A reverse proxy server is a server that typically position itself behind the firewall in a private network and retrieves resources on behalf of a client from one or more servers. A reverse proxy provides an additional level of abstraction like SSL termination, load balancing, request routing, caching, compression etc. It also provides control to ensure smooth flow of traffic between clients and servers. In this tutorial we will setup a reverse proxy in NGINX that will serve two upstream servers, all inside a docker.
The setup
Our setup includes three containers, two containers for two upstream servers and one container for a reverse proxy. The client request will be intercepted by proxy and forwards the same to the upstream.
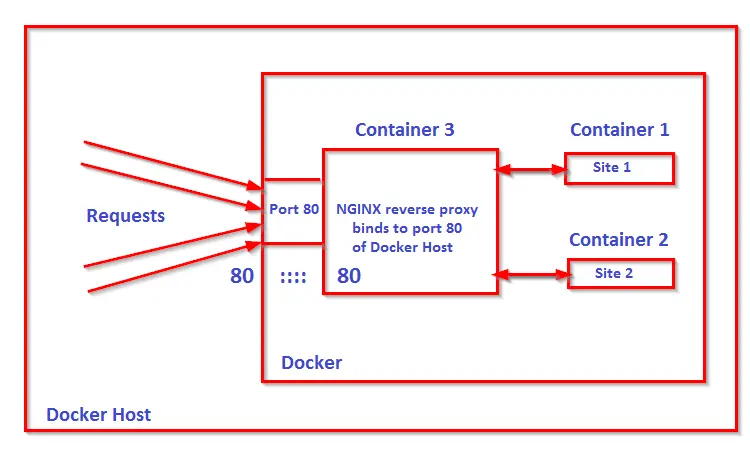
Inside container, ports and IP's are private and cannot be accessed externally unless they are bound to the host. So only one container can bind to port 80 of the docker host. So how can you access multiple web applications running on multiple container through port 80 of docker host ? The answer is through reverse proxy and we will use nginx reverse proxy inside a container which will bind its port 80 to the docker host's port 80 and forwards request to web application running across multiple containers.
Setup web services
Since we will setup two containers for two web services therefore each of them will have its own docker-composer.yml, one for site1 and another for site2. Remember these web services will not bind to any external ports, the communication with outside world will be done through reverse proxy. For this tutorial these web services will return a simple HTML using nginx, although it can be PHP/JSP/Python apps as well. Also we will connect these two web services using the name site1.test and site2.test
Let us create folders and files for webservice1 i.e for site1
site1
├── docker-compose.yml
└── index.html
root@demohost:~# cd ~
root@demohost:~# mkdir site1
root@demohost:~# cd site1
root@demohost:~/site1# vi docker-compose.ymlversion: '2'
services:
app:
image: nginx:1.9
volumes:
- .:/usr/share/nginx/html/
expose:
- "80"
Create a index file for web service 1
root@demohost:~/site1# vi index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Site 1</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a sample "site1" response</h1>
</body>
</html>
The docker-compose.yml is pretty straight forward. This web service is a "app" service and will pull nginx version 1.9 . The root of site1 from docker host is mounted to /usr/share/nginx/html/ and exposed the port 80. Build the web service 1 with the following command.
root@demohost:~/site1# docker-compose build
Now start the container for services.
root@demohost:~/site1# docker-compose up -d
List the container
root@demohost:~# docker ps -a
Similarly create second container i.e web service 2
site2
├── docker-compose.yml
└── index.html
root@demohost:~# cd ~
root@demohost:~# mkdir site2
root@demohost:~# cd site2
root@demohost:~/site2# vi docker-compose.ymlversion: '2'
services:
app:
image: nginx:1.9
volumes:
- .:/usr/share/nginx/html/
expose:
- "80"
Create an index file for web service 2
root@demohost:~/site2# vi index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Site 2</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a sample "site2" response</h1>
</body>
</html>
Build the web service 2 with the following command.
root@demohost:~/site2# docker-compose build
Now start the container for services.
root@demohost:~/site2# docker-compose up -d
List the container
root@demohost:~# docker ps -a
Setup Proxy
Now that two web services are up and running inside container, we proceed to configuring reverse proxy inside a container. We will start by creating folders and files for proxy.
proxy/
├── backend-not-found.html
├── default.conf
├── docker-compose.yml
├── Dockerfile
├── includes
│ ├── proxy.conf
│ └── ssl.conf
└── ssl
├── site1.crt
├── site1.key
├── site2.crt
└── site2.key
root@demohost:~# mkdir proxy
root@demohost:~# cd proxy/
root@demohost:~/proxy# touch Dockerfile
root@demohost:~/proxy# touch backend-not-found.html
root@demohost:~/proxy# touch default.conf
root@demohost:~/proxy# touch docker-compose.yml
root@demohost:~/proxy# mkdir includes
root@demohost:~/proxy# mkdir ssl
root@demohost:~/proxy# cd ../includes
root@demohost:~/proxy/includes# touch proxy.conf
root@demohost:~/proxy/includes# touch ssl.conf
Edit the Dockerfile with the following contents
root@demohost:~/proxy# vi Dockerfile
FROM nginx:1.9
# default conf for proxy service
COPY ./default.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf# NOT FOUND response
COPY ./backend-not-found.html /var/www/html/backend-not-found.html# Proxy and SSL configurations
COPY ./includes/ /etc/nginx/includes/# Proxy SSL certificates
COPY ./ssl/ /etc/ssl/certs/nginx/
Edit backend-not-found.html
root@demohost:~/proxy# vi backend-not-found.html
<html>
<head><title>Proxy Backend Not Found</title></head>
<body >
<h2>Proxy Backend Not Found</h2>
</body>
</html>
Edit default.conf
root@demohost:~/proxy# vi default.conf
# web service1 config.
server {
listen 80;
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name site1.test;# Path for SSL config/key/certificate
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/certs/nginx/site1.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/certs/nginx/site1.key;
include /etc/nginx/includes/ssl.conf;location / {
include /etc/nginx/includes/proxy.conf;
proxy_pass http://site1_app_1;
}access_log off;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log error;
}# web service2 config.
server {
listen 80;
listen 443 ssl http2;
server_name site2.test;# Path for SSL config/key/certificate
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/certs/nginx/site2.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/certs/nginx/site2.key;
include /etc/nginx/includes/ssl.conf;location / {
include /etc/nginx/includes/proxy.conf;
proxy_pass http://site2_app_1;
