A
A题需要看明白题意,其实是01背包问题,题目中说的数字根说白了就是加和%9的意思,第9扇门在%9后也就是第0扇门,根据题意,就可以直接(j[0,8]+x)%9就行了,转移方程dp[i][(j+x)%9]=dp[i-1][j]+dp[i][(j+x)%9],递推式dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j]+dp[i][j]
AC代码:
/* Tips: 1.int? long long? 2.don't submit wrong answer 3.figure out logic first, then start writing please 4.know about the range 5.check if you have to input t or not 6.modulo of negative numbers is not a%b, it is a%b + abs(b) */ #pragma GCC optimize(2) #pragma GCC optimize(3) #pragma GCC optimize("Ofast") #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define lowbit(x) ((x) & -(x)) #define endl '\n' #define IOS1 ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr); #define IOS2 ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); typedef vector<int> vi; typedef vector<long long> vll; typedef vector<char> vc; typedef long long ll; template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; } template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) { return a / gcd(a, b) * b; } template<class T> T power(T a, int b) { T res = 1; for (; b; b >>= 1, a = a * a) { if (b & 1) { res = res * a; } } return res; } template <typename T> inline void read(T& x) { x = 0; int f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) { if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); } while (isdigit(ch)) { x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); } x *= f; } const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 1000000007; const double PI = acos(-1.0); const double eps = 1e-6; const int mode = 998244353; inline int sgn(double x) { return x < -eps ? -1 : x > eps; } void solve() { int n; cin >> n; vector<vector<int>> a(n + 5, vector<int> (10, 0)); a[0][0] = 1; for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++){ int x; cin >> x; for(int j = 0;j < 9;j++){ a[i][(j + x) % 9] = (a[i][(j + x) % 9] + a[i - 1][j]) % mode; a[i][j] = (a[i][j] + a[i - 1][j]) % mode; } } for(int i = 1;i < 9;i++){ cout << a[n][i] << " "; } cout << a[n][0] - 1 << endl; return; } int main() { IOS1; //IOS2; int __t = 1; // cin >> __t; for (int _t = 1; _t <= __t; _t++) { solve(); } return 0; } /* */B
通过B题学到了st表的打法,因为n和q最大都是2e5所以朴素算法肯定超时,而如果提前预处理出st表的话可以达到O(nlogn)的时间复杂度,根据题意,可知初试分数分成三类0,1,2,当初试分数%3=0的时候说明这时正好是3的倍数,所以下一局如果输了是不扣分的,根据倍增算法,st[k][i][j]算的是区间[i,i+(2^j)-1]这个区间内分数的变化量,那么当区间右端点大于n的时候,转移方程是:st[k][i][j] = st[k][i][j - 1],当右端点小于等于n的时候,
转移方程是st[k][i][j] = st[k][i][j - 1] + st[((k + st[k][i][j - 1]) % 3 + 3) % 3][i + 2^(j-1)][j - 1],其中k + st[k][i][j - 1]) % 3 + 3) % 3是在i处初试分数是k时对应的得分 然后%3后相对应的分数,查询的时候直接从左端点开始不断扩大空间,直到达到右端点
AC代码:
#pragma GCC optimize(2) #pragma GCC optimize(3) #pragma GCC optimize("Ofast") #include<bits/stdc++.h> // #include <iostream> // #include <cstdio> // #include <queue> // #include <deque> // #include <stack> // #include <string> // #include <cstring> // #include <numeric> // #include <functional> // #include <cstdlib> // #include <vector> // #include <set> // #include <map> // #include <algorithm> // #include <cmath> // #include <iomanip> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; #define lowbit(x) ((x) & -(x)) #define endl '\n' #define IOS1 ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr); #define IOS2 ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); typedef vector<int> vi; typedef vector<long long> vll; typedef vector<char> vc; typedef long long ll; // typedef long long i64; template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; } template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) { return a / gcd(a, b) * b; } template<class T> T power(T a, int b) { T res = 1; for (; b; b >>= 1, a = a * a) { if (b & 1) { res = res * a; } } return res; } template <typename T> T Myabs(T a) { return a >= 0 ? a : -a; } template <typename T> inline void read(T& x) { x = 0; int f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) { if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); } while (isdigit(ch)) { x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); } x *= f; } const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 1000000007; // const int mod = 998244353; const double PI = acos(-1.0); const double eps = 1e-6; inline int sgn(double x) { return x < -eps ? -1 : x > eps; } /* Tips: 1.int? long long? 2.don't submit wrong answer 3.figure out logic first, then start writing please 4.know about the range 5.check if you have to input t or not 6.modulo of negative numbers is not a%b, it is a%b + abs(b) */ int n, q; int st[3][200010][21]; char s[200010]; void solve() { scanf("%d %d", &n, &q); scanf("%s", s + 1); for (int j = 0; j <= 20; j++) { for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { if (j == 0) { if (s[i] == 'W') { st[0][i][j] = st[1][i][j] = st[2][i][j] = 1; } if (s[i] == 'L') { st[1][i][j] = st[2][i][j] = -1; st[0][i][j] = 0; } if (s[i] == 'D') { st[0][i][j] = st[1][i][j] = st[2][i][j] = 0; } } else { int p1 = i, p2 = i + (1 << (j - 1)); if (p2 > n) { st[0][p1][j] = st[0][p1][j - 1]; st[1][p1][j] = st[1][p1][j - 1]; st[2][p1][j] = st[2][p1][j - 1]; } else { st[0][p1][j] = st[0][p1][j - 1] + st[((0 + st[0][p1][j - 1]) % 3 + 3) % 3][p2][j - 1]; st[1][p1][j] = st[1][p1][j - 1] + st[((1 + st[1][p1][j - 1]) % 3 + 3) % 3][p2][j - 1]; st[2][p1][j] = st[2][p1][j - 1] + st[((2 + st[2][p1][j - 1]) % 3 + 3) % 3][p2][j - 1]; } } } } int l, r, ans; for (int i = 1; i <= q; i++) { scanf("%d %d %d", &l, &r, &ans); int pos = l; while (pos <= r) { int j = 0; while (pos + (1 << j) - 1 <= r) { j++; } j--; ans += st[ans % 3][pos][j]; pos += (1 << j); } cout << ans << endl; } return; } signed main() { IOS1; // IOS2; #ifdef ONLINE_JUDGE #else freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin); #endif int __t = 1; // cin >> __t; for (int _t = 1; _t <= __t; _t++) { solve(); } return 0; }C
C题需要先读懂题意,简化题目,题意大概就是涉及先写后读关系的语句之间必须再间隔至少三个语句才能顺利发生先写后读关系,而且i-j一定大于0时才会存在1的情况,这个就不用担心了
AC代码:
#pragma GCC optimize(2) #pragma GCC optimize(3) #include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <map> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <stack> #include <numeric> #include <iomanip> #define lowbit(x) ((x) & -(x)) using namespace std; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; int a[110]; void solve() { int n; cin >> n; a[0] = 1; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (i > 0) { a[i] = a[i - 1] + 1; } for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) { int x; cin >> x; if (x == 1) { a[i] = max(a[i], a[i - j] + 4); } } } cout << a[n - 1] - n << '\n'; return; } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); solve(); //int _t; //cin >> _t; //while (_t--) { // solve(); //} return 0; } /* */D
问题一的答案为2、2×3、2×3×5、2×3×5×7......这些前若干个素 数的积中,最大的且不超过n的那一个,如n=233,则答案为 2×3×5×7=210。
问题二的答案为[2,n]中最大的素数。
实现细节:对问题一,因为很少的一些素数前缀积就会超过 109 了, 因此预处理出前几十个素数即可,小心溢出问题;对问题二,从n 开始依次递减地暴力判断是否为素数即可,这是因为10^9以内最 大的两个素数间隔是282,所以这样做最多只要判断282个数字, 且判断时往往跑不满根号的复杂度
AC代码:
/* Tips: 1.int? long long? 2.don't submit wrong answer 3.figure out logic first, then start writing please 4.know about the range 5.check if you have to input t or not 6.modulo of negative numbers is not a%b, it is a%b + abs(b) */ #pragma GCC optimize(2) #pragma GCC optimize(3) #pragma GCC optimize("Ofast") #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define lowbit(x) ((x) & -(x)) #define endl '\n' #define IOS1 ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr); #define IOS2 ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); typedef vector<int> vi; typedef vector<long long> vll; typedef vector<char> vc; typedef long long ll; template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; } template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) { return a / gcd(a, b) * b; } template<class T> T power(T a, int b) { T res = 1; for (; b; b >>= 1, a = a * a) { if (b & 1) { res = res * a; } } return res; } template <typename T> inline void read(T& x) { x = 0; int