JAVA-HashMap源码学习-201805
(jdk 8 源码)
一.概述
基于哈希表的 Map 接口的实现。此实现提供所有可选的映射操作,并允许使用 null 值和 null 键。(除了非同步和允许使用 null 之外,HashMap 类与 Hashtable 大致相同。)此类不保证映射的顺序,特别是它不保证该顺序恒久不变。
此实现假定哈希函数将元素适当地分布在各桶之间,可为基本操作(get 和 put)提供稳定的性能。迭代 collection 视图所需的时间与 HashMap 实例的“容量”(桶的数量)及其大小(键-值映射关系数)成比例。所以,如果迭代性能很重要,则不要将初始容量设置得太高(或将加载因子设置得太低)。
注意,此实现不是同步的。如果多个线程同时访问一个哈希映射,而其中至少一个线程从结构上修改了该映射,则它必须 保持外部同步。
二.数据结构
HashMap的底层是哈希数组,数组元素为Entry。HashMap通过key的hashCode来计算hash值,当hashCode相同时,通过“拉链法”解决冲突,如下图所示。

相比于之前的版本,jdk1.8在解决哈希冲突时有了较大的变化,当链表长度大于阈值(默认为8)时,将链表转化为红黑树,以减少搜索时间。原本Map.Entry接口的实现类Entry改名为了Node。转化为红黑树时改用另一种实现TreeNode。
- 底层:HashMap是Map接口基于哈希表的实现。
- 是否允许null:HashMap允许key和value为null。
- 是否有序:HashMap不保证映射的顺序,特别是它不保证该顺序恒久不变。
- 何时rehash:超出当前允许的最大容量。initial capacity*load factor就是当前允许的最大元素数目,超过initial capacity*load factor之后,HashMap就会进行rehashed操作来进行扩容,扩容后的的容量为之前的两倍。
- 初始化容量对性能的影响:不应设置地太小,设置地小虽然可以节省空间,但会频繁地进行rehash操作。rehash会影响性能。总结:小了会增大时间开销(频繁rehash);大了会增大空间开销(占用了更多空间)和时间开销(影响遍历)。
- 加载因子对性能的影响:加载因子过高虽然减少了空间开销,但同时也增加了查询成本。0.75是个折中的选择。总结:小了会增大时间开销(频繁rehash);大了会也增大时间开销(影响遍历)。
- 是否同步:HashMap不是同步的。
- 迭代器:迭代器是fast-fail的。
三.源码
1.实现和继承
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
继承了AbstractMap,实现了 Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable接口
2.静态成员变量
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY -默认初始容量
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY-最大容量
/**
* The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
*/ //默认初始容量16(容量必须是2^n,n为正整数)
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
/**
* The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified
* by either of the constructors with arguments.
* MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30.
*/ //最大容量为2^30,
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; /**
* The load factor used when none specified in constructor.
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; TREEIFY_THRESHOLD--从链表转为红黑树的临界值8
UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD--从红黑树恢复为链表的临界值6
MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY--链表转成树的最小容量
/**
* The bin count threshold for using a tree rather than list for a
* bin. Bins are converted to trees when adding an element to a
* bin with at least this many nodes. The value must be greater
* than 2 and should be at least 8 to mesh with assumptions in
* tree removal about conversion back to plain bins upon
* shrinkage.
*/ //当数组节点=8时,再向其中添加元素,结构将从链表转为树形
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
/**
* The bin count threshold for untreeifying a (split) bin during a
* resize operation. Should be less than TREEIFY_THRESHOLD, and at
* most 6 to mesh with shrinkage detection under removal.
*/ //当数组节点=6时,再减少其中元素,结构将从树形转为链表
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
/**
* The smallest table capacity for which bins may be treeified.
* (Otherwise the table is resized if too many nodes in a bin.)
* Should be at least 4 * TREEIFY_THRESHOLD to avoid conflicts
* between resizing and treeification thresholds.
*/ //当map元素个数>=64时,才会转为树形;若<64,将尝试扩容来减少冲突
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64; //4*TREEIFY_CAPACITY /**
* Basic hash bin node, used for most entries. (See below for
* TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.) //底层hash节点(单向链表)
*/
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { //Nord的构造函数
this.hash = hash; //Nord(key的hash值,key,value,下个Nord)
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value); //计算节点的hashcode=key.hashcode^value.hashcode
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) { //重写equals方法
if (o == this) //当内存地址相同时,返回true;否则,判断1.o是否是Map.Entry<>对象,
return true; //2.key和value是否都相同,若都成立,返回true,否则,返回false。
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}4.静态方法
static final int hash(Object key)-计算key的hash值-扰动函数
/**
* Computes key.hashCode() and spreads (XORs) higher bits of hash
* to lower. Because the table uses power-of-two masking, sets of
* hashes that vary only in bits above the current mask will
* always collide. (Among known examples are sets of Float keys
* holding consecutive whole numbers in small tables.) So we
* apply a transform that spreads the impact of higher bits
* downward. There is a tradeoff between speed, utility, and
* quality of bit-spreading. Because many common sets of hashes
* are already reasonably distributed (so don't benefit from
* spreading), and because we use trees to handle large sets of
* collisions in bins, we just XOR some shifted bits in the
* cheapest possible way to reduce systematic lossage, as well as
* to incorporate impact of the highest bits that would otherwise
* never be used in index calculations because of table bounds.
