AOP 底层实现方式之一是代理,由代理结合通知和目标,提供增强功能。除此以外,aspectj 提供了两种另外的 AOP 底层实现
| 实现方式 | 底层原理 | 区别 |
|---|---|---|
| ajc 编译器 | 通过 ajc 编译器在编译 class 类文件时,就把通知的增强功能,织入到目标类的字节码中 | 编译期间增强 |
| agent探针 | 通过 agent 在加载目标类时,修改目标类的字节码,织入增强功能 | 加载期间通过ASM技术增强 |
| jdk动态代理 | jdk 动态代理要求目标必须实现接口,生成的代理类实现相同接口,因此代理与目标之间是平级兄弟关系 | 代理是运行时生成新的字节码 |
| cglib代理 | cglib 不要求目标实现接口,它生成的代理类是目标的子类,因此代理与目标之间是子父关系 | 代理是运行时生成新的字节码 |
简单比较的话:
- aspectj 在编译和加载时,修改目标字节码,性能较高
- aspectj 因为不用代理,能突破一些技术上的限制,例如对构造、对静态方法、对 final 也能增强
- 但 aspectj 侵入性较强,且需要学习新的 aspectj 特有语法,因此没有广泛流行
AOP 实现之 ajc 编译器
POM 文件中引入aspectj的jar包,并设置编译的时候使用aspectj-maven-plugin插件
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
</dependency>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectj-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.14.0</version>
<configuration>
<complianceLevel>1.8</complianceLevel>
<source>8</source>
<target>8</target>
<showWeaveInfo>true</showWeaveInfo>
<verbose>true</verbose>
<Xlint>ignore</Xlint>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<!-- use this goal to weave all your main classes -->
<goal>compile</goal>
<!-- use this goal to weave all your test classes -->
<goal>test-compile</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
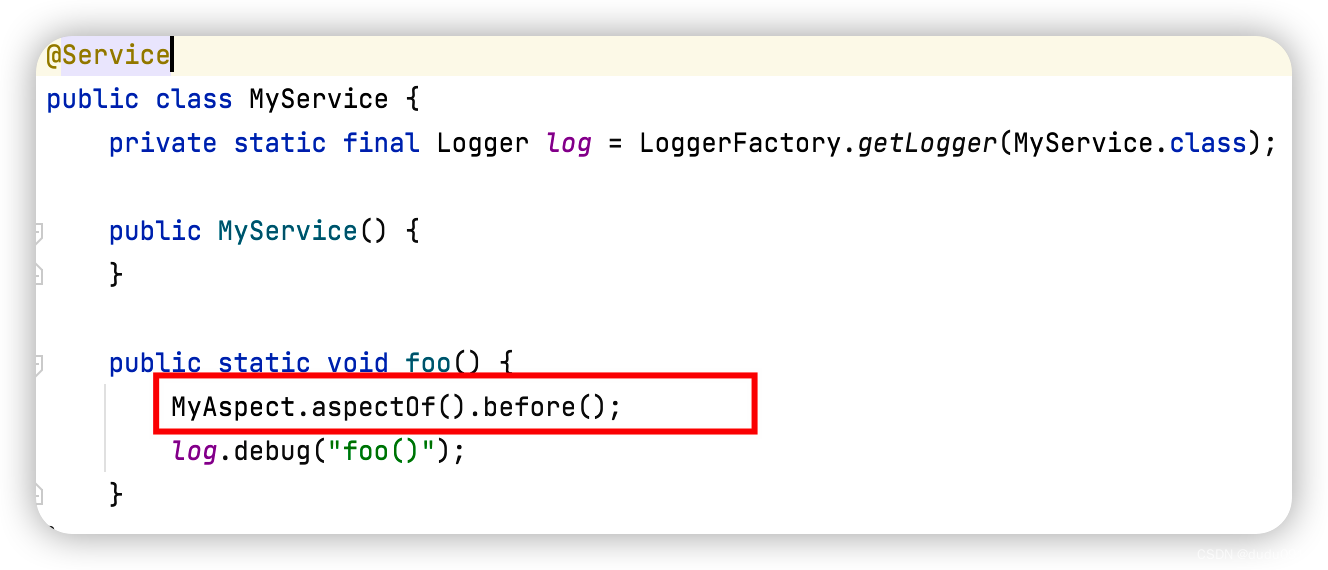
定义Service类和代理类
@Service
public class MyService {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyService.class);
public static void foo() {
log.debug("foo()");
}
}
// ⬅️注意此切面并未被 Spring 管理 这个注解并不是Spring的注解
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyAspect.class);
@Before("execution(* com.itheima.service.MyService.foo())")
public void before() {
log.debug("before()");
}
}
测试:注意:需要使用maven的compile编译;jdk版本选择java 8, 因为目前的 aspectj-maven-plugin 1.14.0 最高只支持到 java 16
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(A09.class, args);
MyService service = context.getBean(MyService.class);
//打印的是代理类吗?
log.debug("service class: {}", service.getClass());
service.foo();
context.close();
new MyService().foo();
}
打印的是代理类吗?
