1. 梯度下降(Gradient Descent)
1.1. What’s Gradient
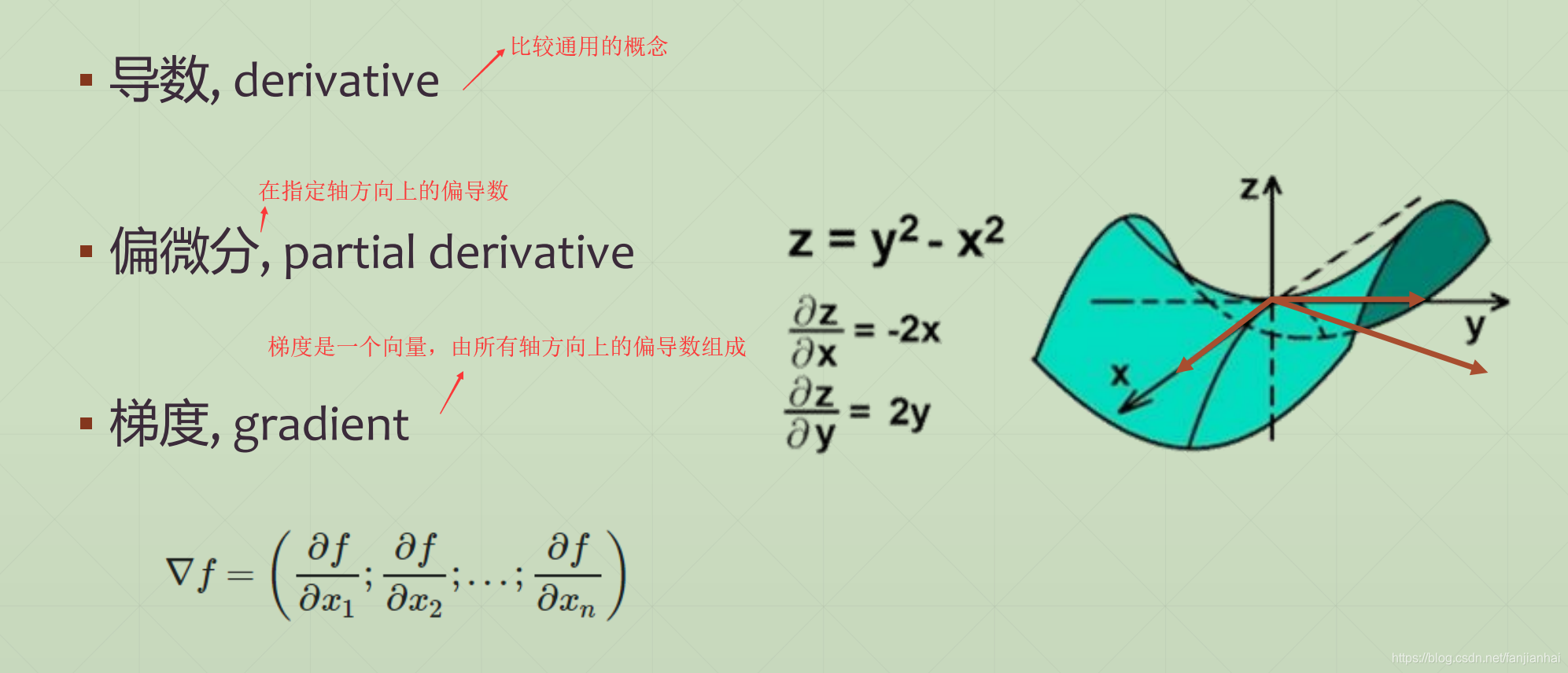
1.2. What does it mean
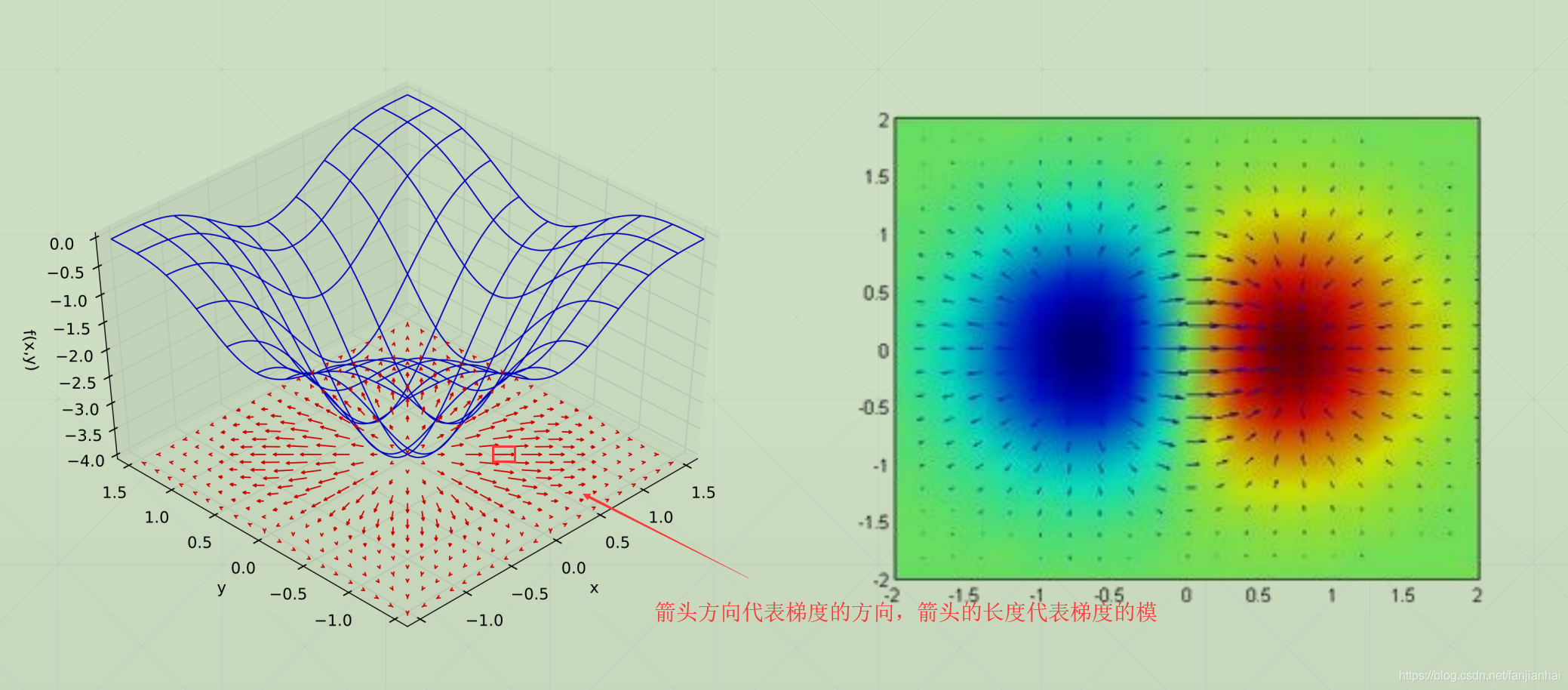