*/
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); //key=null,赋0;否则再做计算
}key!=null时,首先h=key.hashCode().这时h为一个int型散列值,范围在[-2^-31,2^31-1]之间。若将h作为数组下标,很难出现hash碰撞,但内存中无法放下一个接近40亿长度的数组。因此,这里需要h对数组长度n取模,得到的余数来作为下标。例如初始容量16(0000000000000000 0000000000010000),由于这里n是2的整数次幂,取模算法(n-1)&h,这里相当于只对h的后4位进行操作,前面28位的特征全部舍弃。
此时的问题在于,这时的hash碰撞将十分严重,且若散列值本身呈等差数列,将更为严重。这里的做法是使用扰动函数, 将h>>>16右移16位(32bit的一半),将高位区与低位区做异或运算,混合原始hash值的高低位,以此增大随机性。(h^(h>>>16))。
参考:https://www.zhihu.com/question/20733617
测试下不扩容时数组下标的分布:
class Cat{
double length;
String color;
public Cat(double length, String color) {
super();
this.length = length;
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat [length=" + length + ", color=" + color + "]";
}
}
public class ArrayListSource {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayListSource als=new ArrayListSource();
int n=100000;
int capacity=16;
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
Cat cat1=new Cat(Math.random(),als.getRandomString());
int hash=als.getHash(cat1);
int h=als.getIndex(hash, capacity);
list.add(h);
}
//groupBy分组汇总
Map<Integer,Long> map= list.stream().collect(
Collectors.groupingBy(
Function.identity(),Collectors.counting()
));
map.forEach((k,v)->System.out.println(k+"="+(double)v/n));
}
//随机3-8位字符串
public String getRandomString(){
Random r=new Random();
int bound=3+r.nextInt(5);
StringBuilder s=new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i<bound;i++){
Random r2=new Random();
char c=(char)(97+r2.nextInt(26));
s.append(c);
}
return s.toString();
}
//HashMap取到key的hash算法
public int getHash(Cat cat){
int h=cat.hashCode();
int hash=h^(h>>>16);
return hash;
}
//对hash值取模得到index
public int getIndex(int hash,int capacity){
return (capacity-1)&hash;
}
}0=0.06262
1=0.06232
2=0.06206
3=0.06266
4=0.06158
5=0.06397
6=0.06299
7=0.06179
8=0.06158
9=0.06372
10=0.06163
11=0.06127
12=0.06272
13=0.06422
14=0.063
15=0.06187static Class<?> comparableClassFor(Object x) -判断x是否是实现了Comparable接口的对象,若是返回x.class。
/**
* Returns x's Class if it is of the form "class C implements
* Comparable<C>", else null.
*/
static Class<?> comparableClassFor(Object x) {
if (x instanceof Comparable) { //先判断是否实现了Comparable接口
Class<?> c; Type[] ts, as; Type t; ParameterizedType p;
if ((c = x.getClass()) == String.class) // bypass checks //分流检查(String),若是,则返回String.class
return c;
if ((ts = c.getGenericInterfaces()) != null) { //取得ts为c实现的接口的type[]数组
for (int i = 0; i < ts.length; ++i) {
if (((t = ts[i]) instanceof ParameterizedType) && //遍历ts[],若ts[i]为参数化类型(例如Collection<String>),且
((p = (ParameterizedType)t).getRawType() == //其参数化类型的实现接口类型为Comparable.class,且该参数化
Comparable.class) && //类型的参数只有一个c是,返回c
(as = p.getActualTypeArguments()) != null &&
as.length == 1 && as[0] == c) // type arg is c
return c;
}
}
}
return null;
}static int compareComparables(Class<?> kc, Object k, Object x)
/**
* Returns k.compareTo(x) if x matches kc (k's screened comparable
* class), else 0. //若x.class=kc,则返回k.compareTo(x)
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) // for cast to Comparable
static int compareComparables(Class<?> kc, Object k, Object x) {
