本来这节内容是要到后面来说的,因为最近在弄并发的问题,推荐一本书《java并发编程实战》,深入的讲解了多线程问题的。本人最近也刚好在看这本书,还不错的~
多线程的相关概念,就不用说了的,自己可以去网上查找,有一大堆关于它的讲解~
先来看看买票的程序:
package me.javen.thread.one;
public class TicketDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用Thread类的方式
// TicketThead ticketThead1 = new TicketThead();
// TicketThead ticketThead2 = new TicketThead();
// TicketThead ticketThead3 = new TicketThead();
// ticketThead1.start();
// ticketThead2.start();
// ticketThead3.start();
// 使用Runnable的方式
TicketRunnable ticketRunnable = new TicketRunnable();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(ticketRunnable);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(ticketRunnable);
Thread thread3 = new Thread(ticketRunnable);
thread1.run();
thread2.run();
thread3.run();
}
}
class TicketThead extends Thread {
private int ticket = 10;
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
if (this.ticket > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "买票:ticket=" + (ticket--));
}
}
}
}
class TicketRunnable implements Runnable {
private int ticket = 10;
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
if (this.ticket > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "买票:ticket=" + (ticket--));
}
}
}
}
从上面代码可以看出,java实现多线程有两种方式:
- 继承Thread类
- 实现Runnable接口
那么这两者有什么区别呢?为什么要提供两种方式呢?
其实我们在开发过程中主要还是使用Runnable接口。
实现Runnable接口比继承Thread类有明显的优点:
- 适合多个形同程序代码的线程去处理同一个资源
- 可以避免由于单继承局限所带来的影响
- 增强了程序的健壮性
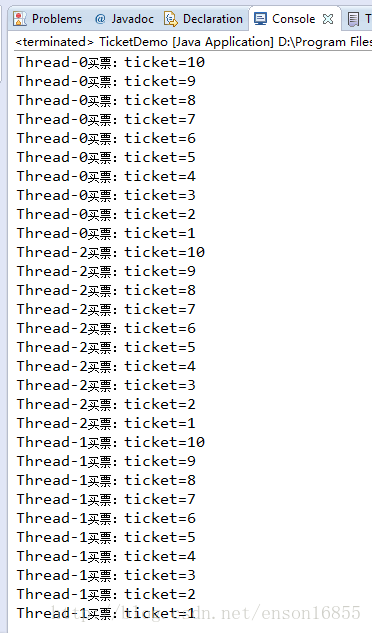
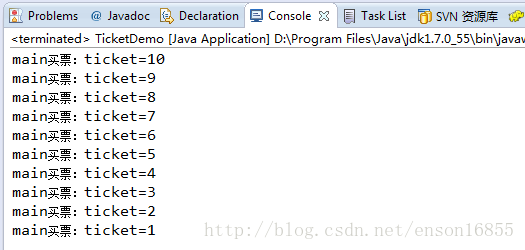
我们分别通过两种方式(使用Thread和使用runnable的方式)去运行以上的代码,可以看到,Thread总共卖出的票是30张,Runnable卖出的是10张(达到了资源共享)。
Thread方式:
Runnable方式:
代码解释:
Thread.currentThread() -->表示获取当前进程

























 930
930

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










