上篇博文关于快速报错fail-fast想说的之fail-fast的实现原理(一) 讨论了fail-fast的基本知识及实现原理,了解了ArrayList的fail-fast在多线程工作下的缺陷,这篇博文说下解决办法,主要是讨论CopyOnWriteArrayList的用法。
注意,本文讨论的内容基于JDK 1.8
示例代码(一)
1. 代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
//这里使用了COW技术
String string = "a b c d e";
List<String> stringList1 = Arrays.asList(string.split(" "));
List<String> stringList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>(stringList1);
System.out.println(stringList);
Iterator<String> iterator = stringList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
if(iterator.next().equals("c")) {
stringList.remove("c");
//会抛 不支持的操作异常 "UnsupportedOperationException"
//iterator.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(stringList);
}2.执行结果

3.解析
这个的代码实现,跟上篇文章的区别只有一句:
List<String> stringList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>(stringList1);可以看到使用接口技术的优点了吧。
所谓CopyOnWrite(即COW)技术,是指:在执行写操作时,会重新复制一份数据,而不是使用加锁等同步机制。
我们来看看CopyOnWriteArrayList的相关实现。
//CopyOnWriteArrayList的iterator实现
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new COWIterator<E>(getArray(), 0);
}看下CopyOnWriteArrayList的内部类COWIterator:
static final class COWIterator<E> implements ListIterator<E> {
/** Snapshot(快照) of the array */
private final Object[] snapshot;
/** Index of element to be returned by subsequent call to next. */
private int cursor;
private COWIterator(Object[] elements, int initialCursor) {
cursor = initialCursor;
snapshot = elements;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor < snapshot.length;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
if (! hasNext())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return (E) snapshot[cursor++];
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public void set(E e) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public void add(E e) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}从上面源码可以看到,在调用CopyOnWriteArrayList#iterator时会将当前list内容的引用和当前下标传递给COWIterator的构造方法,使之有一个list内容的快照,注意这个private final Object[] snapshot; 是一个final的,所以不能再被修改,因此该迭代器不支持remove、set、add等操作。
CopyOnWriteArrayList#next方法仅仅判断了一下hasNext,没有任何其他判断,然后就返回了当前下标的数据。
再看看CopyOnWriteArrayList的remove()方法。
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If this list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* {@code i} such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>
* (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
Object[] snapshot = getArray();
int index = indexOf(o, snapshot, 0, snapshot.length);
return (index < 0) ? false : remove(o, snapshot, index);
}
/**
* A version of remove(Object) using the strong hint that given
* recent snapshot contains o at the given index.
*/
private boolean remove(Object o, Object[] snapshot, int index) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
Object[] current = getArray();
