
@Conditional(MacCondition.class)
@Bean("jobs")
public Person person02(){
return new Person("Steve Jobs", "66");
}
}
测试方法:
@Test
public void testConditional(){
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ConditionTestConfig.class);
Environment environment = ac.getEnvironment();
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
System.out.println(property);
// 获取容器中所有 Person 类的定义
String[] beanNamesForType = ac.getBeanNamesForType(Person.class);
for (String s : beanNamesForType) {
System.out.println(s);
}
Map<String, Person> beansOfType = ac.getBeansOfType(Person.class);
System.out.println(beansOfType);
}
测试结果:
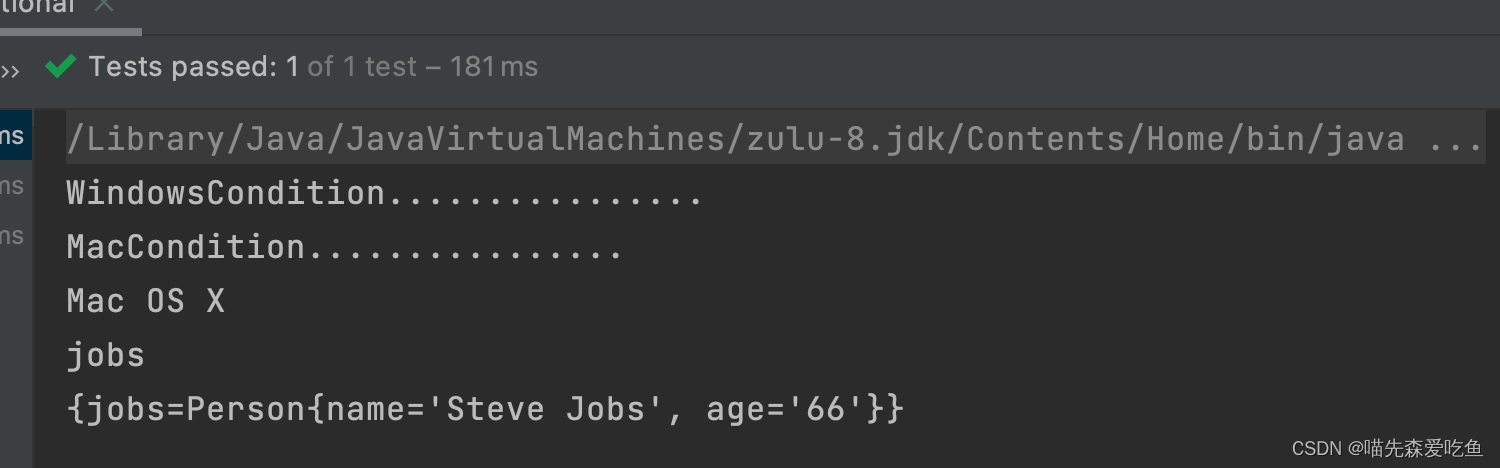
可以看出,Condition 接口的两个实现类其实都执行了,但是由于系统是 Mac OS,所以只有 MacCondition 中的 matches 方法返回了 true,从而只有 jobs 注入到容器中。
三、@Conditional 注解配置在类上
当 @Conditional 注解配置在类上时,只有当条件满足时,这个类中配置的所有 bean 才会被注册到容器中。
将注解 @Conditional(WindowsCondition.class) 配置到配置类上进行测试:
package org.example.config;
import org.example.condition.MacCondition;
import org.example.condition.WindowsCondition;
import org.example.pojo.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Conditional(WindowsCondition.class)
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("org.example")
public class ConditionTestConfig {
@Bean("bill")
public Person person01(){
return new Person("Bill Gates", "62");
}
@Bean("jobs")
public Person person02(){
return new Person("Steve Jobs", "66");
}
}
测试方法同上,测试结果如下:
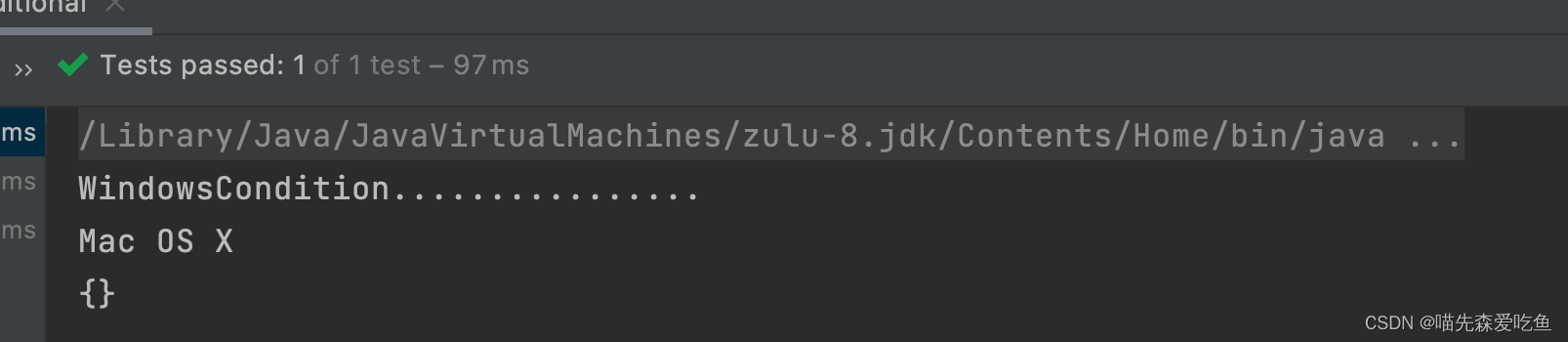
总结
- @Conditional 注解可以按照一定的条件进行判断,满足条件则向容器中注册 bean,该注解可以配置在类上、方法上。当配置在类上时,只有当条件被满足时,当前类中的所有的 bean 才会被注册到容器中。
- @Conditional 中的条件需要实现 Condition 接口,该接口中定义了唯一的方法 matches,在该方法中可以编写需要实现的条件,当条件结果返回true,说明条件被满足,可以被注册到容器中,返回false,则表示条件不满足,无法注册到容器中。





















 5563
5563











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