}access_log off;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log error;
}# Default
server {
listen 80 default_server;server_name _;
root /var/www/html;charset UTF-8;
error_page 404 /backend-not-found.html;
location = /backend-not-found.html {
allow all;
}
location / {
return 404;
}access_log off;
log_not_found off;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log error;
}
In nginx configuration, each of the two web services have its own server block. This block instructs nginx to pass requests to the appropriate web services apps container and they are namely site1_app_1 and site2_app_1. Find this name in the output of docker ps -a under name column. The proxy_intercept_errors option is set to on so that nginx return error from the web apps container itself rather than the default nginx response. The path for SSL configuration/key/certificates instructs nginx from where to pick these files.
Edit docker-compose.yml
version: '2'
services:
proxy:
build: ./
networks:
- site1
- site2
ports:- 80:80
- 443:443
The above docker-compose.yml will create a proxy service and that connects to two external network namely our two web services. This is due to fact that the proxy service need to connect to these external networks for proxy the request it receives from web services docker container. The binding of port no 80/443 of proxy service is done to the docker host's port 80/443. The name of the two external web services/containers are site1_default and site2_default.
Generate certificates and keys for both the web services inside ssl folder.
For Site1
root@demohost:~/proxy# cd ssl
root@demohost:~/proxy/ssl# sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout site1.key -out site1.crt
Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key
..........................+++
..............+++
writing new private key to 'site1.key'
-----
For Site2
root@demohost:~/proxy/ssl# sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout site2.key -out site2.crt
Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key
....................+++
..........................................+++
writing new private key to 'site2.key'
-----
Edit proxy.conf inside include directory.
root@demohost:~/proxy/includes# vi proxy.conf
proxy_set_header Host remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For scheme;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_request_buffering off;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_intercept_errors on;
Edit SSL configuration inside include folder
root@demohost:~/proxy/includes# vi ssl.conf
ssl_session_timeout 1d;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:50m;
ssl_session_tickets off;ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-
ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-
SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-
GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-
AES128-SHAECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-
SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:
DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-
DES-CBC3-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-DES-CBC3-SHA:EDH-RSA-DES-CBC3-SHA:AES128-GCM-SHA256:
AES256-GCM-SHA384:AES128-SHA256:AES256-SHA256:AES128-SHA:AES256-SHA:DES-
CBC3-SHA:!DSS';
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
For name resolution for two web services, add the following two lines in /etc/hosts
root@demohost:~/proxy# vi /etc/hosts
172.31.30.78 site1.test
172.31.30.78 site2.test
The above IP address is the private IP of docker-host. Remember, the request from client will arrive at port 80 of dockerhost which will be mapped to port 80 of nginx container.
Build the proxy container
root@demohost:~/proxy# docker-compose build
Building proxy
Step 1 : FROM nginx:1.9
---> c8c29d842c09
Step 2 : COPY ./default.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
---> Using cache
---> 4c459326c3a2
Step 3 : COPY ./backend-not-found.html /var/www/html/backend-not-found.html
---> Using cache
---> e3d817f5fb8e
Step 4 : COPY ./includes/ /etc/nginx/includes/
---> Using cache
---> 0c5ca9eb16d8
Step 5 : COPY ./ssl/ /etc/ssl/certs/nginx/
---> Using cache
---> 92007e83d405
Successfully built 92007e83d405
Run the proxy container
root@demohost:~/proxy# docker-compose up -d
Building proxy
Step 1 : FROM nginx:1.9
---> c8c29d842c09
Step 2 : COPY ./default.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
---> 4c459326c3a2
Removing intermediate container 86c1ea72022e
Step 3 : COPY ./backend-not-found.html /var/www/html/backend-not-found.html
---> e3d817f5fb8e
Removing intermediate container 51b12caded59
Step 4 : COPY ./includes/ /etc/nginx/includes/
---> 0c5ca9eb16d8
Removing intermediate container 66f2c8dd0d56
Step 5 : COPY ./ssl/ /etc/ssl/certs/nginx/
---> 92007e83d405
Removing intermediate container 29bca9e3ba0a
Successfully built 92007e83d405
Creating proxy_proxy_1
Now list all the running containers.
root@demohost:~/# docker ps -a
The above command will list all the three containers.

To verify that, we have set up reverse proxy correctly, use curl to get a response from two web services from docker host.
root@demohost:~/proxy# curl site1.test
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Site1</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a sample "Site1" response</h1>
</body>
</html>
root@demohost:~/proxy# curl site2.test
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Site2</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a sample "Site2" response</h1>
</body>
</html>
Conclusion
Since we have containerized reverse proxy, you can add more web services when you need. But this method needs to start and stop container each time you add services. This can be automated using the Docker APIs and some basic template. This leads to painless deployments as well as improve availability.























 1828
1828

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