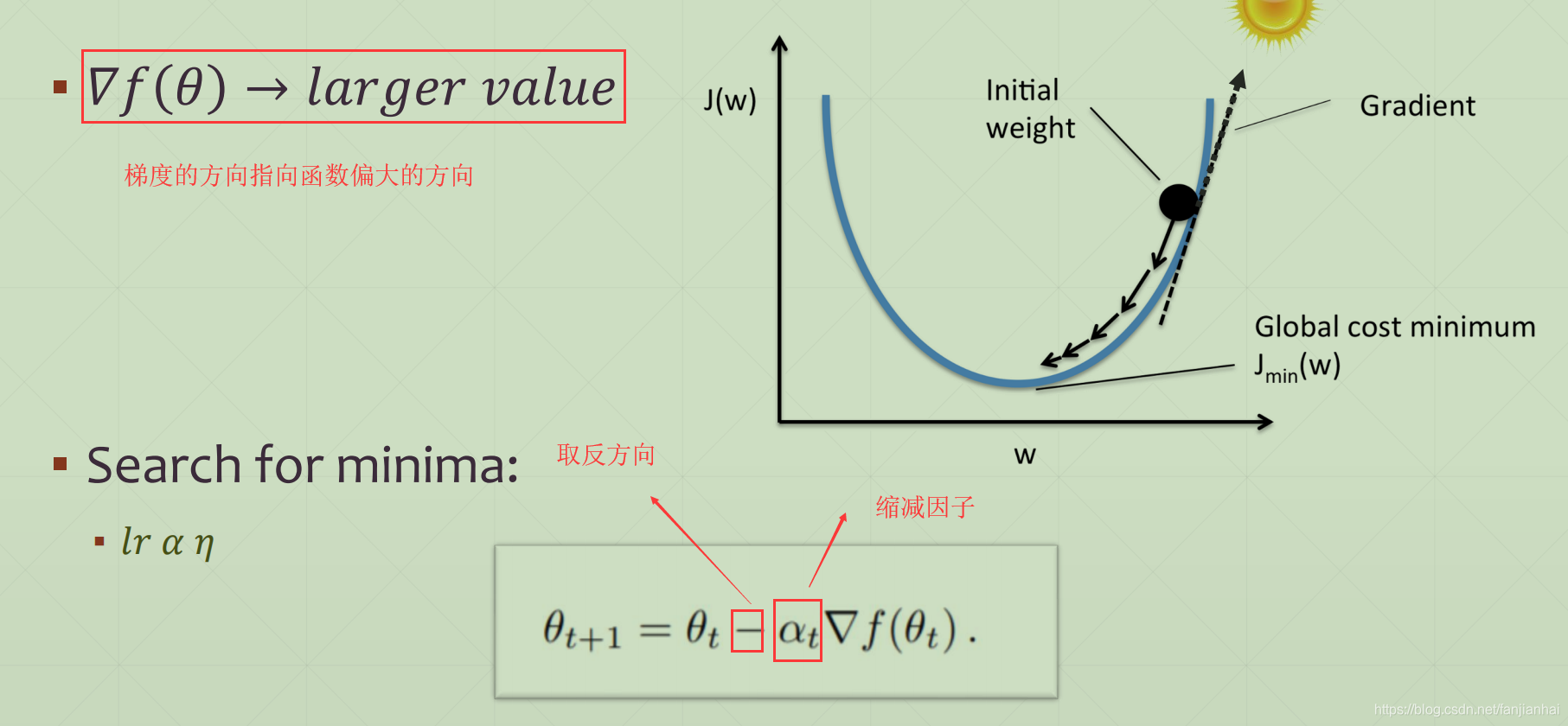
1.3. How to Search
1.4. AutoGrad
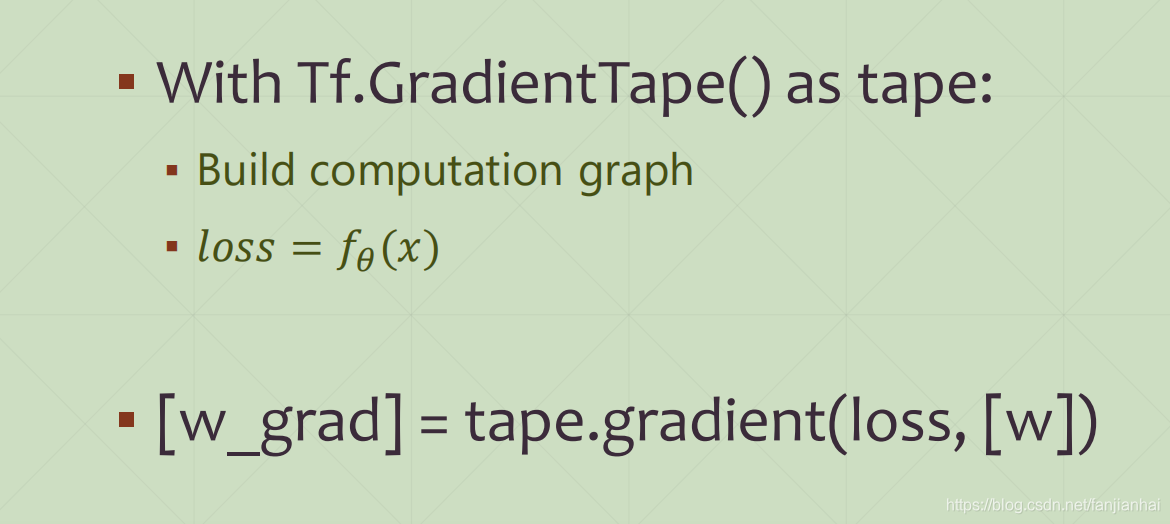
-
GradientTape
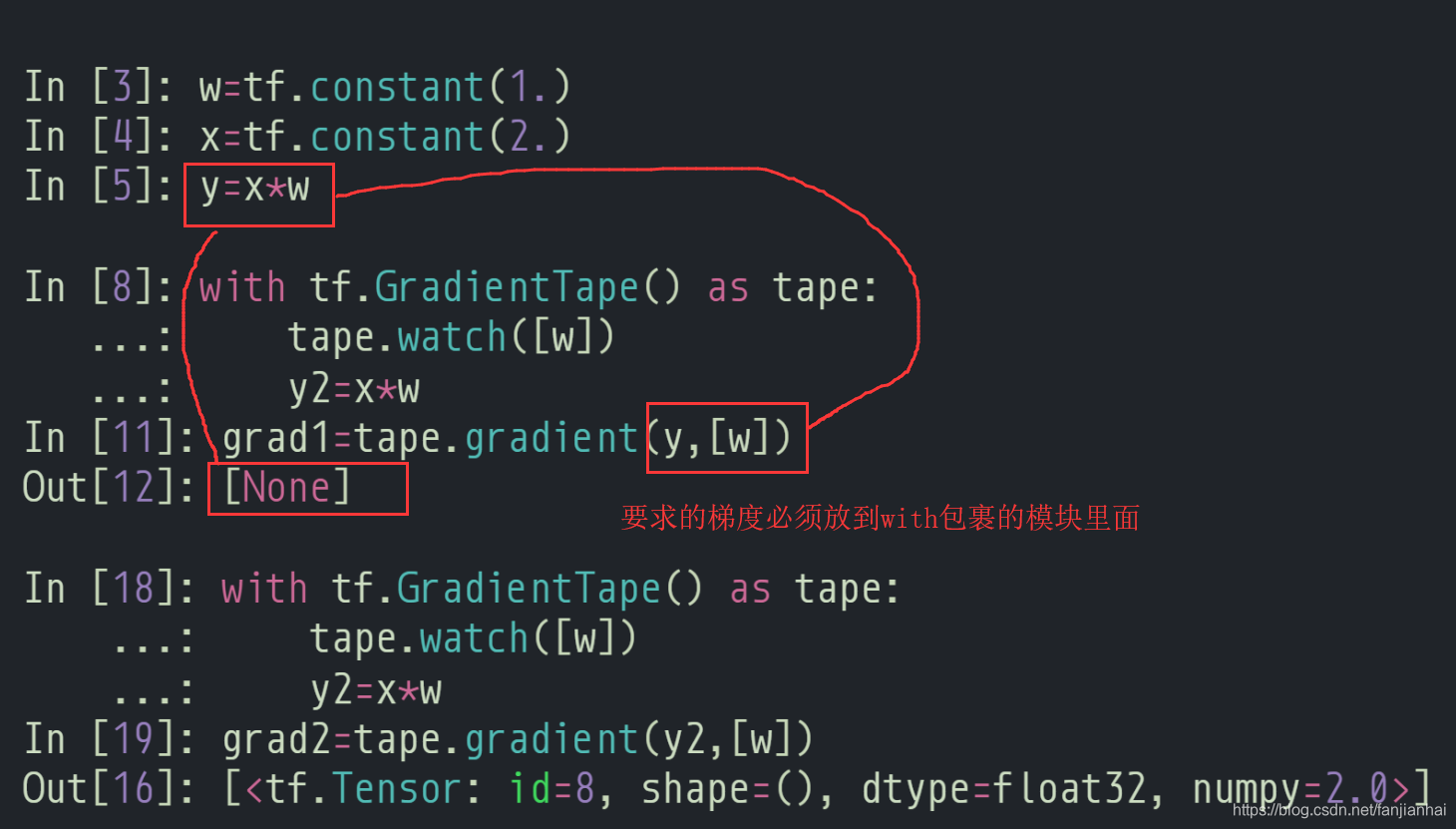
-