f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) { if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); } while (isdigit(ch)) { x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); } x *= f; } const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 1000000007; const double PI = acos(-1.0); const double eps = 1e-6; inline int sgn(double x) { return x < -eps ? -1 : x > eps; } bool is_prime[210]; int prime[210], cnt; void init() { long long sum = 1; memset(is_prime, 1, sizeof(is_prime)); is_prime[0] = is_prime[1] = 0; for (int i = 2; i <= 100; i++) { if (is_prime[i]) { prime[++cnt] = i; sum *= i; for (int j = 2; j * i <= 100; j++) { is_prime[i * j] = 0; } } if (sum > 1000000000) { break; } } return; } void solve() { long long n, sum = 1; cin >> n; if (n == 1) { cout << "-1" << endl; return; } long long ans1, ans2; for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) { sum *= prime[i]; if (sum > n) { ans1 = sum / prime[i]; break; } } for (int i = n; i >= 2; i--) { bool ok = false; for (int j = 2; j * j <= i; j++) { if (i % j == 0) { ok = true; break; } } if (!ok) { ans2 = i; break; } } cout << ans1 << " " << ans2 << endl; return; } int main() { IOS1; //IOS2; init(); int __t = 1; cin >> __t; for (int _t = 1; _t <= __t; _t++) { solve(); } return 0; } /* */E
E题考虑多种情况,需要特判n==1和m==1,因为每次一定会有一个人必须占用一张校园卡来回接人,所以先把这个人除去,然后再算需要进出多少次,如果恰好整除就直接输出,否则最后一次肯定是不够m个人的情况,必须再进入一次
AC代码:
#pragma GCC optimize(2) #pragma GCC optimize(3) #include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <map> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <stack> #include <numeric> #include <iomanip> #define lowbit(x) ((x) & -(x)) using namespace std; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const long long inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 1000000007; void solve(){ int n, m; cin >> n >> m; long long ans = 0; if (m == 1 && n > 1) { cout << "-1" << endl; } else if (n == m) { cout << "1" << endl; } else { n--, m--; ans += 2 * (n / m); if (n % m == 0) { cout << ans << endl; } else { ans += 1; cout << ans << endl; } } return; } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); //solve(); int _t; cin >> _t; while (_t--) { solve(); } return 0; } /* */F
F
AC代码:
#pragma GCC optimize(2) #pragma GCC optimize(3) #include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <map> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <stack> #include <numeric> #include <iomanip> #define lowbit(x) ((x) & -(x)) using namespace std; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const long long inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 1000000007; int a[100010]; void solve() { int n, m; scanf("%d %d", &n, &m); int cnt1 = 0, cnt2 = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { scanf("%d", &a[i]); if (a[i] >= m) { cnt1++; } else { cnt2++; } } if (cnt1 - cnt2 <= 0) { cout << "-1\n"; } else { cout << cnt1 - cnt2 << '\n'; } return; } int main() { //ios::sync_with_stdio(0); //cin.tie(0); //solve(); int _t; cin >> _t; while (_t--) { solve(); } return 0; } /* */G
对于位置 𝑖 , 可以发现能够使得变换后 a𝑖 < min(a𝑖+1, a𝑖−1)的𝑏值一定是连续的一段(但可能会到正无穷,这种情况可以规定一个比较大的数代替正无穷),于是,我们对于每个𝑖,可以求出区间[𝑙𝑖 , 𝑟𝑖 ]表示若𝑏在这个区间里 取值就可以使得位置𝑖满足条件,这样问题其实就转变成了给出𝑛 − 2个区间,求被区间覆盖最多的点被覆盖的次数(令b取该点的值,则覆盖该点的区 间所对应的位置都可以取到最小值),然后对区间端点进行排序,找出重合最多的点重合的次数
AC代码:
#pragma GCC optimize(2) #pragma GCC optimize(3) #pragma GCC optimize("Ofast") #include<bits/stdc++.h> // #include <iostream> // #include <cstdio> // #include <queue> // #include <deque> // #include <stack> // #include <string> // #include <cstring> // #include <numeric> // #include <functional> // #include <cstdlib> // #include <vector> // #include <set> // #include <map> // #include <algorithm> // #include <cmath> // #include <iomanip> using i64 = long long; using namespace std; #define lowbit(x) ((x) & -(x)) #define endl '\n' #define IOS1 ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr); #define IOS2 ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); typedef vector<int> vi; typedef