通过打印日子发现MyService并未生成代理类,查看生成的class文件是在MyService里面直接织入了代理的代码。Spring不是所有类都会生成代理类
通过案例可以发现:
- 编译器也能修改 class 实现增强
- 编译器增强能突破代理仅能通过方法重写增强的限制:可以对构造方法、静态方法等实现增强
AOP 实现之 agent 类加载
同理,agent也是通过aspectj技术实现的。引入对应jar包,但是不需要在build设置编译插件,而是通过java agent技术在VM参数中加上配置:
-javaagent:/Users/tianming/.m2/repository/org/aspectj/aspectjweaver/1.9.7/aspectjweaver-1.9.7.jar
如何查看运行期间的类
通过Arthas的jad命令反编译class类:Arthas下载地址
发现加载的MyService类已经加入了切面的代码。
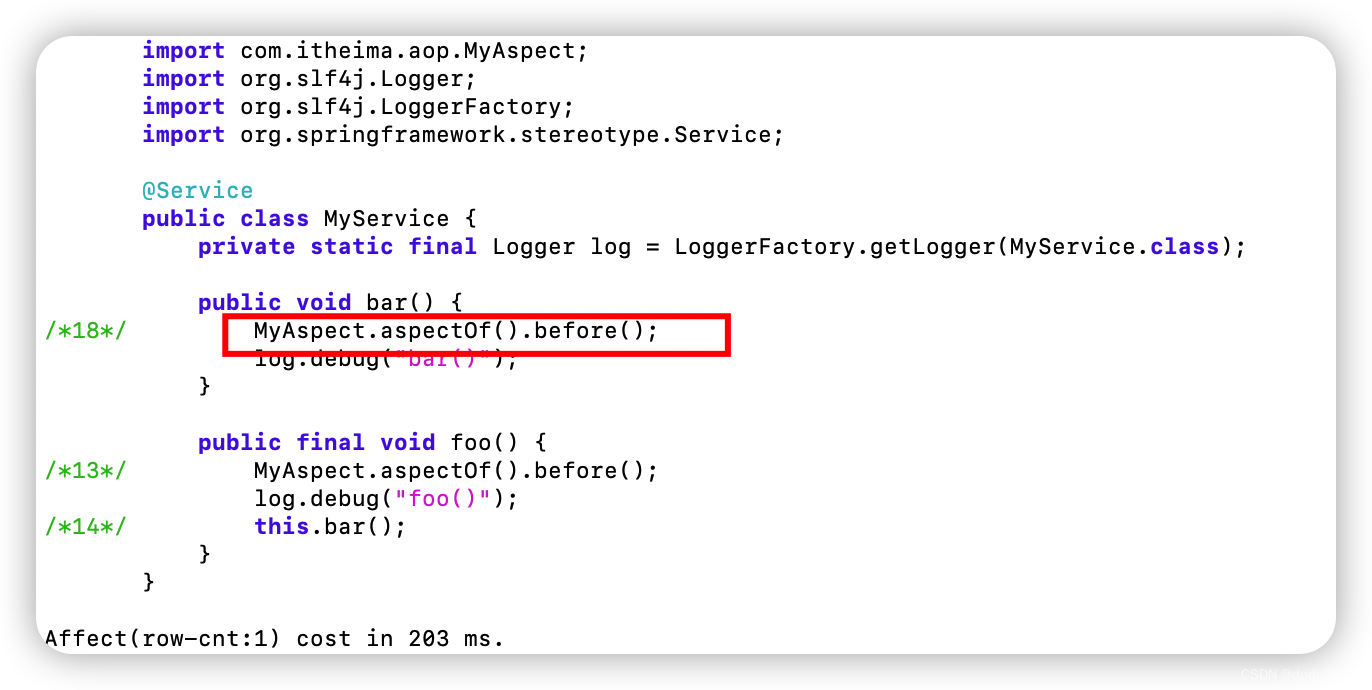
AOP 实现之 proxy
jdk 动态代理
jdk 动态代理要求目标必须实现接口,生成的代理类实现相同接口,因此代理与目标之间是平级兄弟关系
public class JdkProxyDemo {
interface Foo {
void foo();
}
static final class Target implements Foo {
public void foo() {
System.out.println("target foo");
}
}
// jdk 只能针对接口代理
// cglib
public static void main(String[] param) throws IOException {
// 目标对象
Target target = new Target();
ClassLoader loader = JdkProxyDemo.class.getClassLoader(); // 用来加载在运行期间动态生成的字节码
Foo proxy = (Foo) Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, new Class[]{Foo.class}, (p, method, args) -> {
System.out.println("before...");
// 目标.方法(参数)
// 方法.invoke(目标, 参数);
Object result = method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("after....");
return result; // 让代理也返回目标方法执行的结果