Persistent GradientTape
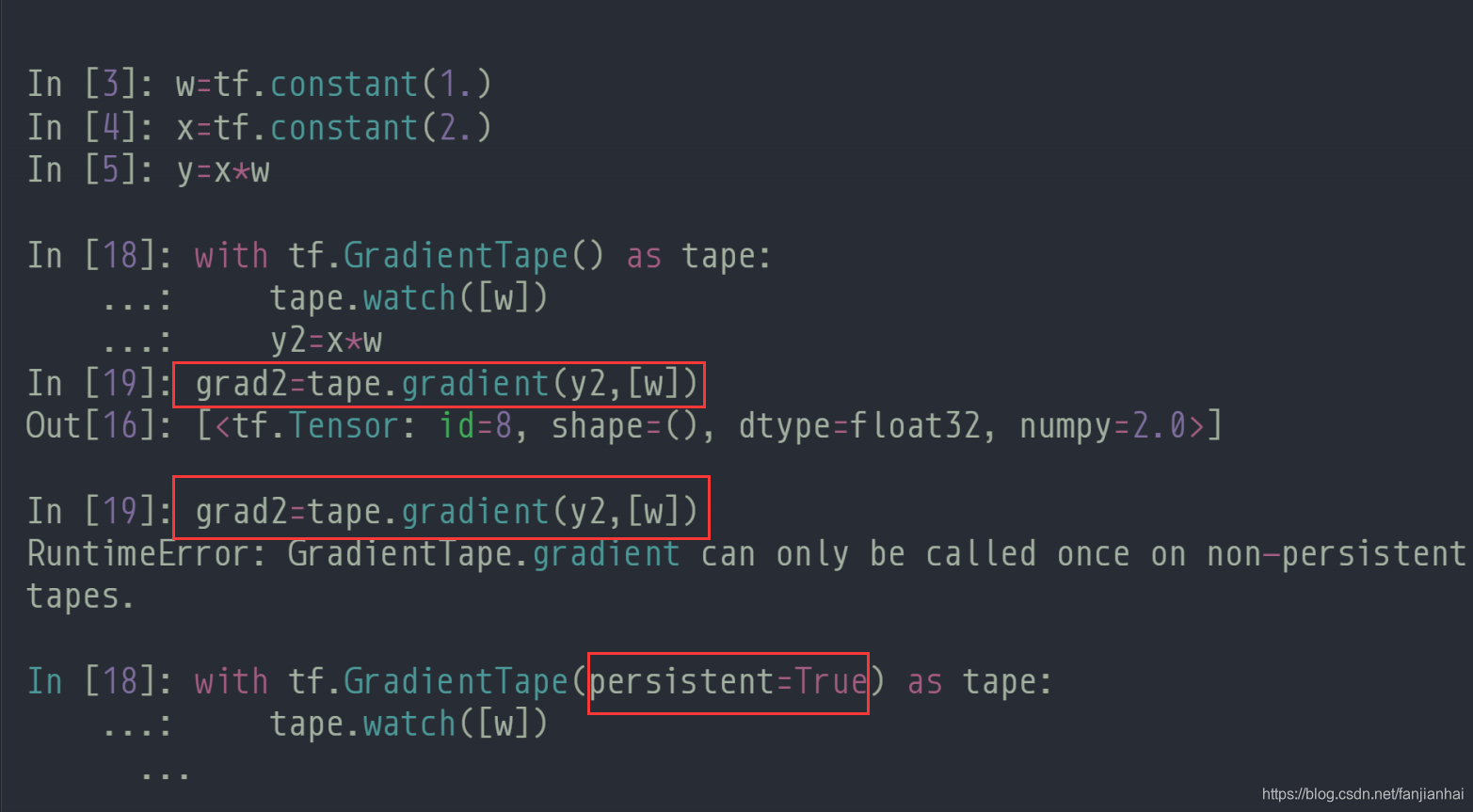
-
2nd-order
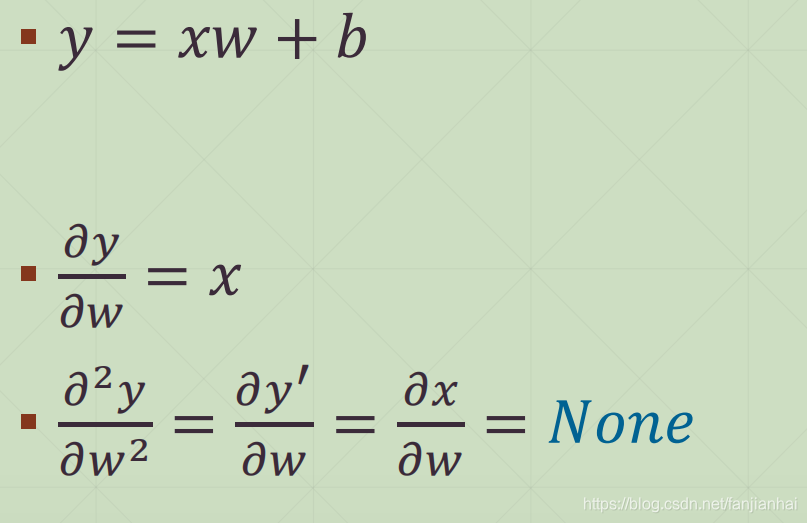
import tensorflow as tf
w = tf.Variable(1.)