return (x == null || x.getClass() != kc ? 0 :
((Comparable)k).compareTo(x));
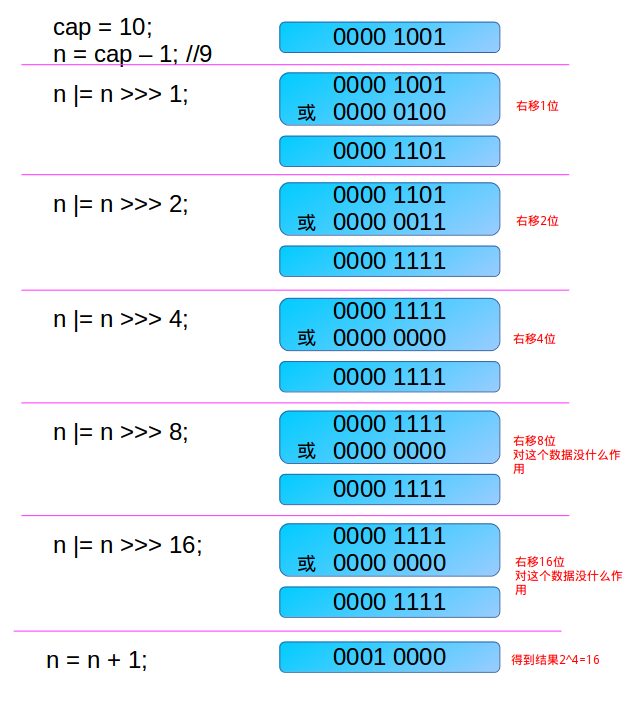
} static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1; //确保cap本身为2^n的情况适用
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}求大于等于cap的最小2^x。
2的n次方的二进制数为 0000 1000 形式(这里只写下后8位,实际为32位,前面补0),而大于等于cap的2^x:
若cap=2^x,则cap本身即为要求的数,通过第一步cap-1,使其适配整个过程。
若cap<2^x,则要求的数m的二进制数:cap的二进制数中1的最高位的前一位取1,其余位取0.
如12: 0000 1100,大于12的最小2^x为 16: 0001 0000。
通过下图的操作使n=2^x-1,即令n的二进制数中从最高位到末尾都取1. 最后取n+1,即2^x-1+1=2^x。
这里从最高位开始复制1,因为int型有32bit,最后右移16位完成1的复制。
图解:
5.成员变量
transient Node<K,V>[] table;-存储键值对的Node[]数组
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;-键值对缓存的Set
/**
* The table, initialized on first use, and resized as
* necessary. When allocated, length is always a power of two.
* (We also tolerate length zero in some operations to allow
* bootstrapping mechanics that are currently not needed.)
*/
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
/**
* Holds cached entrySet(). Note that AbstractMap fields are used
* for keySet() and values().
*/
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet; transient int size;-键值对数量
transient int modCount;-结构性修改次数
int threshold;-临界值
final float loadFactor;-加载因子
/**
* The number of key-value mappings contained in this map.
*/
transient int size; //键值对的数量
/**
* The number of times this HashMap has been structurally modified
* Structural modifications are those that change the number of mappings in
* the HashMap or otherwise modify its internal structure (e.g.,
* rehash). This field is used to make iterators on Collection-views of
* the HashMap fail-fast. (See ConcurrentModificationException).
*/
transient int modCount; //结构性修改次数
/**
* The next size value at which to resize (capacity * load factor).
*
* @serial
*/
// (The javadoc description is true upon serialization.
// Additionally, if the table array has not been allocated, this
// field holds the initial array capacity, or zero signifying
// DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY.)
int threshold; //table数组重构数据结构的临界值
/**
* The load factor for the hash table.
*
* @serial
*/
final float loadFactor; //加载因子 public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)-指定初始容量,加载因子构造
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial
* capacity and load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; //initialCapacity的大小(0,2^30]
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity); //计算临界值
}public HashMap(int initialCapacity)-指定初始容量,加载因子0.75
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the specified initial
* capacity and the default load factor (0.75).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative.
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
} public HashMap()-指定初始容量16,加载因子0.75
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m)-通过已有Map构造
/**
* Constructs a new <tt>HashMap</tt> with the same mappings as the
* specified <tt>Map</tt>. The <tt>HashMap</tt> is created with
* default load factor (0.75) and an initial capacity sufficient to
* hold the mappings in the specified <tt>Map</tt>.
