一. 回溯法 – 深度优先搜素
1. 简单概述
回溯法思路的简单描述是:把问题的解空间转化成了图或者树的结构表示,然后使用深度优先搜索策略进行遍历,遍历的过程中记录和寻找所有可行解或者最优解。
基本思想类同于:
- 图的深度优先搜索
- 二叉树的后序遍历
【
分支限界法:广度优先搜索
思想类同于:图的广度优先遍历
二叉树的层序遍历
】
2. 详细描述
详细的描述则为:
回溯法按深度优先策略搜索问题的解空间树。首先从根节点出发搜索解空间树,当算法搜索至解空间树的某一节点时,先利用剪枝函数判断该节点是否可行(即能得到问题的解)。如果不可行,则跳过对该节点为根的子树的搜索,逐层向其祖先节点回溯;否则,进入该子树,继续按深度优先策略搜索。
回溯法的基本行为是搜索,搜索过程使用剪枝函数来为了避免无效的搜索。剪枝函数包括两类:1. 使用约束函数,剪去不满足约束条件的路径;2.使用限界函数,剪去不能得到最优解的路径。
问题的关键在于如何定义问题的解空间,转化成树(即解空间树)。解空间树分为两种:子集树和排列树。两种在算法结构和思路上大体相同。
3. 回溯法应用
当问题是要求满足某种性质(约束条件)的所有解或最优解时,往往使用回溯法。
它有“通用解题法”之美誉。
二. 回溯法实现 - 递归和递推(迭代)
回溯法的实现方法有两种:递归和递推(也称迭代)。一般来说,一个问题两种方法都可以实现,只是在算法效率和设计复杂度上有区别。【类比于图深度遍历的递归实现和非递归(递推)实现】
1. 递归
思路简单,设计容易,但效率低,其设计范式如下:-
//针对N叉树的递归回溯方法
-
void backtrack (int t)
-
{
-
if (t>n) output(x);
//叶子节点,输出结果,x是可行解
-
else
-
for i =
1 to k
//当前节点的所有子节点
-
{
-
x[t]=value(i);
//每个子节点的值赋值给x
-
//满足约束条件和限界条件
-
if (constraint(t)&&bound(t))
-
backtrack(t+
1);
//递归下一层
-
}
-
}
-
2. 递推
算法设计相对复杂,但效率高。-
//针对N叉树的迭代回溯方法
-
void iterativeBacktrack ()
-
{
-
int t=
1;
-
while (t>
0) {
-
if(ExistSubNode(t))
//当前节点的存在子节点
-
{
-
for i =
1 to k
//遍历当前节点的所有子节点
-
{
-
x[t]=value(i);
//每个子节点的值赋值给x
-
if (constraint(t)&&bound(t))
//满足约束条件和限界条件
-
{
-
//solution表示在节点t处得到了一个解
-
if (solution(t)) output(x);
//得到问题的一个可行解,输出
-
else t++;
//没有得到解,继续向下搜索
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
else
//不存在子节点,返回上一层
-
{
-
t--;
-
}
-
}
-
}
三. 子集树和排列树
1. 子集树
所给的问题是从n个元素的集合S中找出满足某种性质的子集时,相应的解空间成为子集树。如0-1背包问题,从所给重量、价值不同的物品中挑选几个物品放入背包,使得在满足背包不超重的情况下,背包内物品价值最大。它的解空间就是一个典型的子集树。
回溯法搜索子集树的算法范式如下:
-
void backtrack (int t)
-
{
-
if (t>n) output(x);
-
else
-
for (
int i=
0;i<=
1;i++) {
-
x[t]=i;
-
if (constraint(t)&&bound(t)) backtrack(t+
1);
-
}
-
}
-
2. 排列树
所给的问题是确定n个元素满足某种性质的排列时,相应的解空间就是排列树。如旅行售货员问题,一个售货员把几个城市旅行一遍,要求走的路程最小。它的解就是几个城市的排列,解空间就是排列树。
回溯法搜索排列树的算法范式如下:
-
void backtrack (int t)
-
{
-
if (t>n) output(x);
-
else
-
for (
int i=t;i<=n;i++) {
-
swap(x[t], x[i]);
-
if (constraint(t)&&bound(t)) backtrack(t+
1);
-
swap(x[t], x[i]);
-
}
-
}
-
四. 经典问题
(1)装载问题(2)0-1背包问题