b = tf.Variable(2.)
x = tf.Variable(3.)
with tf.GradientTape() as t1:
with tf.GradientTape() as t2:
y = x * w + b
dy_dw, dy_db = t2.gradient(y, [w, b])
d2y_dw2 = t1.gradient(dy_dw, w)
print(dy_dw, dy_db, d2y_dw2)
assert dy_dw.numpy() == 3.0
assert d2y_dw2 is None
2. 激活函数及其梯度
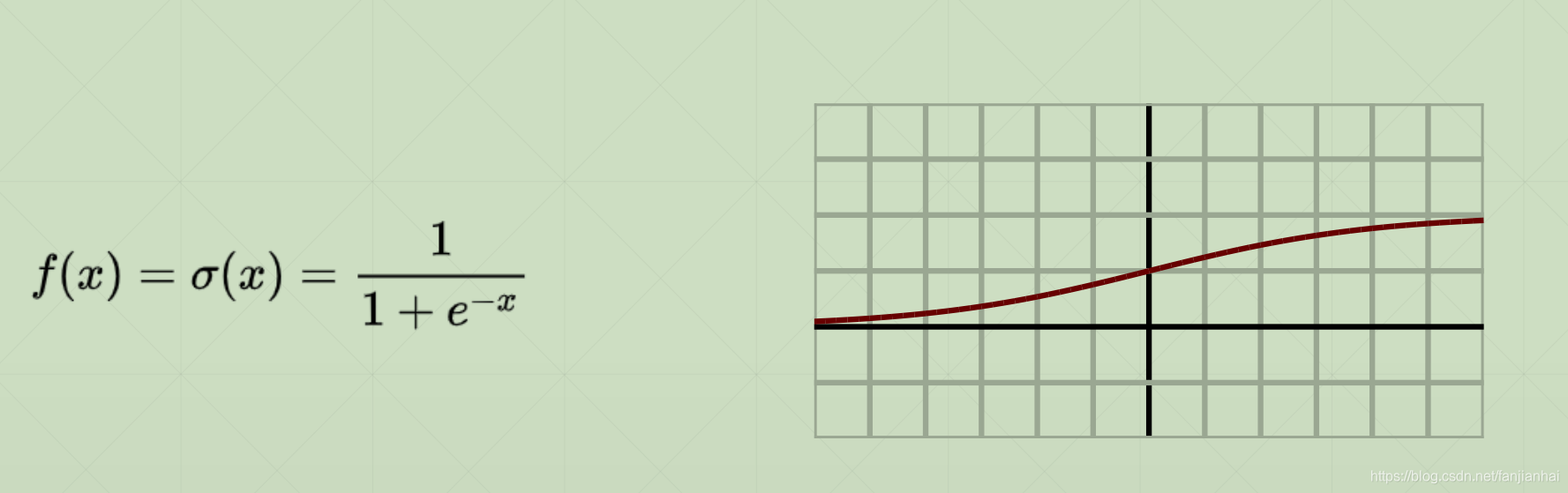
2.1. Sigmoid / Logistic(0~1)
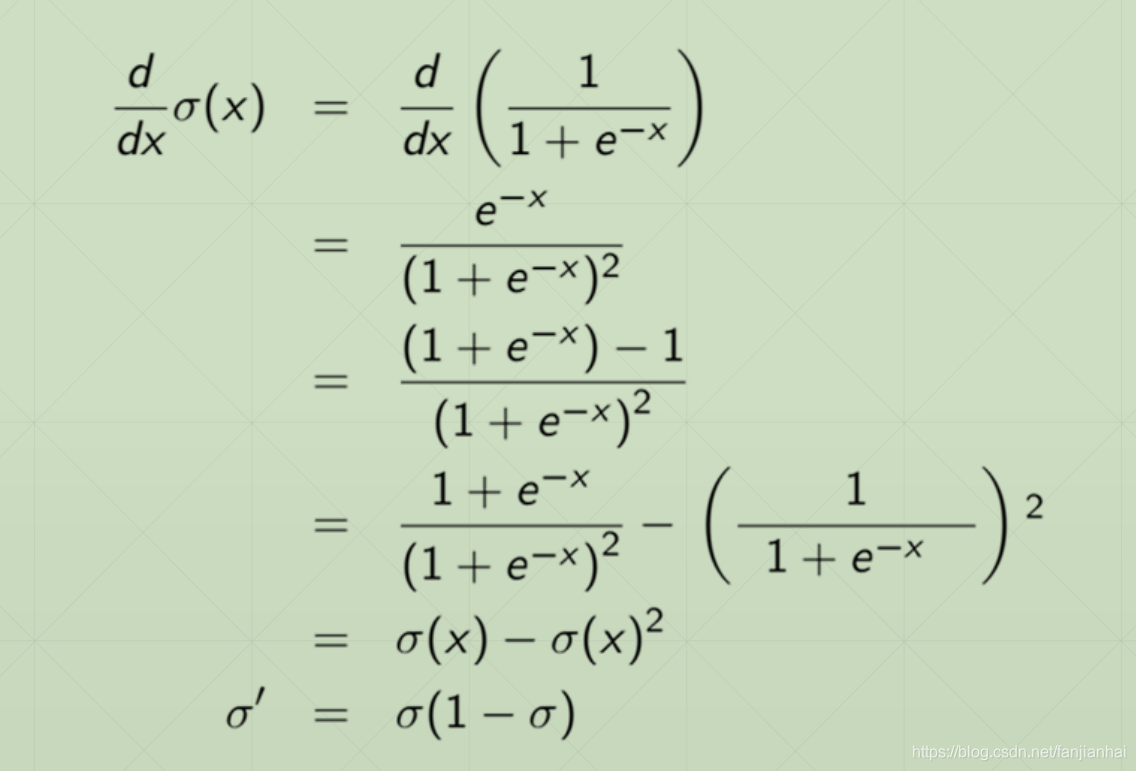
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.linspace(-10., 10., 10)
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch(a)
y = tf.sigmoid(a)
grads = tape.gradient(y, [a])
print(a)
print(y)
print(grads)
2.2. tanh(-1~1)
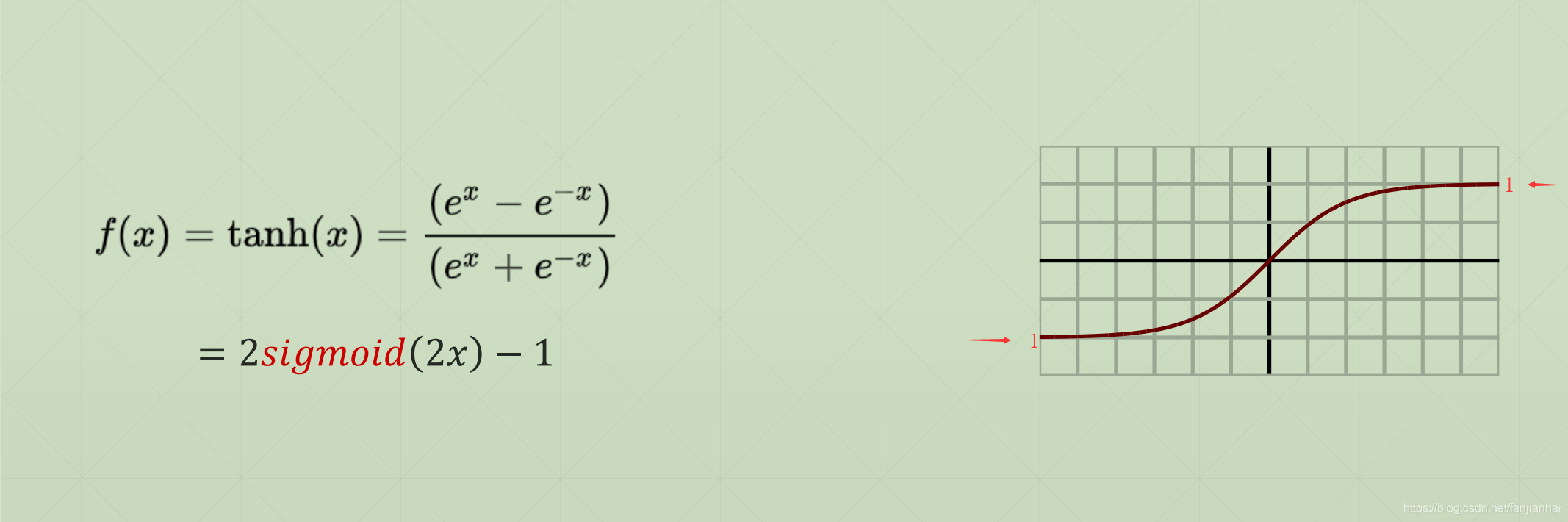
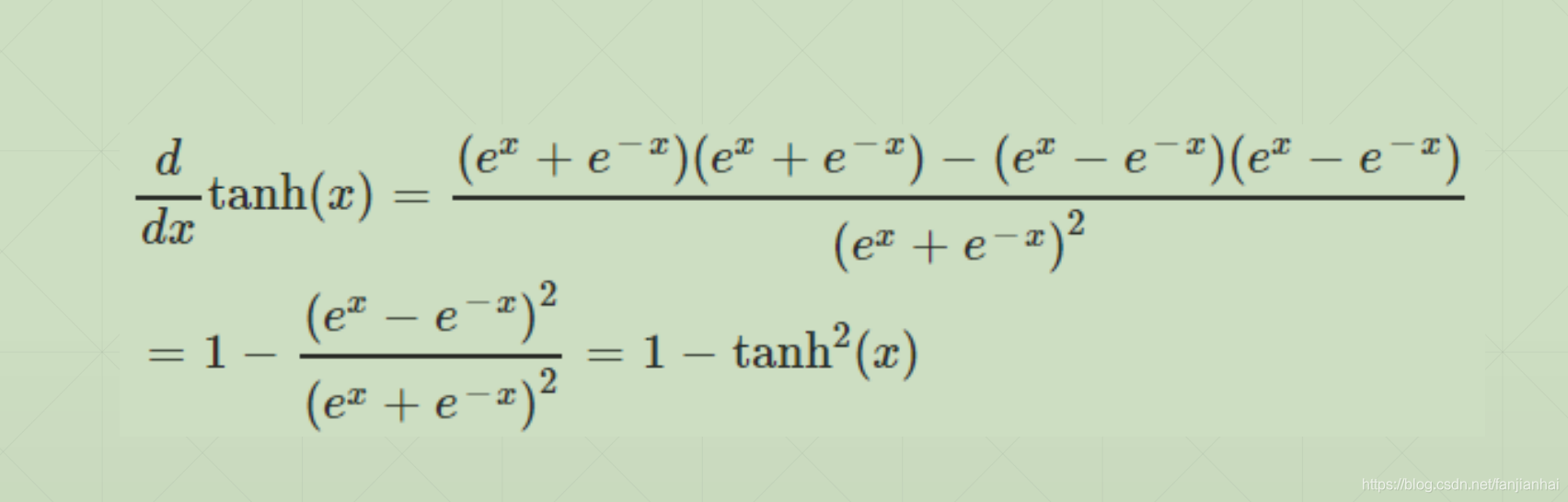
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.linspace(-5., 5., 10)
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch(a)
y = tf.tanh(a)
grads = tape.gradient(y, [a])