*
* @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; //直接调用putMapEntries(m,false)
putMapEntries(m, false);
}7.public V get(Object key)-根据给定key获取对应value
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value; //直接调用下面的方法返回该key对应的Nord e,返回e.value
}final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key)-根据key和key的hash值获得该Nord
/**
* Implements Map.get and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @return the node, or null if none
*/
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && //键值对Nord[] table赋给tab,table的长度赋给n,使用给定hash计算
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { //到该hash对应的Nord[index]赋给first
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //检查first,是否所寻Nord,若是,返回first
return first; //first是所寻Nord的概率很大
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode) //将first的后继节点赋给e,若e不为null,判断first是树形节点还是单链节点
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); //若first为树形节点,调用getTreeNord(hash,key)
do {
if (e.hash == hash && //若first为单向链表结构,则通过后继节点向后遍历,直到
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //取得key值相同的Nord
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null; //若未取得Nord,返回null
} public V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue)-若查不到对应key的nord,就返回默认值defaultValue
@Override
public V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? defaultValue : e.value;
}8.public V put(K key, V value)-在map中添加键值对<key,value>,若key存在,则替换原value,并返回
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); //调用下面的putVal方法
}final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict)
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key //key的hash值
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value //若为true,则当key值已存在时,不替换原值
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode. //若为false,数组为创建模式
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) //当table[]为空,扩容
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) //若key的槽位p为null,则在该位置new一个nord(链表型)存放键值对
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else { //若槽位非空,p即为第一个节点Nord first
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //当p.key等于key时,令e=p;
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode) //当两者不等时,先判断p是否已树化,若已是树形节点,调用putTreeVal方法
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); //若key不存在,直接插入;若存在,返回原节点
else { //若p为普通链表节点,通过p.next向后,在队尾加入
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st //若该槽位内元素已达8个,就调用treeifBin树化或扩容
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //在槽内已有元素中找到key相同的,也跳出
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key //当key在map中已存在时,返回oldvalue
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) //当onlyIfAbsent为false或oldvalue为null时,用value代替oldvalue
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e); //这个方法是给继承类LinkedHashMap用的,在HashMap中是空实现
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold) //size+1,若>临界值(=cap*loadfactor),扩容
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict); //空实现
return null;
}putVal中调用到的方法:
final Node<K,V>[] resize()--扩容函数
/**
* Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in
* accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold.
* Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the
* elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move
* with a power of two offset in the new table.
* //若table为null,分配初始容量
* @return the table
*/
final Node<K,V>[] resize() { //注意前提条件,这里容量满足 2^n
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) { //当原容量>0,
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { //当原容量>2^30,令threshold=2^31-1(意为不能再扩容),返回原数组
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && //新容量=old*2,当newCap<2^30 且 oldCap>16(初始容量)
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) //令新临界值为 oldThr*2
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold //当table为空,oldThr有设置值,初始化其容量为oldThr
newCap = oldThr; //对应的情况:putAll方法,当前map中无元素时
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults //若table为空,亦无Threshold值,此时使用默认
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; //配置,容量为16,临界值=16*0.75=12.
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) { //上面未设置newThr的情况,重新设置下
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) //下面是将旧数组元素分布到新数组的操作
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; //新数组
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) { //遍历旧数组,当找到非空元素
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null) //若该槽位只有一个元素
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e; //则将该元素赋到新数组的hash &(newCap-1)位,这里就是根据新的最高位1或0分配
else if (e instanceof TreeNode) //若e.next不为空,且e为树形,调用split方法拆分树形
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order //当e.next不为空,为链表时, 这里在jdk1.7多线程时,存在死链问题,且按原序
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next; //通过e.next遍历链表
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {//判断e.hash对应的oldCap的二进制位是否为0,即根据hash%newCap的不同结果分组
if (loTail == null) //若为0,则放到原槽位,低位low
loHead = e; //若为1,则放到原槽位+旧容量 位,高位high
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null; //将tail.next设为null
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}以上涉及的位运算:
/**
* 0001010111011011 1001011101000010 h=cat.hashcode
* 0000000000000000 0001010111011011 h>>>16
* 0001010111011011 1000001010011001 hash=h^(h>>>16)
* 0000000000000000 0000000001111111 n-1=127
* 0000000000000000 0000000000011001 (n-1)&hash=25
*
* 若扩容:hash&(newCap-1) [newCap=oldCap<<1]
* 0000000000000000 0000000011111111 n-1=255
* 0000000000000000 0000000010011001 (n-1)&hash=25+128=153
*
* oldCap&hash
* 0000000000000000 0000000010000000 n=128
*
* */关于jdk 7中多线程操作HashMap造成死锁,参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/z69183787/article/details/64920074?locationNum=15&fps=1
final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash)--将链表转为双向,并重构Nord为TreeNord,最后转为红黑树结构
/**
* Replaces all linked nodes in bin at index for given hash unless
* table is too small, in which case resizes instead.
*/
final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) {
int n, index; Node<K,V> e;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY) //当tab槽位<64时,扩容
resize();
else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { //e时给定hash值对应槽位的第一个元素
TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
do {
TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null); //这里遍历这个单向链表,把Nord转为TreeNord型
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else {
p.prev = tl; //并补充prev属性,作为双向链表
tl.next = p;
}
tl = p;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
if ((tab[index] = hd) != null) //最后调用treeify函数,将该槽位链表结构转为红黑树
hd.treeify(tab);
}
}public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m)-将map m中所有的键值对插入,若重复,则更新
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
putMapEntries(m, true); //直接调putMapEntries()方法
}final void putMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict)
/**
* Implements Map.putAll and Map constructor
*
* @param m the map
* @param evict false when initially constructing this map, else
* true (relayed to method afterNodeInsertion).