(3)旅行售货员问题
(4)八皇后问题
(5)迷宫问题
(6)图的m着色问题
1. 0-1背包问题
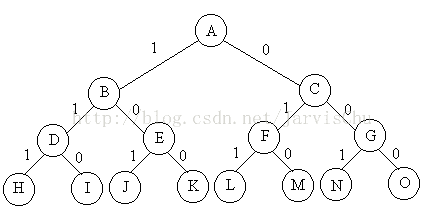
问题:给定n种物品和一背包。物品i的重量是wi,其价值为pi,背包的容量为C。问应如何选择装入背包的物品,使得装入背包中物品的总价值最大?分析:问题是n个物品中选择部分物品,可知,问题的解空间是子集树。比如物品数目n=3时,其解空间树如下图,边为1代表选择该物品,边为0代表不选择该物品。使用x[i]表示物品i是否放入背包,x[i]=0表示不放,x[i]=1表示放入。回溯搜索过程,如果来到了叶子节点,表示一条搜索路径结束,如果该路径上存在更优的解,则保存下来。如果不是叶子节点,是中点的节点(如B),就遍历其子节点(D和E),如果子节点满足剪枝条件,就继续回溯搜索子节点。
代码:
-
#include <stdio.h>
-
-
#define N 3 //物品的数量
-
#define C 16 //背包的容量
-
-
int w[N]={
10,
8,
5};
//每个物品的重量
-
int v[N]={
5,
4,
1};
//每个物品的价值
-
int x[N]={
0,
0,
0};
//x[i]=1代表物品i放入背包,0代表不放入
-
-
int CurWeight =
0;
//当前放入背包的物品总重量
-
int CurValue =
0;
//当前放入背包的物品总价值
-
-
int BestValue =
0;
//最优值;当前的最大价值,初始化为0
-
int BestX[N];
//最优解;BestX[i]=1代表物品i放入背包,0代表不放入
-
-
//t = 0 to N-1
-
void backtrack(int t)
-
{
-
//叶子节点,输出结果
-
if(t>N
-1)
-
{
-
//如果找到了一个更优的解
-
if(CurValue>BestValue)
-
{
-
//保存更优的值和解
-
BestValue = CurValue;
-
for(
int i=
0;i<N;++i) BestX[i] = x[i];
-
}
-
}
-
else
-
{
-
//遍历当前节点的子节点:0 不放入背包,1放入背包
-
for(
int i=
0;i<=
1;++i)
-
{
-
x[t]=i;
-
-
if(i==
0)
//不放入背包
-
{
-
backtrack(t+
1);
-
}
-
else
//放入背包
-
{
-
//约束条件:放的下
-
if((CurWeight+w[t])<=C)
-
{
-
CurWeight += w[t];
-
CurValue += v[t];
-
backtrack(t+
1);
-
CurWeight -= w[t];
-
CurValue -= v[t];
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
//PS:上述代码为了更符合递归回溯的范式,并不够简洁
-
}
-
}
-
-
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
-
{
-
backtrack(
0);
-
-
printf(
"最优值:%d\n",BestValue);
-
-
for(
int i=
0;i<N;i++)
-
{
-
printf(
"最优解:%-3d",BestX[i]);
-
}
-
return
0;
-
}
2. 旅行售货员问题
回溯法----旅行售货员问题3. 详细描述N皇后问题
问题:在n×n格的棋盘上放置彼此不受攻击的n个皇后。按照国际象棋的规则,皇后可以攻击与之处在同一行或同一列或同一斜线上的棋子。
N皇后问题等价于在n×n格的棋盘上放置n个皇后,任何2个皇后不放在同一行或同一列或同一斜线上。
分析:从n×n个格子中选择n个格子摆放皇后。可见解空间树为子集树。
使用Board[N][N]来表示棋盘,Board[i][j]=0 表示(I,j)位置为空,Board[i][j]=1 表示(I,j)位置摆放有一个皇后。
全局变量way表示总共的摆放方法数目。
使用Queen(t)来摆放第t个皇后。Queen(t) 函数符合子集树时的递归回溯范式。当t>N时,说明所有皇后都已经摆 放完成,这是一个可行的摆放方法,输出结果;否则,遍历棋盘,找皇后t所有可行的摆放位置,Feasible(i,j) 判断皇后t能否摆放在位置(i,j)处,如果可以摆放则继续递归摆放皇后t+1,如果不能摆放,则判断下一个位置。