print(a)
print(y)
print(grads)
2.3. relu(Rectified Linear Unit)
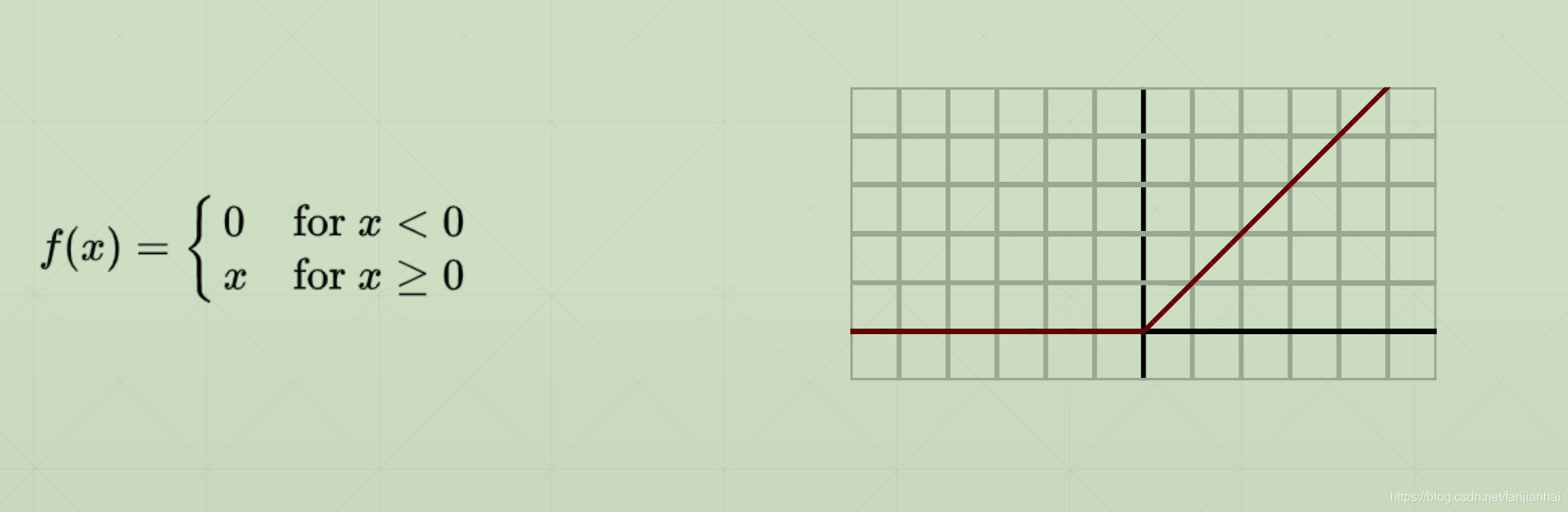
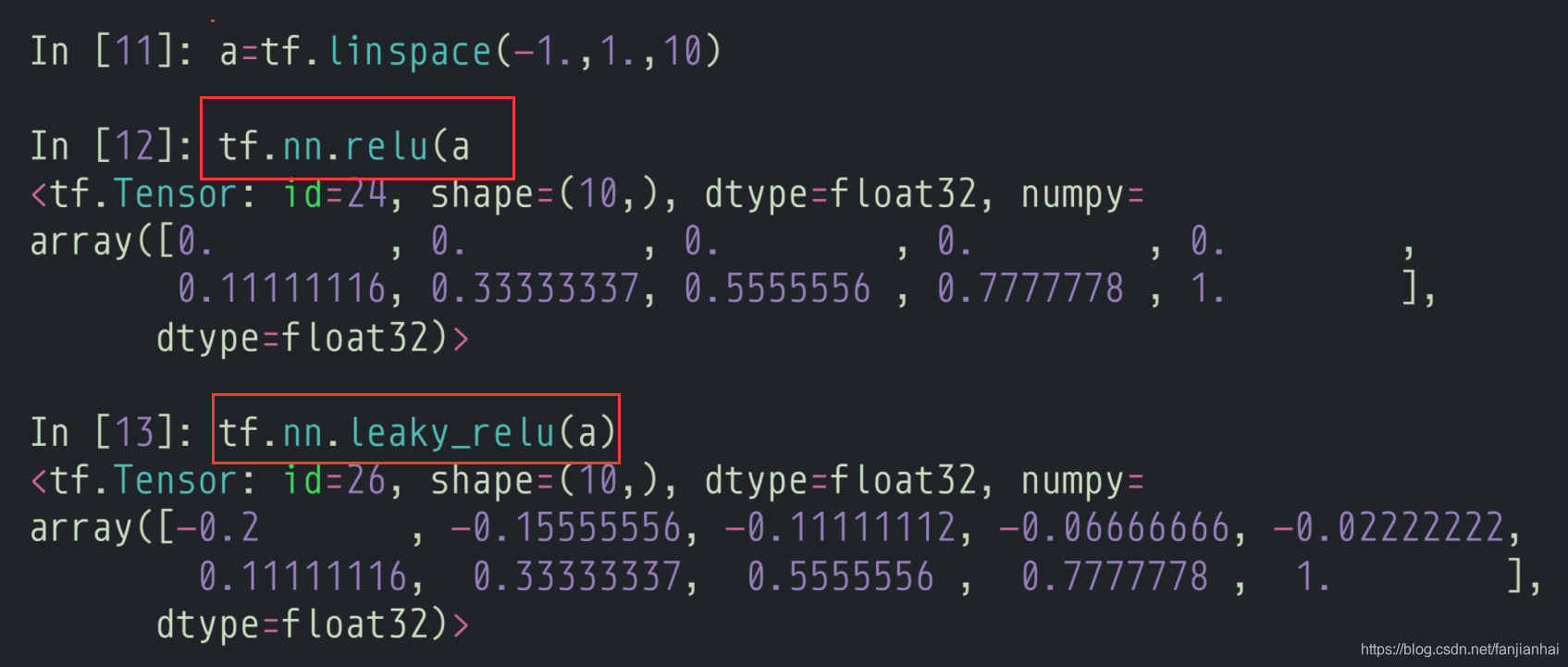
3. 损失函数及其梯度
3.1. Mean Squared Error
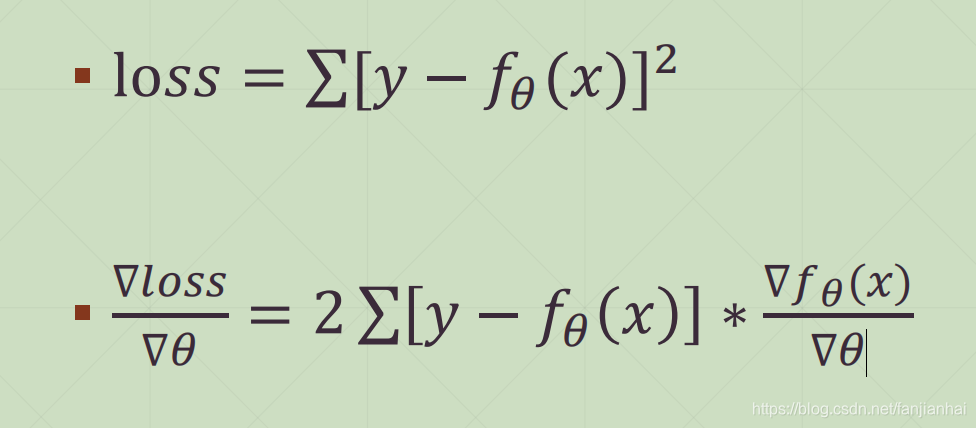
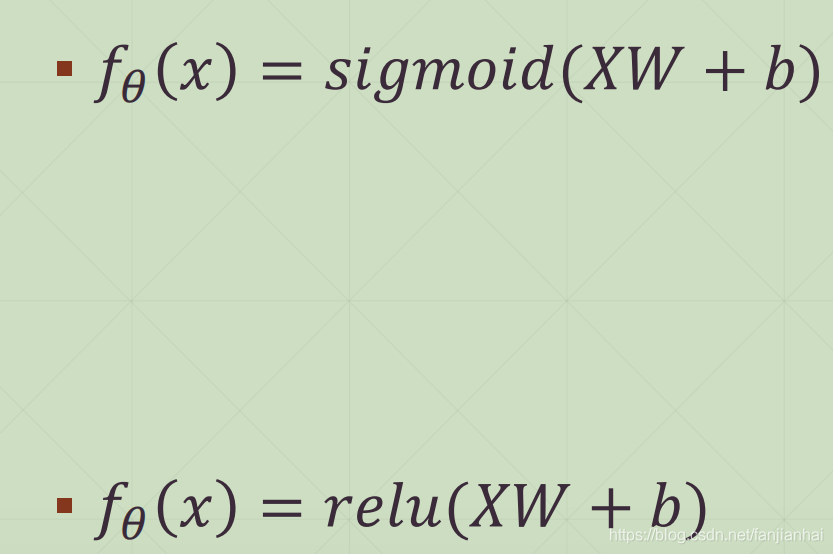
- MSE Gradient
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.random.normal([2, 4])
w = tf.random.normal([4, 3])
b = tf.zeros([3])
y = tf.constant([2, 0])
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch([w, b]) # 注意: 这里如果不写watch,则w, b必须定义成tf.Variable类型
prob = tf.nn.softmax(x@w+b, axis=1)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.losses.MSE(tf.one_hot(y, depth=3), prob))
grads = tape.gradient(loss, [w, b])
print(grads[0])
print(grads[1])
3.2. Cross Entropy Loss
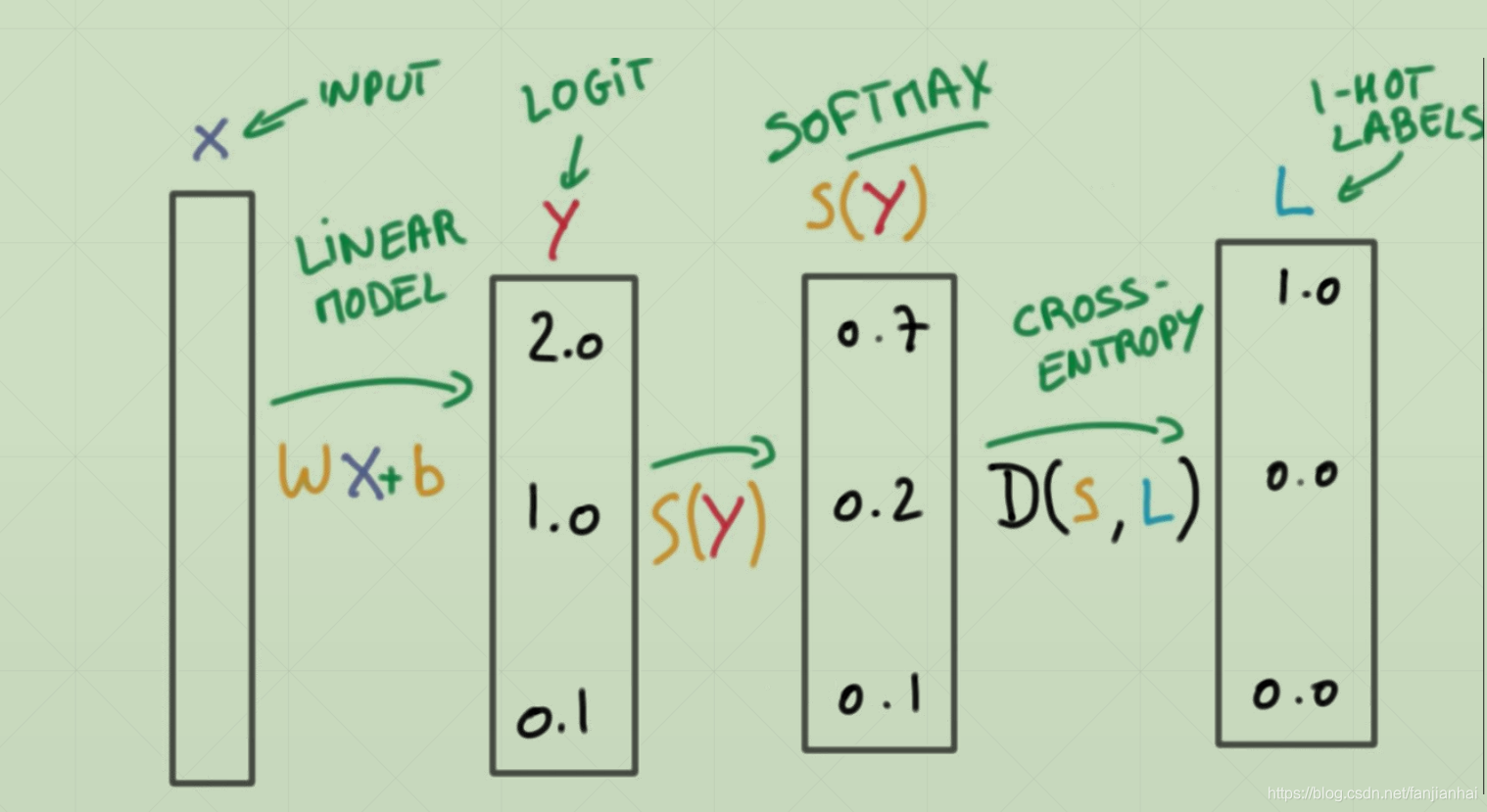
- softmax函数的作用
- 把logit的值映射到0~1之间, 并且使得概率之后为1
- 使强的更强,弱的更弱