*/
final void putMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict) { //evict在LinkedHashMap中才会用到,这里都为true
int s = m.size();
if (s > 0) {
if (table == null) { // pre-size //当table为空时,根据map m中元素个数s初始化本map
float ft = ((float)s / loadFactor) + 1.0F; //这里把s视作临界值,t为需要的最小容量
int t = ((ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);
if (t > threshold) //若t>threshold,先取threshold=大于t的最小2^n,后面调用putVal时,会调用
threshold = tableSizeFor(t); //到resize方法时,对应到table=null,oldCap=0,oldThr>0的情况,这时将newCap=oldThr
}
else if (s > threshold) //当table非空,若s>threshold,扩容
resize();
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet()) { //遍历m,调用putVal方法插入
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, evict);
}
}
}9.public V remove(Object key)-按key删除,若key存在则返回原value,若不存在返回null
/**
* Removes the mapping for the specified key from this map if present.
*
* @param key key whose mapping is to be removed from the map
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V remove(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ? //这边直接调removeNode方法
null : e.value;
}final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,boolean matchValue, boolean movable)
/**
* Implements Map.remove and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to match if matchValue, else ignored
* @param matchValue if true only remove if value is equal //matchValue为true,则key/value都相同时才删除;false,只要求key
* @param movable if false do not move other nodes while removing //若moveable为false,删除后不移动其他节点
* @return the node, or null if none
*/
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {//对照上面的参数removeNode(hash(key),key,null,false,true)
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index; //只要key相同就删除,删除后可以移动其他节点
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { //传下参,tab=table[],n=tab容量,index:对应hash值的下标
Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v; //p=tab[index],index槽位的第一元素
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) //当key与p.key相同时,nord=p
node = p;
else if ((e = p.next) != null) { //当key与p.key不同,若p有next,
if (p instanceof TreeNode) //先判断p若为树形,调用getTreeNode方法
node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
do {
if (e.hash == hash && //若p为链表,则通过next指针遍历,找到相同的key,则nord赋该节点
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value || //若nord不为空,即要删除的节点存在,且matchValue为false
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) { //或matchValue为true,但value相等时
if (node instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable); //若nord为树形,调用removeTreeNode方法删除
else if (node == p)
tab[index] = node.next; //若nord为链表,若nord==p,把nord.next位元素赋给table[index]
else
p.next = node.next; //若nord非第一元素,则令p.next=nord.next
++modCount;
--size; //元素个数-1
afterNodeRemoval(node); //空实现
return node; //返回已删除的节点
}
}
return null; //若要删除的节点不存在,则返回null
}public void clear()--删除map中所有元素
/**
* Removes all of the mappings from this map.
* The map will be empty after this call returns.
*/
public void clear() {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
modCount++;
if ((tab = table) != null && size > 0) { //这里直接遍历然后删除整个数组,size=0
size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i)
tab[i] = null;
}
}public boolean containsValue(Object value)-判断map中是否存在该value
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the
* specified value.
*
* @param value value whose presence in this map is to be tested
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the
* specified value
*/
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; V v;
if ((tab = table) != null && size > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { //遍历table数组,再直接用next位遍历每个槽位
if ((v = e.value) == value || //树形是以key为索引构造的,使用不了
(value != null && value.equals(v)))
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}10.public boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue)--查找<key,oldValue>以newValue代替
@Override
public boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {
Node<K,V> e; V v;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) != null &&
((v = e.value) == oldValue || (v != null && v.equals(oldValue)))) { //key和oldValue都对应才替换
e.value = newValue;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return true;
}
return false;
}public V replace(K key, V value)-查找key,并替换value
@Override
public V replace(K key, V value) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) != null) { 只要key对应就替换
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
return null;
}11.static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>-树节点(红黑树)
成员变量和构造方法
TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links //父节点
TreeNode<K,V> left; //左节点
TreeNode<K,V> right; //右节点
TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion //删除辅助节点
boolean red; //颜色
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) { //构造方法
super(hash, key, val, next);
} final TreeNode<K,V> root()-返回此树的根节点
/**
* Returns root of tree containing this node.
*/
final TreeNode<K,V> root() {
for (TreeNode<K,V> r = this, p;;) {
if ((p = r.parent) == null)
return r;
r = p;
}
}static <K,V> void moveRootToFront(Node<K,V>[] tab, TreeNode<K,V> root)-将根节点移到第一位
static <K,V> void moveRootToFront(Node<K,V>[] tab, TreeNode<K,V> root) {
int n;
if (root != null && tab != null && (n = tab.length) > 0) { //当root和tab都非空时,先算出root的index
int index = (n - 1) & root.hash;
TreeNode<K,V> first = (TreeNode<K,V>)tab[index]; //取tab[index]为first
if (root != first) { //当first不是root时,先赋tab[index]=root
Node<K,V> rn;
tab[index] = root;
TreeNode<K,V> rp = root.prev; //rp为root前驱节点,rn为后继节点
if ((rn = root.next) != null)
((TreeNode<K,V>)rn).prev = rp; //这里将root从rp与rn间移出,赋rp.next=rn,rn.prev=rp;
if (rp != null)
rp.next = rn;
if (first != null) //再将first移到root之后,移玩后,root.prev=null
first.prev = root;
root.next = first;
root.prev = null;
}
assert checkInvariants(root); //检查是否仍是红黑树
}
}/**
* Finds the node starting at root p with the given hash and key. //kc初始值设为null,为第一次取到时,记录下的k.class
* The kc argument caches comparableClassFor(key) upon first use //若k是Comparable的实现类,kc=k.class;否则为null
* comparing keys.