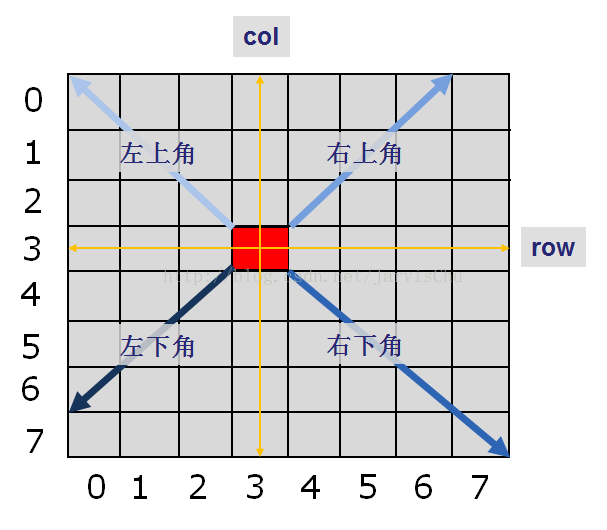
Feasible(row,col)函数首先判断位置(row,col)是否合法,继而判断(row,col)处是否已有皇后,有则冲突,返回0,无则继续判断行、列、斜方向是否冲突。斜方向分为左上角、左下角、右上角、右下角四个方向,每次从(row,col)向四个方向延伸一个格子,判断是否冲突。如果所有方向都没有冲突,则返回1,表示此位置可以摆放一个皇后。
代码:
-
/************************************************************************
-
* 名 称:NQueen.cpp
-
* 功 能:回溯算法实例:N皇后问题
-
* 作 者:JarvisChu
-
* 时 间:2013-11-13
-
************************************************************************/
-
-
#include <stdio.h>
-
-
#define N 8
-
-
int Board[N][N];
//棋盘 0表示空白 1表示有皇后
-
int way;
//摆放的方法数
-
-
-
//判断能否在(x,y)的位置摆放一个皇后;0不可以,1可以
-
int Feasible(int row,int col)
-
{
-
//位置不合法
-
if(row>N || row<
0 || col >N || col<
0)
-
return
0;
-
-
//该位置已经有皇后了,不能
-
if(Board[row][col] !=
0)
-
{
//在行列冲突判断中也包含了该判断,单独提出来为了提高效率
-
return
0;
-
}
-
-
//
-
//下面判断是否和已有的冲突
-
-
//行和列是否冲突
-
for(
int i=
0;i<N;++i)
-
{
-
if(Board[row][i] !=
0 || Board[i][col]!=
0)
-
return
0;
-
}
-
-
//斜线方向冲突
-
-
for(
int i=
1;i<N;++i)
-
{
-
/* i表示从当前点(row,col)向四个斜方向扩展的长度
-
-
左上角 \ / 右上角 i=2
-
\/ i=1
-
/\ i=1
-
左下角 / \ 右下角 i=2
-
*/
-
//左上角
-
if((row-i)>=
0 && (col-i)>=
0)
//位置合法
-
{
-
if(Board[row-i][col-i] !=
0)
//此处已有皇后,冲突
-
return
0;
-
}
-
-
//左下角
-
if((row+i)<N && (col-i)>=
0)
-
{
-
if(Board[row+i][col-i] !=
0)
-
return
0;
-
}
-
-
//右上角
-
if((row-i)>=
0 && (col+i)<N)
-
{
-
if(Board[row-i][col+i] !=
0)
-
return
0;
-
}
-
-
//右下角
-
if((row+i)<N && (col+i)<N)
-
{
-
if(Board[row+i][col+i] !=
0)
-
return
0;
-
}
-
}
-
-
return
1;
//不会发生冲突,返回1
-
}
-
-
-
//摆放第t个皇后 ;从1开始
-
void Queen(int t)
-
{
-
//摆放完成,输出结果
-
if(t>N)
-
{
-
way++;
-
/*如果N较大,输出结果会很慢;N较小时,可以用下面代码输出结果
-
for(int i=0;i<N;++i){
-
for(int j=0;j<N;++j)
-
printf("%-3d",Board[i][j]);
-
printf("\n");
-
}
-
printf("\n------------------------\n\n");
-
*/
-
}
-
else
-
{
-
for(
int i=
0;i<N;++i)
-
{
-
for(
int j=
0;j<N;++j)
-
{
-
//(i,j)位置可以摆放皇后,不冲突
-
if(Feasible(i,j))
-
{
-
Board[i][j] =
1;
//摆放皇后t
-
Queen(t+
1);
//递归摆放皇后t+1
-
Board[i][j] =
0;
//恢复
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
-
//返回num的阶乘,num!