vector<long long> vll; typedef vector<char> vc; typedef long long ll; // typedef long long i64; template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; } template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) { return a / gcd(a, b) * b; } template<class T> T power(T a, int b) { T res = 1; for (; b; b >>= 1, a = a * a) { if (b & 1) { res = res * a; } } return res; } template <typename T> T Myabs(T a) { return a >= 0 ? a : -a; } template <typename T> inline void read(T& x) { x = 0; int f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) { if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); } while (isdigit(ch)) { x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); } x *= f; } const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // const int mod = 1000000007; const int mod = 998244353; const double PI = acos(-1.0); const double eps = 1e-6; inline int sgn(double x) { return x < -eps ? -1 : x > eps; } /* Tips: 1.int? long long? 2.don't submit wrong answer 3.figure out logic first, then start writing please 4.know about the range 5.check if you have to input t or not 6.modulo of negative numbers is not a%b, it is a%b + abs(b) */ void solve() { int n; cin >> n; vector<int> a(n); vector<pair<int, int>> e; for (int &x : a) { cin >> x; } int cur = 0; for (int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++) { int l = 0, r = 1e9 + 1; if (a[i] < a[i - 1]) { r = min(r, (a[i] + a[i - 1] - 1) / 2); } else if (a[i] > a[i - 1]) { l = max(l, (a[i] + a[i - 1] + 2) / 2); } else { r = l - 1; } if (a[i] < a[i + 1]) { r = min(r, (a[i] + a[i + 1] - 1) / 2); } else if (a[i] > a[i + 1]) { l = max(l, (a[i] + a[i + 1] + 2) / 2); } else { r = l - 1; } if (l <= r) { if (l == 0) { cur++; } else { e.emplace_back(l, -1); } if (r < 1e9 + 1) { e.emplace_back(r + 1, 1); } } } int ans = cur; sort(e.begin(), e.end()); for (auto [v, x] : e) { cur -= x; ans = min(ans, cur); } cout << ans << endl; return; } signed main() { IOS1; // IOS2; #ifdef ONLINE_JUDGE #else freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin); #endif int __t = 1; cin >> __t; for (int _t = 1; _t <= __t; _t++) { solve(); } return 0; } /* */H
根据题目数据,当数据量很大的时候肯定会出现很多重复的数字,根据式子展开,我们可以发现每个ai都会出现n+1次,然后根据组合,当ai==aj的时候会出现cnt*(cnt+1)/2个情况,当ai!=aj的时候会出现cnt[i]*cnt[j]种情况,因此时间复杂度最多就是1e6
AC代码:
#pragma GCC optimize(2) #pragma GCC optimize(3) #include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <map> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <stack> #include <numeric> #include <iomanip> #define lowbit(x) ((x) & -(x)) using namespace std; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const long long inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 1000000007; int cnt[1000010]; long long ans; void solve() { int n,a; cin >> n; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { cin >> a; cnt[a]++; ans += abs(a + a - 1000); } for (int i = 0; i <= 1000; i++) { for (int j = i; j <= 1000; j++) { if (i == j) { ans += 1ll * cnt[i] * (cnt[i] - 1) / 2 * abs(i + i - 1000); } else { ans += 1ll * cnt[i] * cnt[j] * abs(i + j - 1000); } } } cout << ans << '\n'; return; } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); solve(); //int _t; //cin >> _t; //while (_t--) { // solve(); //} return 0; } /* */I
假设第i个主播唱这一句的概率为pi,那么都唱的概率就是m*pi,都不唱的概率就是m*(1-pi),那么n个主播的失败的概率就是m*(
),不难想到当pi=
的时候乘积最小,相反成功的概率就是最大的,所以可以得出
,最后就是求
的逆元了
AC代码:
// #pragma GCC optimize(2) // #pragma GCC optimize(3) // #pragma GCC optimize("Ofast") // #include<bits/stdc++.h> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <queue> #include <deque> #include <stack> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <numeric> #include <functional> #include <cstdlib> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <map> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; // using i64 = long long; #define lowbit(x) ((x) & -(x)) #define endl '\n' #define IOS1 ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr); #define IOS2 ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); typedef vector<int> vi; typedef vector<long long> vll; typedef vector<char> vc; typedef long long ll; typedef long long i64; template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; } template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) { return a / gcd(a, b) * b; } template<class T> T power(T a, int b) { T res = 1; for (; b; b >>= 1, a = a * a) { if (b & 1) { res = res * a; } } return res; } template <typename T> T Myabs(T a) { return a >= 0 ? a : -a; } template <typename T> inline void read(T& x) { x = 0; int f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) { if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); } while (isdigit(ch)) { x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); } x *= f; } const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 1000000007; // const int mod = 998244353; const double PI = acos(-1.0); const double eps = 1e-6; inline int sgn(double x) { return x < -eps ? -1 : x > eps; } /* Tips: 1.int? long long? 2.don't submit wrong answer 3.figure out logic first, then start writing please 4.know about the range 5.check if you have to input t or not 6.modulo of negative numbers is not a%b, it is a%b + abs(b) */ i64 ksm(i64 a, i64 b) { i64 res = 1; for (; b; b >>= 1, a = a * a % mod) { if (b & 1) { res = res * a % mod; } } return res % mod; } void solve() { int n, m; cin >> n >> m; i64 p = ksm(2, n - 1); p = ksm(p, mod - 2); i64 ans; ans = 1ll * m * (1 + mod - p) % mod; cout << ans << endl; return; } signed main() { // IOS1; IOS2; #ifdef ONLINE_JUDGE #else freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin); #endif int __t = 1; cin >> __t; for (int _t = 1; _t <= __t; _t++) { solve(); } return 0; } /* */J
不断贪心就好了,肯定想到放进幸福度高的而且安静的小孩,如果要放进一个幸福度高的吵闹的小孩的话,他的周围肯定有两个安静的小孩,根据题意模拟模拟就好了
AC代码:
#pragma GCC optimize(2) #pragma GCC optimize(3) #include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <map> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <stack> #include <numeric> #include <iomanip> #define lowbit(x) ((x) & -(x)) using namespace std; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const long long inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 1000000007; int x[10010], y[10010]; bool cmp(int x, int y) { return x > y; } void solve() { int a, b, n; cin >> a >> b >> n; for (int i = 1; i <= a; i++) { cin >> x[i]; } for (int i = 1; i <= b; i++) { cin >> y[i]; } if (2 * a < n) { cout << "-1" << endl; } else { sort(x + 1, x + 1 + a, cmp); sort(y + 1, y + 1 + b, cmp); long long ans = 0; int cnt1 = n / 2, cnt2 = 0; int j = 1, i = 1; while (cnt2 < n) { if ((x[i] >= y[j] || cnt1 <= 0 || j > b) && (i <= a)) { cnt2++; ans += x[i]; i++; } else if ((cnt1 > 0 && y[j] > x[i]) || (cnt1 > 0 && i > a && j <= b)) { cnt1--; ans += y[j]; j++; cnt2++; } if (i > a && cnt2 < n && cnt1 <= 0) { cout << "-1" << endl; return; } } cout << ans << endl; } return; } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); //solve(); int _t; cin >> _t; while (_t--) { solve(); } return 0; } /* */K
K题是个比较复杂的DP题,dp[i][j][k][l]表示考虑到前𝑖个字符,当前结尾的三个字符(𝑖, 𝑖 − 1, 𝑖 − 2)分别放了𝑗, 𝑘, 𝑙( 𝑗, 𝑘, 𝑙 ∈ 0,1,2 )时最大的绿岛数; 状态转移:在求dp[i][j][k][l]的时候考虑所有形如dp[i-1][k][l][p]的状态,判断(k, l, p)是否满足𝑠[𝑖]的限制;然后可以分别枚举每一个的三种情况,定义G为0,R为1,B为2
通过这个表我们便可以确定转移方程dp[i][j][k][l]=max(dp[i][j][k][l],dp[i-1][k][l][p]+(j==0))其中i表示截止到第i个字符,j==0是判断在这个情况下的j按G算还是按R算还是按B算,同时还得保证dp[i-1][k][l][p]的存在性,否则这种转移是没有意义的,因此这就要求我们要提前预处理出前三个字符的所有情况,然后才能继续往下dp
AC代码:
#pragma GCC optimize(2) #pragma GCC optimize(3) #pragma GCC optimize("Ofast") #include<bits/stdc++.h> // #include <iostream> // #include <cstdio> // #include <queue> // #include <deque> // #include <stack> // #include <string> // #include <cstring> // #include <numeric> // #include <functional> // #include <cstdlib> // #include <vector> // #include <set> // #include <map> // #include <algorithm> // #include <cmath> // #include <iomanip> using i64 = long long; using namespace std; #define lowbit(x) ((x) & -(x)) #define endl '\n' #define IOS1 ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr); #define IOS2 ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); typedef vector<int> vi; typedef vector<long long> vll; typedef vector<char> vc; typedef long long ll; // typedef long long i64; template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; } template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) { return a / gcd(a, b) * b; } template<class T> T power(T a, int b) { T res = 1; for (; b; b >>= 1, a = a * a) { if (b & 1) { res = res * a; } } return res; } template <typename T> T Myabs(T a) { return a >= 0 ? a : -a; } template <typename T> inline void read(T& x) { x = 0; int f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) { if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); } while (isdigit(ch)) { x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); } x *= f; } const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; // const int mod = 1000000007; const int mod = 998244353; const double PI = acos(-1.0); const double eps = 1e-6; inline int sgn(double x) { return x < -eps ? -1 : x > eps; } /* Tips: 1.int? long long? 2.don't submit wrong answer 3.figure out logic first, then start writing please 4.know about the range 5.check if you have to input t or not 6.modulo of negative numbers is not a%b, it is a%b + abs(b) */ int dp[100010][3][3][3]; void solve() { int n; cin >> n; string s; cin >> s; s = '.' + s; memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp)); for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) { int g = !i + !j + !k, r = (i == 1) + (j == 1) + (k == 1); if (g > r && s[3] == 'G') { dp[3][i][j][k] = g; } if (g < r && s[3] == 'R') { dp[3][i][j][k] = g; } if (g == r && s[3] == 'B') { dp[3][i][j][k] = g; } } } } for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {//i for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) {//i-1 for (int l = 0; l < 3; l++) {//i-2 for (int p = 0; p < 3; p++) {//i-3 if (dp[i - 1][k][l][p] == -1) { continue; } int g = !j + !k + !l, r = (j == 1) + (k == 1) + (l == 1); if (g > r && s[i] == 'G') { dp[i][j][k][l] = max(dp[i][j][k][l], dp[i - 1][k][l][p] + (j == 0)); } if (g < r && s[i] == 'R') { dp[i][j][k][l] = max(dp[i][j][k][l], dp[i - 1][k][l][p] + (j == 0)); } if (g == r && s[i] == 'B') { dp[i][j][k][l] = max(dp[i][j][k][l], dp[i - 1][k][l][p] + (j == 0)); } } } } } } int ans = -1; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) { if (dp[n][i][j][k] == -1) { continue; } ans = max(ans, dp[n][i][j][k]); } } } cout << (ans == -1 ? -1 : ans) << endl; return; } signed main() { IOS1; // IOS2; #ifdef ONLINE_JUDGE #else freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin); #endif int __t = 1; // cin >> __t; for (int _t = 1; _t <= __t; _t++) { solve(); } return 0; } /* */L
签到题,初中数学
AC代码:
#pragma GCC optimize(2) #pragma GCC optimize(3) #include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <map> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <stack> #include <numeric> #include <iomanip> #define lowbit(x) ((x) & -(x)) using namespace std; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const long long inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 1000000007; void solve(){ int n; string s; cin >> n >> s; int x = 0, y = 0; double ans1, ans = 0.0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (s[i] == 'U') { y++; } else if (s[i] == 'D') { y--; } else if (s[i] == 'R') { x++; } else { x--; } ans1 = sqrt((x * x) + (y * y)); ans = max(ans1, ans); } cout << fixed << setprecision(12) << ans << endl; return; } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); //solve(); int _t; cin >> _t; while (_t--) { solve(); } return 0; } /* */
2022牛客寒假算法基础集训营1(12/12)
于 2022-02-15 13:47:58 首次发布















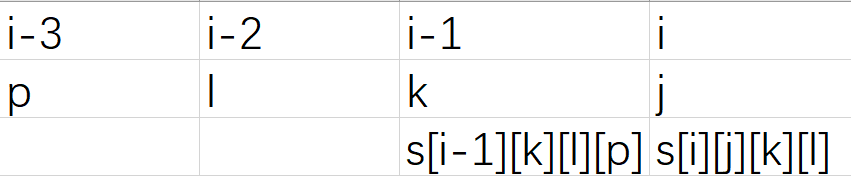














 3956
3956











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