*/
final TreeNode<K,V> find(int h, Object k, Class<?> kc) {
TreeNode<K,V> p = this;
do {
int ph, dir; K pk;
TreeNode<K,V> pl = p.left, pr = p.right, q;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h) //若h>p节点的hash,则指针向右;若小于,则向左
p = pl;
else if (ph < h)
p = pr;
else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk))) //若hash值相等且key相同,则返回该节点
return p;
else if (pl == null) //若hash值相同,但key不同,判断其若无左孩子,则指针向右;无右孩子,则向左
p = pr;
else if (pr == null)
p = pl;
else if ((kc != null || //若k实现了Comparable接口,则比较pk,k
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) != null) &&
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) != 0)
p = (dir < 0) ? pl : pr; //若k<pk,向左;k>=pk向右
else if ((q = pr.find(h, k, kc)) != null) //若k未实现Comparable接口,向右遍历
return q;
else //若右边未找到,则向左
p = pl;
} while (p != null);
return null; //若未找到,return null
}final TreeNode<K,V> getTreeNode(int h, Object k)-从根节点开始找指定key
/**
* Calls find for root node.
*/
final TreeNode<K,V> getTreeNode(int h, Object k) {
return ((parent != null) ? root() : this).find(h, k, null); //用根节点调用find [find中的初始p为this]
}static int tieBreakOrder(Object a, Object b)--当hash值相同且对象不支持Comparable接口时,强制判断大小的方法
/**
* Tie-breaking utility for ordering insertions when equal
* hashCodes and non-comparable. We don't require a total
* order, just a consistent insertion rule to maintain
* equivalence across rebalancings. Tie-breaking further than //红黑树插入元素的时候,需要一种确定的大小顺序
* necessary simplifies testing a bit.
*/
static int tieBreakOrder(Object a, Object b) {
int d;
if (a == null || b == null ||
(d = a.getClass().getName(). //当对象为null时,也能判断
compareTo(b.getClass().getName())) == 0)
d = (System.identityHashCode(a) <= System.identityHashCode(b) ? //当a=null,System.indentityHashCode(a)=0
-1 : 1);
return d;
}final void treeify(Node<K,V>[] tab)-将链表结构转化为红黑树
/**
* Forms tree of the nodes linked from this node.
* @return root of tree
*/
final void treeify(Node<K,V>[] tab) {
TreeNode<K,V> root = null;
for (TreeNode<K,V> x = this, next; x != null; x = next) { //使用Nord.next遍历整条链表,再插入红黑树
next = (TreeNode<K,V>)x.next;
x.left = x.right = null;
if (root == null) { //若root为null,将该节点x赋为root
x.parent = null;
x.red = false;
root = x;
}
else {
K k = x.key; //若root不为null时
int h = x.hash;
Class<?> kc = null;
for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) { //从root开始向下遍历树
int dir, ph;
K pk = p.key;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
dir = -1;
else if (ph < h)
dir = 1;
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) || //当key不支持Comparable接口或比较值=0时,强转判断
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) //dir:判断p与root的大小,dir>0,则p>root,指针向右;
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk); // dir<=0,则p<root,指针向左
TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) { //遍历到其叶节点时,插入该元素
x.parent = xp;
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
root = balanceInsertion(root, x); //插入完后,修正红黑树
break;
}
}
}
}
moveRootToFront(tab, root); //把root节点移到该槽位的第一位
}final Node<K,V> untreeify(HashMap<K,V> map)-将红黑树转化为链表-返回链表的头
/**
* Returns a list of non-TreeNodes replacing those linked from
* this node.
*/
final Node<K,V> untreeify(HashMap<K,V> map) {
Node<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;
for (Node<K,V> q = this; q != null; q = q.next) {
Node<K,V> p = map.replacementNode(q, null); //将q=this的结构改为 new Nord<>(p.hash,p.key,p.value,p.next)
if (tl == null) //设置两个指针head和tail 第一次遍历取得的元素赋为head,tail位后移直到q.next为null
hd = p;
else
tl.next = p;
tl = p;
}
return hd;
}final TreeNode<K,V> putTreeVal(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab,int h, K k, V v)--向红黑数中插入元素
/**
* Tree version of putVal.