-
int factorial(int num)
-
{
-
if(num==
0 || num==
1)
-
return
1;
-
return num*factorial(num
-1);
-
}
-
-
-
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
-
{
-
//初始化
-
for(
int i=
0;i<N;++i)
-
{
-
for(
int j=
0;j<N;++j)
-
{
-
Board[i][j]=
0;
-
}
-
}
-
-
way =
0;
-
-
Queen(
1);
//从第1个皇后开始摆放
-
-
//如果每个皇后都不同
-
printf(
"考虑每个皇后都不同,摆放方法:%d\n",way);
//N=8时, way=3709440 种
-
-
//如果每个皇后都一样,那么需要除以 N!出去重复的答案(因为相同,则每个皇后可任意调换位置)
-
printf(
"考虑每个皇后都不同,摆放方法:%d\n",way/factorial(N));
//N=8时, way=3709440/8! = 92种
-
-
return
0;
-
}
PS:该问题还有更优的解法。充分利用问题隐藏的约束条件:每个皇后必然在不同的行(列),每个行(列)必然也只有一个皇后。这样我们就可以把N个皇后放到N个行中,使用Pos[i]表示皇后i在i行中的位置(也就是列号)(i = 0 to N-1)。这样代码会大大的简洁,因为节点的子节点数目会减少,判断冲突也更简单。
4. 迷宫问题
问题:给定一个迷宫,找到从入口到出口的所有可行路径,并给出其中最短的路径
分析:用二维数组来表示迷宫,则走迷宫问题用回溯法解决的的思想类似于图的深度遍历。从入口开始,选择下一个可以走的位置,如果位置可走,则继续往前,如果位置不可走,则返回上一个位置,重新选择另一个位置作为下一步位置。
N表示迷宫的大小,使用Maze[N][N]表示迷宫,值为0表示通道(可走),值为1表示不可走(墙或者已走过);
Point结构体用来记录路径中每一步的坐标(x,y)
(ENTER_X,ENTER_Y) 是迷宫入口的坐标
(EXIT_X, EXIT _Y) 是迷宫出口的坐标
Path容器用来存放一条从入口到出口的通路路径
BestPath用来存放所有路径中最短的那条路径
Maze()函数用来递归走迷宫,具体步骤为:
1. 首先将当前点加入路径,并设置为已走
2. 判断当前点是否为出口,是则输出路径,保存结果;跳转到4
3. 依次判断当前点的上、下、左、右四个点是否可走,如果可走则递归走该点
4. 当前点推出路径,设置为可走
代码:
-
/************************************************************************
-
* 名 称:Maze.cpp
-
* 功 能:回溯算法实例:迷宫问题
-
* 作 者:JarvisChu
-
* 时 间:2013-11-13
-
************************************************************************/
-
#include <iostream>
-
#include <vector>
-
-
using
namespace
std;
-
-
typedef
struct
-
{
-
int x;
-
int y;
-
}Point;
-
-
#define N 10 //迷宫的大小
-
#define ENTER_X 0 //入口的位置(0,0)
-
#define ENTER_Y 0
-
#define EXIT_X N-1 //出口的位置(N-1,N-1)
-
#define EXIT_Y N-1
-
-
-
int Maze[N][N];
//定义一个迷宫,0表示通道,1表示不可走(墙或已走)
-
int paths;
//路径条数
-
vector<Point> Path;
//保存一条可通的路径
-
vector<Point> BestPath;
//保存最短的路径
-
-
bool First =
true;
//标志,找到第一条路径
-
-
//初始化迷宫
-
void InitMaze()
-
{
-
//简单起见,本题定义一个固定大小10*10的迷宫
-
//定义一个迷宫,0表示通道,1表示墙(或不可走)
-
int mz[
10][
10]={
-
{
0,
0,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1},
//0
-
{
1,
0,
0,
1,
1,
0,
0,
1,
0,
1},
//1
-
{
1,
0,
0,
1,
0,
0,
0,
1,
0,
1},
//2
-
{
1,
0,
0,
0,
0,
1,
1,
0,
0,
1},
//3
-
{
1,
0,
1,
1,
1,
0,
0,
0,
0,
1},
//4
-
{
1,
0,
0,
0,
1,
0,
0,
0,
0,
1},
//5
-
{
1,
0,
1,
0,
0,
0,
1,
0,
0,
1},
//6
-
{
1,
0,
1,
1,
1,
0,
1,
1,
0,
1},
//7
-
{
1,
1,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0},
//8
-
{
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
0}
//9
-
// 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-
};
-
-
//复制到迷宫
-
memcpy(Maze,mz,
sizeof(mz));
-
-
paths =
0;
-
}
-
-
//从(x,y)位置开始走;初始为(0,0)
-
void MazeTrack(int x,int y)
-
{
-
///
-
//当前点加入到路径
-
Point p={x,y};
-
Path.push_back(p);
-
Maze[x][y] =
1;
//设置为已走,不可走
-
-
//cout<<"来到("<<x<<","<<y<<")"<<endl;
-
-
///
-
//如果该位置是出口,输出结果
-
if(x == EXIT_X && y== EXIT_Y)
-
{
-
cout<<
"找到一条道路"<<
endl;
-
paths++;
-
-
//输出路径
-
vector<Point>::iterator it;
-
for(it=Path.begin();it!=Path.end();++it)