- Crossentropy gradient
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.random.normal([2, 4])
w = tf.random.normal([4, 3])
b = tf.zeros([3])
y = tf.constant([2, 0])
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch([w, b]) # 注意: 这里如果不写watch,则w, b必须定义成tf.Variable类型
logits = x@w+b
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.losses.categorical_crossentropy(tf.one_hot(y, depth=3), logits, from_logits=True))
grads = tape.gradient(loss, [w, b])
print(grads[0])
print(grads[1])
4. Himmelblau函数优化
4.1. Himmelblau function
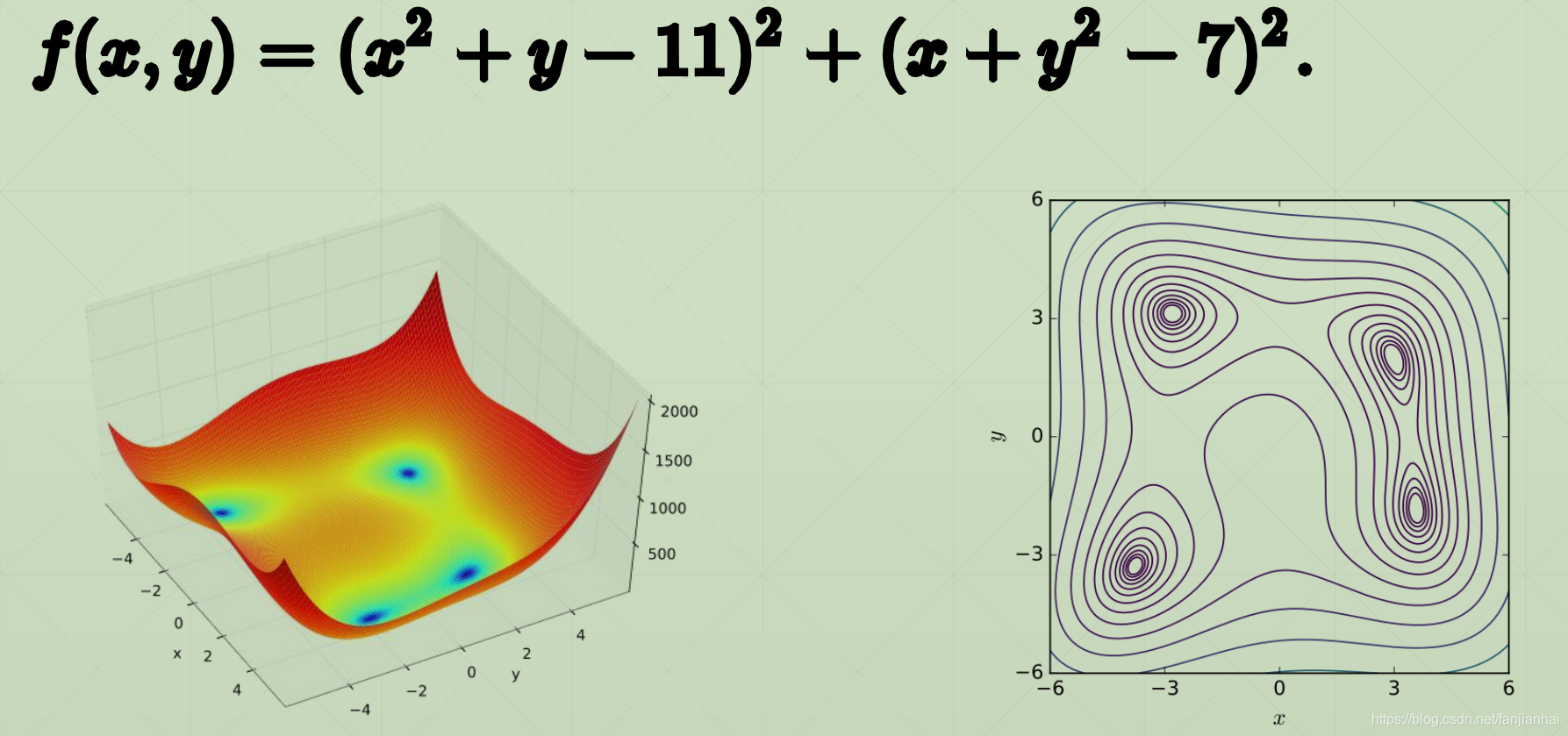
4.2. Minima
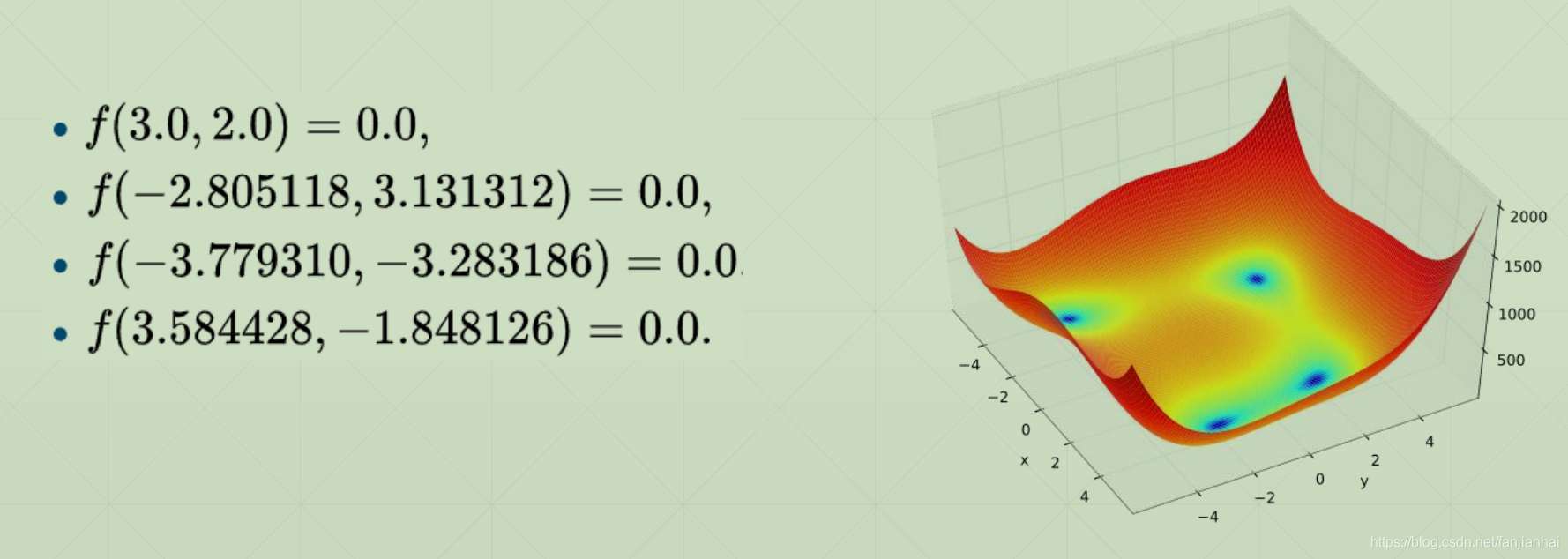
4.3. Gradient Descent
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def himmelblau(x):
return (x[0] ** 2 + x[1] - 11) ** 2 + (x[0] + x[1] ** 2 - 7)
x = np.arange(-6, 6, 0.1)
y = np.arange(-6, 6, 0.1)