*/
final TreeNode<K,V> putTreeVal(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab, //若该key值存在,则返回原节点;否则,返回null
int h, K k, V v) {
Class<?> kc = null;
boolean searched = false;
TreeNode<K,V> root = (parent != null) ? root() : this; //找到root节点,由root向下遍历
for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) {
int dir, ph; K pk;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
dir = -1;
else if (ph < h)
dir = 1;
else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk))) //这边和前面一样
return p;
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) {
if (!searched) { //searche初始为false,在运行一次后就重新赋值为true
TreeNode<K,V> q, ch;
searched = true;
if (((ch = p.left) != null && //第一次运行时,通过递归,先向左再向右寻找相同的key,若找到则返回;
(q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null) ||
((ch = p.right) != null &&
(q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null))
return q;
}
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk); //若未找到,则强制定义大小
}
TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) { //由dir判断指针方向,向下找到合适位置插入
Node<K,V> xpn = xp.next;
TreeNode<K,V> x = map.newTreeNode(h, k, v, xpn);
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
xp.next = x;
x.parent = x.prev = xp;
if (xpn != null)
((TreeNode<K,V>)xpn).prev = x;
moveRootToFront(tab, balanceInsertion(root, x)); //插入完成后修正红黑树,并将root移到第一位
return null;
}
}
} final void split(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab, int index, int bit)--分割树形
final void split(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab, int index, int bit) { //按hash的bit位0/1分割树形 bit一般为2^n
TreeNode<K,V> b = this;
// Relink into lo and hi lists, preserving order
TreeNode<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
TreeNode<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
int lc = 0, hc = 0;
for (TreeNode<K,V> e = b, next; e != null; e = next) { //按照bit的1/0 分成两个槽位low/high,和上面resize方法中相似
next = (TreeNode<K,V>)e.next;
e.next = null;
if ((e.hash & bit) == 0) {
if ((e.prev = loTail) == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
++lc;
}
else {
if ((e.prev = hiTail) == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
++hc; //lc、hc用于记录高位、低位分别分入了几个元素
}
}
if (loHead != null) {
if (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) //当lc链表长度<=6时,化为链表
tab[index] = loHead.untreeify(map);
else { //lc长度>6时,重新构造树形
tab[index] = loHead;
if (hiHead != null) // (else is already treeified) //hihead==null时,index槽位与原来的一样,不需要重新构造
loHead.treeify(tab);
}
}
if (hiHead != null) {
if (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) //与lc相同
tab[index + bit] = hiHead.untreeify(map);
else {
tab[index + bit] = hiHead;
if (loHead != null) //lchead==null时,只需将原index槽位的结构移至index+bit位
hiHead.treeify(tab);
}
}
}final void removeTreeNode(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab, boolean movable)-删除调用该方法的TreeNode
/**
* Removes the given node, that must be present before this call.
* This is messier than typical red-black deletion code because we
* cannot swap the contents of an interior node with a leaf
* successor that is pinned by "next" pointers that are accessible
* independently during traversal. So instead we swap the tree
* linkages. If the current tree appears to have too few nodes,
* the bin is converted back to a plain bin. (The test triggers
* somewhere between 2 and 6 nodes, depending on tree structure).
*/
final void removeTreeNode(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab,
boolean movable) {
int n;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
return;
int index = (n - 1) & hash;
TreeNode<K,V> first = (TreeNode<K,V>)tab[index], root = first, rl; //first为该节点key.hash对应槽位的第一元素
TreeNode<K,V> succ = (TreeNode<K,V>)next, pred = prev; //根节点=first,succ为next位,pred为prev位
if (pred == null) //下面处理next和prev指针
tab[index] = first = succ; //当prev为空,即this元素为first,删除this即将tab[index]赋this.next,同时first=next
else
pred.next = succ; //当prev不为空,则this非first元素,这时将pred.next=succ
if (succ != null) //若succ非空,则this非尾元素,则将succ.prev=pred
succ.prev = pred;
if (first == null) //若first为空,即该槽位只有一个元素时,上面tab[index]=first=succ=null,删除完成,返回
return;
if (root.parent != null) //找到真实的root
root = root.root();
if (root == null || root.right == null || //当树中元素过少时(2-6个),结构转为链表,返回,不参与下面红黑树的删除过程