-
{
-
cout<<
"("<<it->x<<
","<<it->y<<
") ";
-
}
-
cout<<
endl;
-
-
//判断是否更优
-
if(First)
//如果是找到的第一条路径,直接复制到最优路径
-
{
-
for(it=Path.begin();it!=Path.end();++it)
-
{
-
BestPath.push_back(*it);
-
}
-
First =
false;
-
}
-
else
//不是第一条,则判断是否更短
-
{
-
//更短,复制到最优路径
-
if(Path.size()<BestPath.size())
-
{
-
BestPath.clear();
-
for(it=Path.begin();it!=Path.end();++it)
-
{
-
BestPath.push_back(*it);
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
-
///
-
//判断(x,y)位置的上、下、左、右是否可走
-
-
if((x
-1)>=
0 && Maze[x
-1][y]==
0)
//上(x-1,y);存在且可走
-
{
-
MazeTrack(x
-1,y);
-
}
-
-
if((x+
1)<N && Maze[x+
1][y]==
0)
//下(x+1,y);存在且可走
-
{
-
MazeTrack(x+
1,y);
-
}
-
-
if((y
-1)>=
0 && Maze[x][y
-1]==
0)
//左(x,y-1);存在且可走
-
{
-
MazeTrack(x,y
-1);
-
}
-
-
if((y+
1)<N && Maze[x][y+
1]==
0)
//右(x,y+1);存在且可走
-
{
-
MazeTrack(x,y+
1);
-
}
-
-
///
-
//返回上一步
-
Path.pop_back();
-
Maze[x][y] =
0;
//设置为未走
-
}
-
-
-
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
-
{
-
//初始化迷宫
-
InitMaze();
-
-
/* //显示迷宫
-
for(int i=0;i<N;++i){
-
for(int j=0;j<N;++j)
-
cout<<Maze[i][j]<<" ";
-
cout<<endl;
-
}*/
-
-
//回溯法走迷宫
-
MazeTrack(ENTER_X,ENTER_Y);
-
-
//显示最优的路径
-
cout<<
"可行路径总条数为"<<paths<<
";最优路径为"<<
endl;
-
vector<Point>::iterator it;
-
for(it=BestPath.begin();it!=BestPath.end();++it)
-
{
-
cout<<
"("<<it->x<<
","<<it->y<<
") ";
-
}
-
cout<<
endl;
-
return
0;
-
}
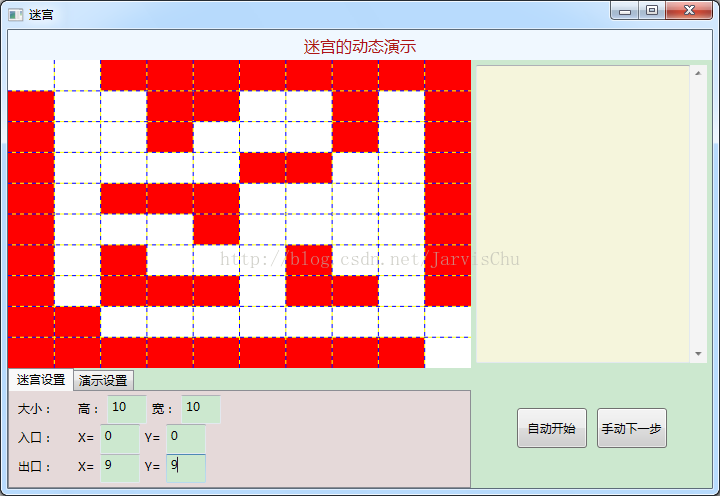
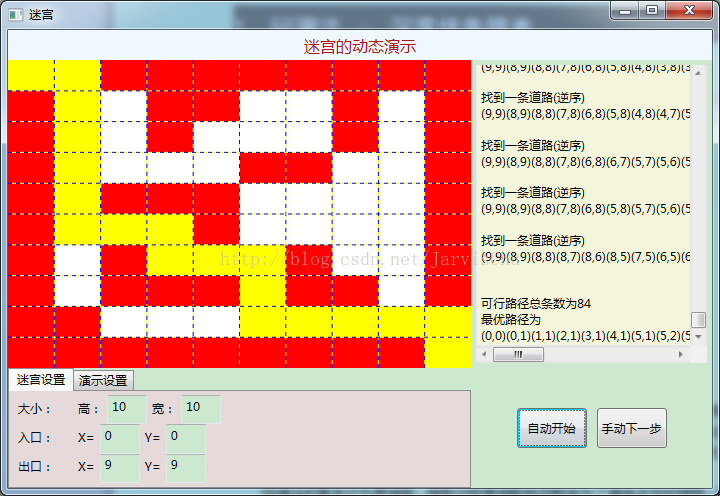
PS:用WPF实现了一个简单的图形化迷宫程序。白色表示通道,红色表示墙,最短的路径用黄色显示。目前实现了一个10*10的迷宫自动搜素最短通路,右侧显示搜索过程中得到的每一个可行通路。
由于构造一个迷宫比较复杂,所以暂时“迷宫设置”功能没有做实现,至于手动一步步查看搜素过程的动画也没有做实现。
实现的大致思路如下:迷宫的数据使用二维数据mazeData表示。迷宫的显示使用Grid控件表示,每个方格处添加一个Rectangle控件,如果该方格mazeData值为0,则填充白色值为1,则填充红色,值为2则填充黄色。
XAML代码为:
-
<Window x:Class="MazeAnimation.MainWindow"
-
xmlns=
"http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
-
xmlns:x=
"http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
-
Title=
"迷宫"
Height=
"496"
Width=
"673"
Loaded=
"Window_Loaded">
-
<Grid>
-
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
-
<RowDefinition Height="30">
</RowDefinition>
-
<RowDefinition Height="*">
</RowDefinition>
-
<RowDefinition Height="120">
</RowDefinition>
-
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
-
-
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
-
<ColumnDefinition Width="463">
</ColumnDefinition>
-
<ColumnDefinition Width="*">
</ColumnDefinition>
-
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
-
-
<DockPanel Name="dpTips" Grid.Row="0" Grid.ColumnSpan="2" Background="AliceBlue" >
-
<Label FontSize="16" Foreground="#FFAD1616" HorizontalAlignment="Center">迷宫的动态演示
</Label>
-
</DockPanel>
-
-
<Grid Name="gdMaze" Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="0" HorizontalAlignment="Stretch" VerticalAlignment="Stretch" >
-
-
</Grid>
-
-
<ScrollViewer Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1" Margin="5" HorizontalAlignment="Stretch" HorizontalScrollBarVisibility="Auto">
