引言
String类的format()方法用于创建格式化的字符串以及连接多个字符串对象。熟悉C语言应该记得C语言的sprintf()方法,两者有类似之处。format()方法有两种重载形式。
重载
// 使用当前本地区域对象(Locale.getDefault()),制定字符串格式和参数生成格式化的字符串
String String.format(String fmt, Object... args);
// 自定义本地区域对象,制定字符串格式和参数生成格式化的字符串
String String.format(Locale locale, String fmt, Object... args);占位符
格式化说明最多会有5个部分(不包括%符号) . 下面的[]符号里面都是选择性的项目,因此只有%与type是必要的. 格式化说明的顺序是有规定的,必须要以这个顺序章指定.


超过一项以上的参数时
把新的参数加到后面,因此会有3个参数来调用format()而不是两个,并且在第一个参数中,也就是格式化串中,会有两个不同的格式化设定,也就是两个%开头的字符组合,第二个会应用在第一个%上面,第三个参数会用在第二%上,也就是参数会依照顺序应用在%上面" 。
int one = 123456789;
double two = 123456.789;
String s = String.format("第一个参数:%,d 第二个参数:%,.2f", one, two);
System.out.println(s); 
转换符
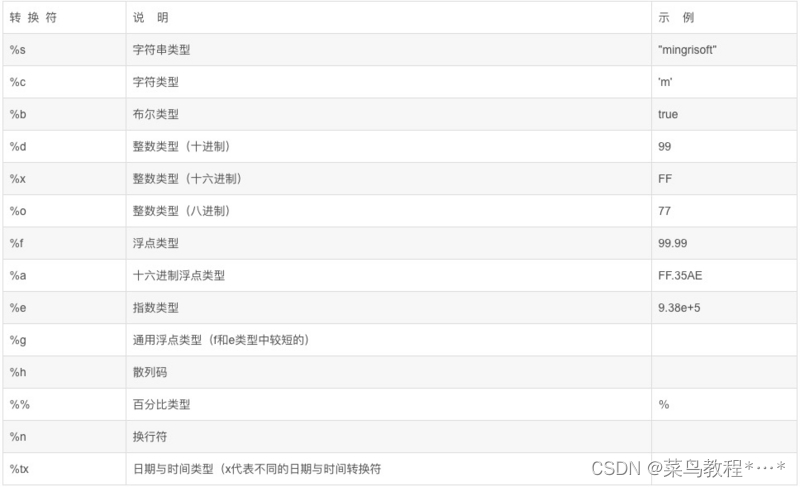
转换符的标志

对字符串进行格式化
示例——将"hello"格式化为"hello "(左对齐)
String raw = "hello word";
String str = String.format("|%-15s|", raw);
System.out.println(str);
对整数进行格式化
示例——将-1000显示为(1,000)
int num = -1000;
String str = String.format("%(,d", num);
System.out.println(str);
对浮点数进行格式化
double num = 123.456789;
System.out.print(String.format("浮点类型:%.2f %n", num));
System.out.print(String.format("十六进制浮点类型:%a %n", num));
System.out.print(String.format("通用浮点类型:%g ", num));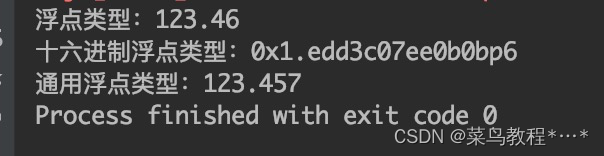
对日期时间进行格式化
- 日期的转换符
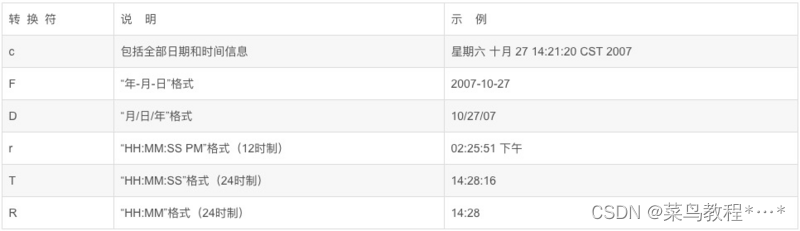
- 时间的转换符

- 实例 Date date = new Date(); System.out.printf("全部日期和时间信息:%tc%n",date); System.out.printf("年-月-日格式:%tF%n",date); System.out.printf("月/日/年格式:%tD%n",date); System.out.printf("HH:MM:SS PM格式(12时制):%tr%n",date); System.out.printf("HH:MM:SS格式(24时制):%tT%n",date); System.out.printf("HH:MM格式(24时制):%tR",date);
























 4451
4451

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