int len = current.length;
if (snapshot != current) findIndex: {
int prefix = Math.min(index, len);
for (int i = 0; i < prefix; i++) {
if (current[i] != snapshot[i] && eq(o, current[i])) {
index = i;
break findIndex;
}
}
if (index >= len)
return false;
if (current[index] == o)
break findIndex;
index = indexOf(o, current, index, len);
if (index < 0)
return false;
}
Object[] newElements = new Object[len - 1];
System.arraycopy(current, 0, newElements, 0, index);
System.arraycopy(current, index + 1,
newElements, index,
len - index - 1);
setArray(newElements);
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Sets the array.
*/
final void setArray(Object[] a) {
array = a;
}
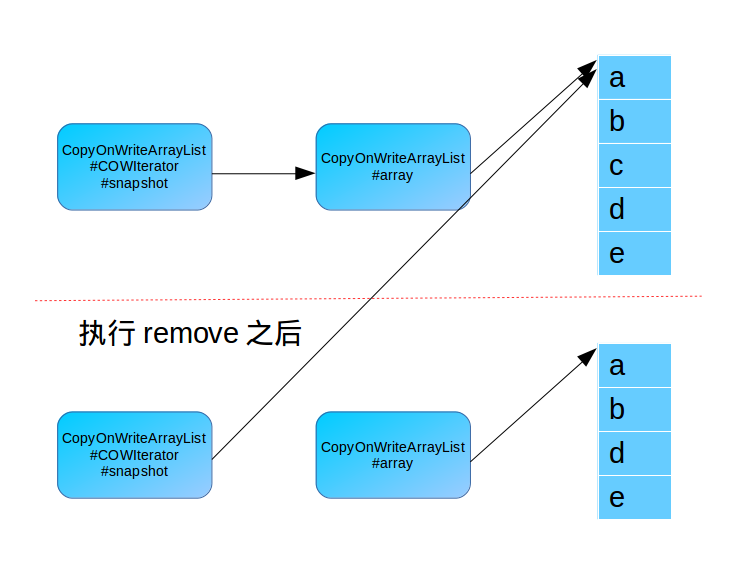
首先得到数组的快照,找到要删除元素的位置,如果没找到直接返回false,否则执行删除操作。
new出一个比原来少一个元素的数组,先将current的[0, index)的元素(共index个数据)复制到新数组中,然后再将current的[index+1, len)的元素(共len-index-1个数据)复制到新数组中。最后修改指针。
这个时候迭代器中的snapshot指向的还是原来的内存数据,而list中的array已经指向了新的内存数据。
其内存模型如下所示:
对于这个
//会抛 不支持的操作异常 "UnsupportedOperationException"
//iterator.remove();上文也解释了为什么。
示例代码(二)
public static void main(String[] args) {
//这里使用了COW技术
String string = "a b c d e";
List<String> stringList1 = Arrays.asList(string.split(" "));
List<String> stringList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>(stringList1);
System.out.println(stringList);
Iterator<String> iterator = stringList.iterator();
stringList.remove("c");
System.out.println(stringList);
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println("iterator: " + iterator.next());
}
System.out.println(stringList);
}上面代码的输出为:
[a, b, c, d, e]
[a, b, d, e]
iterator: a
iterator: b
iterator: c
iterator: d
iterator: e
[a, b, d, e]
可以看到,即使stringList中remove了“c”,在迭代器中也能访问到c。
这也很正常,因为迭代器在前,remove在后。
示例代码(三)
1.代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("1", "A");
map.put("2", "B");
map.put("3", "C");
System.out.println(map);
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getKey().equals("1")) {
//抛并发修改异常 ConcurrentModificationException
map.remove(entry.getKey());
//抛并发修改异常 ConcurrentModificationException
//map.put("4", "D");
//以下两句正常
//entry.setValue("123");
//map.put(entry.getKey(), "123");
}
}
}2.执行结果
(1)map.remove(entry.getKey());的执行结果:
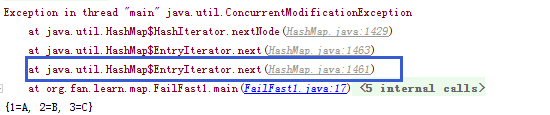
(2)map.put(“4”, “D”);的执行结果:
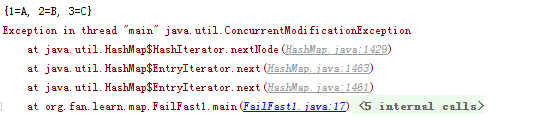
(3)entry.setValue(“123”); 与 map.put(entry.getKey(), “123”); 的执行结果:
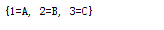
3.解析
remove、put新KV操作都属于对map进行结构性修改的操作。
setValue、put修改已有key的value不属于结构性修改。
结束语
本文讨论了CopyOnWriteArrayList关于避免fail-fast的方法。CopyOnWriteArrayList是线程安全的。
然后又举了一个HashMap关于fail-fast的例子。
参考资料
1.关于快速报错fail-fast想说的之fail-fast的实现原理(一)
2. 《Thinking in java》
3. Java中Iterator的fast-fail分析
4. Java提高篇(三四)—–fail-fast机制






















 3684
3684

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