-
<TextBox Name="tbLog" Background="Beige">
</TextBox>
-
</ScrollViewer>
-
-
<DockPanel Name="dpSetting" Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="0" VerticalAlignment="Stretch">
-
-
<TabControl Name="tcMazeSetting" Background="#FFE5D9D9" VerticalAlignment="Stretch" HorizontalAlignment="Stretch">
-
<TabItem Header="迷宫设置" Name="tabItemMaze">
-
<Grid>
-
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
-
<RowDefinition Height="*">
</RowDefinition>
-
<RowDefinition Height="*">
</RowDefinition>
-
<RowDefinition Height="*">
</RowDefinition>
-
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
-
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
-
<ColumnDefinition Width="60">
</ColumnDefinition>
-
<ColumnDefinition Width="*">
</ColumnDefinition>
-
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
-
-
<Label Content="大小:" Name="label1" Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="0"/>
-
<Label Content="入口:" Name="label2" Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="0"/>
-
<Label Content="出口:" Name="label3" Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="0"/>
-
-
<StackPanel Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="1" Orientation="Horizontal">
-
<Label Content="高:">
</Label>
-
<TextBox Name="tbMazeHeight" HorizontalAlignment="Left" MinWidth="40">
</TextBox>
-
<Label Content="宽:">
</Label>
-
<TextBox Name="tbMazeWidth" HorizontalAlignment="Left" MinWidth="40">
</TextBox>
-
</StackPanel>
-
-
<StackPanel Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1" Orientation="Horizontal">
-
<Label Content="X=">
</Label>
-
<TextBox Name="tbEnterX" HorizontalAlignment="Left" MinWidth="40">
</TextBox>
-
<Label Content="Y=">
</Label>
-
<TextBox Name="tbEnterY" HorizontalAlignment="Left" MinWidth="40">
</TextBox>
-
</StackPanel>
-
-
<StackPanel Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="1" Orientation="Horizontal">
-
<Label Content="X=">
</Label>
-
<TextBox Name="tbExitX" HorizontalAlignment="Left" MinWidth="40">
</TextBox>
-
<Label Content="Y=">
</Label>
-
<TextBox Name="tbExitY" HorizontalAlignment="Left" MinWidth="40">
</TextBox>
-
</StackPanel>
-
</Grid>
-
-
</TabItem>
-
<TabItem Header="演示设置" Name="tabItemDemo">
-
<StackPanel Orientation="Vertical" HorizontalAlignment="Stretch">
-
<CheckBox Name="cbAutoRun" Content="自动执行" Margin="10">
</CheckBox>
-
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal">
-
<Label Content="执行速度:" Margin="10">
</Label>
-
<TextBox Name="tbAutoRunSpeed" MinWidth="50" Margin="10">
</TextBox>
-
<Label Content="毫秒" Margin="0,10,0,10">
</Label>
-
</StackPanel>
-
</StackPanel>
-
</TabItem>
-
</TabControl>
-
</DockPanel>
-
-
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="1" HorizontalAlignment="Center">
-
<Button Name="btnStart" Content="自动开始" Height="40" Width="70" Margin="5" Click="btnStart_Click">