(rl = root.left) == null || rl.left == null) {
tab[index] = first.untreeify(map); // too small
return;
}
TreeNode<K,V> p = this, pl = left, pr = right, replacement;//红黑树删除操作需要记录替代节点1.原位置2.原色彩
if (pl != null && pr != null) { //首先左右孩子都在的情况
TreeNode<K,V> s = pr, sl;
while ((sl = s.left) != null) // find successor //寻找p的后继successor(大于p的最小节点)
s = sl; //此时因右孩子存在,找到右孩子树中的最小节点即可
boolean c = s.red; s.red = p.red; p.red = c; // swap colors //这里保存替代节点的颜色到p节点中
TreeNode<K,V> sr = s.right;
TreeNode<K,V> pp = p.parent; //整体思路是 把p与s换位置,由p占据s的原位
if (s == pr) { // p was s's direct parent //若s为p的右孩子,先把p设为s的右孩子
p.parent = s;
s.right = p;
}
else {
TreeNode<K,V> sp = s.parent; //若s非p的右孩子,则将p设为s.parent的孩子节点
if ((p.parent = sp) != null) {
if (s == sp.left)
sp.left = p;
else
sp.right = p;
}
if ((s.right = pr) != null) //再将p.right赋给s.right
pr.parent = s;
}
p.left = null; //令p.left=null
if ((p.right = sr) != null)
sr.parent = p;
if ((s.left = pl) != null) //继续换位操作,令p.right=s.right;s.left=pl
pl.parent = s;
if ((s.parent = pp) == null) //将p的原父节点赋给s.parent,若该节点为空,则s为根节点
root = s;
else if (p == pp.left) //若非空,判断p是其左或右孩子,再将s赋给其相同的孩子位
pp.left = s;
else
pp.right = s;
if (sr != null) //若sr不为null,则replacement=sr;否则为p
replacement = sr;
else
replacement = p;
}
else if (pl != null) //孩子位只有一个的情况,将replacement赋存在的那个孩子位
replacement = pl;
else if (pr != null)
replacement = pr;
else
replacement = p; //若不存在孩子位,replacement=p
if (replacement != p) { //当replacement!=p,两种情况1.p存在两个孩子,sr非空 2.p存在一个孩子
TreeNode<K,V> pp = replacement.parent = p.parent; //此时把p删除,replacement移到p位,p的各项属性赋null
if (pp == null)
root = replacement;
else if (p == pp.left)
pp.left = replacement;
else
pp.right = replacement;
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null; //这时replacement的位置即为替代节点的原位置
}
//当replacement=p,情况有1.p无孩子 2.p有两孩子,且sr为空(此时sr为p的右孩子).这时若删除p无法表示替代节点原位置,直接用p代表该位置
TreeNode<K,V> r = p.red ? root : balanceDeletion(root, replacement); //p.red有两种情况 1.p有两孩子,p.red保存了
//原替代节点s的颜色,s为黑,影响黑高 2.p有1个或0个孩子这时若p为black,则删除肯定影响黑高,必须修正。r存为修正后新的root
if (replacement == p) { // detach
TreeNode<K,V> pp = p.parent; //最后把replacement=p时,p删除
p.parent = null;
if (pp != null) {
if (p == pp.left)
pp.left = null;
else if (p == pp.right)
pp.right = null;
}
}
if (movable)
moveRootToFront(tab, r); //若可移动,则把root移到槽位的第一位
}这里操作比较复杂,首先要处理next和prev指针,然后在处理红黑树的删除操作。红黑树的删除操作的具体情况和步骤,参考自己的文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/ever_who/article/details/80323956
TreeNode内部类还剩余的几个方法:
static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> rotateLeft(TreeNode<K,V> root,TreeNode<K,V> p)--左旋
static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> rotateRight(TreeNode<K,V> root,TreeNode<K,V> p)--右旋
static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> balanceInsertion(TreeNode<K,V> root,TreeNode<K,V> x)-插入修正
static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> balanceDeletion(TreeNode<K,V> root,TreeNode<K,V> x)-删除修正
这里就不表了:参考上面自己文章的链接。
static <K,V> boolean checkInvariants(TreeNode<K,V> t)--通过递归的方式检验红黑树的性质
/**
* Recursive invariant check
*/
static <K,V> boolean checkInvariants(TreeNode<K,V> t) {
TreeNode<K,V> tp = t.parent, tl = t.left, tr = t.right,
tb = t.prev, tn = (TreeNode<K,V>)t.next;
if (tb != null && tb.next != t)
return false;
if (tn != null && tn.prev != t)
return false;
if (tp != null && t != tp.left && t != tp.right)
return false;
if (tl != null && (tl.parent != t || tl.hash > t.hash))
return false;
if (tr != null && (tr.parent != t || tr.hash < t.hash))
return false;
if (t.red && tl != null && tl.red && tr != null && tr.red)
return false;
if (tl != null && !checkInvariants(tl))
return false;
if (tr != null && !checkInvariants(tr))
return false;
return true;
}参考自己的文章:https://blog.csdn.net/ever_who/article/details/79979114
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/ITtangtang/p/3948406.html
https://blog.csdn.net/panweiwei1994/article/details/77244920
https://www.zhihu.com/question/20733617
https://www.cnblogs.com/liujinhong/p/6576543.html
https://blog.csdn.net/liyantianmin/article/details/79401854
https://blog.csdn.net/u011642663/article/details/49853087
https://blog.csdn.net/z69183787/article/details/64920074?locationNum=15&fps=1


























 488
488

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