});
System.out.println(proxy.getClass());
proxy.foo();
System.in.read();
}
}
通过Arthas查看生成的代理类
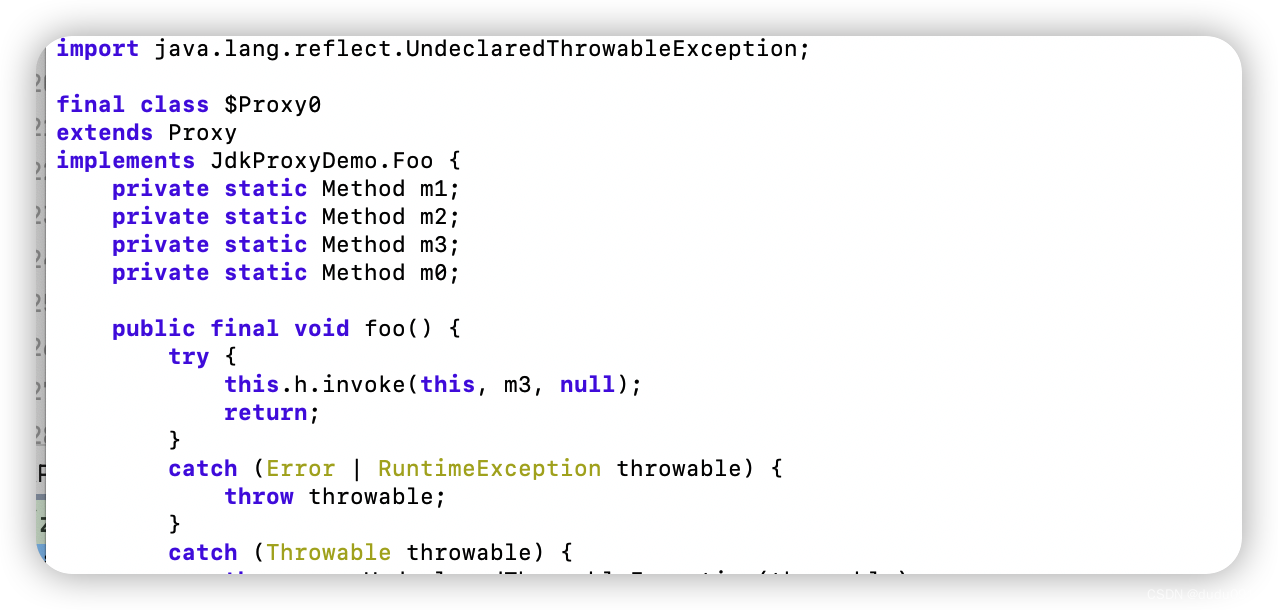
cglib 代理
- cglib 不要求目标实现接口,它生成的代理类是目标的子类,因此代理与目标之间是子父关系
- 限制⛔:根据上述分析 final 类无法被 cglib 增强
public class CglibProxyDemo {
static class Target {
public void foo() {
System.out.println("target foo");
}
}
// 代理是子类型, 目标是父类型
public static void main(String[] param) {
// Target target = new Target();
Target proxy = (Target) Enhancer.create(Target.class, (MethodInterceptor) (p, method, args, methodProxy) -> {
System.out.println("before...");
// Object result = method.invoke(target, args); // 用方法反射调用目标
// methodProxy 它可以避免反射调用
// Object result = methodProxy.invoke(target, args); // 内部没有用反射, 需要目标 (spring)
Object result = methodProxy.invokeSuper(p, args); // 内部没有用反射, 需要代理
System.out.println("after...");
return result;
});
proxy.foo();
}
}
为什么Cglib代理类多了参数methodProxy
methodProxy 它可以避免反射调用
// 内部没有用反射, 需要使用代理的目标类,Spring使用的正是这种方式
Object result = methodProxy.invoke(target, args);
// 内部没有用反射, 需要使用到代理类
Object result = methodProxy.invokeSuper(p, args);






















 2758
2758











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