</Button>
-
<Button Name="btnNext" Content="手动下一步" Height="40" Width="70" Margin="5" Click="btnNext_Click">
</Button>
-
</StackPanel>
-
</Grid>
-
</Window>
对应的MainWindow.xaml.cs代码为:
-
using System;
-
using System.Collections.Generic;
-
using System.Linq;
-
using System.Text;
-
using System.Windows;
-
using System.Windows.Controls;
-
using System.Windows.Data;
-
using System.Windows.Documents;
-
using System.Windows.Input;
-
using System.Windows.Media;
-
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
-
using System.Windows.Navigation;
-
using System.Windows.Shapes;
-
-
namespace
MazeAnimation
-
{
-
-
-
-
/// <summary>
-
/// Interaction logic for MainWindow.xaml
-
/// </summary>
-
public
partial
class
MainWindow :
Window
-
{
-
public
struct Point
-
{
-
public
int x;
-
public
int y;
-
public Point(int a, int b) { x = a; y = b; }
-
};
-
-
public
bool bAutoRun =
true;
-
public
int mazeHeight =
10;
-
public
int mazeWidth =
10;
-
-
int[,] mazeData =
new
int[
10,
10]
-
{
-
{
0,
0,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1},
//0
-
{
1,
0,
0,
1,
1,
0,
0,
1,
0,
1},
//1
-
{
1,
0,
0,
1,
0,
0,
0,
1,
0,
1},
//2
-
{
1,
0,
0,
0,
0,
1,
1,
0,
0,
1},
//3
-
{
1,
0,
1,
1,
1,
0,
0,
0,
0,
1},
//4
-
{
1,
0,
0,
0,
1,
0,
0,
0,
0,
1},
//5
-
{
1,
0,
1,
0,
0,
0,
1,
0,
0,
1},
//6
-
{
1,
0,
1,
1,
1,
0,
1,
1,
0,
1},
//7
-
{
1,
1,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0},
//8
-
{
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
1,
0}
//9
-
// 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
-
};
-
-
public
int enterX =
0;
-
public
int enterY =
0;
-
public
int exitX =
9;
-
public
int exitY =
9;
-
public
int runSpeed =
100;
-
-
public
int paths =
0;
//总条数
-
public Stack<Point> path =
new Stack<Point>();
//一条找到的路径
-
public Stack<Point> bestPath =
new Stack<Point>();
//最优路径
-
public
bool bFrist =
true;
-
-
-
public MainWindow()
-
{
-
InitializeComponent();
-
}
-
-
//显示迷宫,白色0表示通道,红色1表示不可走,黄色2表示最优的路径,绿色3表示已经走过的路径
-
private void DisplayMaze()
-
{
-
gdMaze.Children.Clear();
-
//设置可走和不可走
-
for (
int i =
0; i < mazeHeight; i++)
-
{
-
for (
int j =
0; j < mazeWidth; j++)
-
{
-
Rectangle rect =
new Rectangle();
-
rect.SetValue(Grid.RowProperty, i);
-
rect.SetValue(Grid.ColumnProperty, j);
-
-
if (mazeData[i, j] ==
0)
-
{
-
rect.Fill = Brushes.White;
-
}
-
else
if (mazeData[i, j] ==
1)
-
{
-
rect.Fill = Brushes.Red;
-
}
-
else
if (mazeData[i, j] ==
2)
-
{
-
rect.Fill = Brushes.Yellow;
-
}
-
else
if (mazeData[i, j] ==
3)
-
{
-
rect.Fill = Brushes.Blue;
-
}
-
gdMaze.Children.Add(rect);
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
-
//初始化迷宫
-
private void InitMaze()
-
{
-
-
gdMaze.Background = Brushes.LightGray;
-
gdMaze.ShowGridLines =
true;
-
-
for (
int i =
0; i < mazeHeight; i++)
-
{
-
gdMaze.RowDefinitions.Add(
new RowDefinition());
-
}
-
-
for (
int i =
0; i < mazeWidth; i++)
-
{
-
gdMaze.ColumnDefinitions.Add(
new ColumnDefinition());
-
}
-
-
DisplayMaze();
-
}
-
-
//从(x,y)位置开始走;初始为(0,0)
-
private void MazeTrack(int x, int y)
-
{
-
///////////////////////////////////////
-
//当前点加入到路径
-
Point p =
new Point(x, y);
-
path.Push(p);
-
-
mazeData[x, y] =
3;
//设置为已走,不可走
-
//DisplayMaze();
-
//System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(runSpeed);//休眠
-
-
-
///////////////////////////////////////
-
//如果该位置是出口,输出结果
-
if (x == exitX && y == exitY)
-
{
-
string msg =
"找到一条道路(逆序)\n";
-
tbLog.AppendText(msg);
-
-
paths++;
-
-
//输出路径
-
foreach (Point pnt
in path)
-
{
-
msg =
"(" + pnt.x +
"," + pnt.y +
")";
-
tbLog.AppendText(msg);
-
}
-
tbLog.AppendText(
"\n\n");
-
-
//判断是否更优
-
if (bFrist)
//如果是找到的第一条路径,直接复制到最优路径
-
{
-
foreach (Point pnt
in path)
-
{
-
bestPath.Push(pnt);
-
}
-
-
bFrist =
false;
-
}
-
else
//不是第一条,则判断是否更短
-
{
-
//更短,复制到最优路径
-
if (path.Count < bestPath.Count)
-
{
-
bestPath.Clear();
-
foreach (Point pnt
in path)
-
{
-
bestPath.Push(pnt);
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
-
///////////////////////////////////////
-
//判断(x,y)位置的上、下、左、右是否可走
-
-
if ((x -
1) >=
0 && mazeData[x -
1, y] ==
0)
//上(x-1,y);存在且可走
-
{
-
MazeTrack(x -
1, y);
-
}
-
-
if ((x +
1) < mazeHeight && mazeData[x +
1, y] ==
0)
//下(x+1,y);存在且可走
-
{
-
MazeTrack(x +
1, y);
-
}
-
-
if ((y -
1) >=
0 && mazeData[x, y -
1] ==
0)
//左(x,y-1);存在且可走
-
{
-
MazeTrack(x, y -
1);
-
}
-
-
if ((y +
1) < mazeWidth && mazeData[x, y +
1] ==
0)
//右(x,y+1);存在且可走
-
{
-
MazeTrack(x, y +
1);
-
}
-
-
///////////////////////////////////////
-
//返回上一步
-
path.Pop();
-
mazeData[x, y] =
0;
//设置为未走
-
-
//DisplayMaze();
-
//System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(runSpeed);//休眠
-
}
-
-
-
private void Window_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
-
{
-
//初始化变量
-
tbMazeHeight.Text = mazeHeight.ToString();
-
tbMazeWidth.Text = mazeWidth.ToString();
-
tbEnterX.Text = enterX.ToString();
-
tbEnterY.Text = enterY.ToString();
-
tbExitX.Text = exitX.ToString();
-
tbExitY.Text = exitY.ToString();
-
-
cbAutoRun.IsChecked = bAutoRun;
-
tbAutoRunSpeed.Text = runSpeed.ToString();
-
-
//初始化迷宫
-
InitMaze();
-
}
-
-
//点击开始
-
private void btnStart_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
-
{
-
string msg =
"开始走迷宫\n";
-
tbLog.AppendText(msg);
-
MazeTrack(enterX, enterY);
-
-
//显示最优的路径
-
msg =
"\n可行路径总条数为" + paths +
"\n最优路径为\n";
-
tbLog.AppendText(msg);
-
-
foreach (Point pnt
in bestPath)
-
{
-
msg =
"(" + pnt.x +
"," + pnt.y +
")";
-
tbLog.AppendText(msg);
-
-
mazeData[pnt.x, pnt.y] =
2;
-
-
}
-
DisplayMaze();
-
}
-
-
//下一步
-
private void btnNext_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
-
{
-
string msg =
"手动开始走迷宫 暂未实现\n";
-
tbLog.AppendText(msg);
-
}
-
-
}
-
}
参考文献: 《计算机算法设计与分析》(王晓东)
转载本文请注明作者和出处
作者 :JarvisChu






















 5万+
5万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