print('x, y range:', x.shape, y.shape)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
print('X, Y maps: ', X.shape, Y.shape)
Z = himmelblau([X, Y])
fig = plt.figure('himmelblau')
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z)
ax.view_init(60, -30)
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y')
plt.show()
# [1., 0.], [-4, 0.], [4, 0.]
x = tf.constant([-4, 0.])
for step in range(200):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch([x])
y = himmelblau(x)
grads = tape.gradient(y, [x])[0]
x -= 0.01 *grads
if step % 20 == 0:
print('step {}: x = {}, f(x) = {}'
.format(step, x.numpy(), y.numpy()))
5. FashionMNIST实战
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import datasets, Sequential, layers, optimizers
def pre_process(x, y):
# 在预处理之间, 数据类型已经从numpy类型转换成tensor类型
x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.int32)
return x, y
(x, y), (x_test, y_test) = datasets.fashion_mnist.load_data()
print(x.shape, y.shape, type(x), type(y), x.dtype, y.dtype)
db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x, y))
db = db.map(pre_process).shuffle(10000).batch(128)
db_test = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test, y_test))
db_test = db_test.map(pre_process).batch(128) # 测试集不需要打散
# db_iter = iter(db)
# sample = next(db_iter)
# print("batch: ", sample[0].shape, sample[1].shape)
# 构建模型
model = Sequential([
layers.Dense(256, activation=tf.nn.relu), # [b, 784] ==> [b, 256]
layers.Dense(128, activation=tf.nn.relu), # [b, 256] ==> [b, 128]
layers.Dense(64, activation=tf.nn.relu), # [b, 128] ==> [b, 64]
layers.Dense(32, activation=tf.nn.relu), # [b, 64] ==> [b, 32]
layers.Dense(10, activation=tf.nn.relu), # [b, 32] ==> [b, 10]
])
model.build(input_shape=[None, 28*28])
model.summary()
# 优化器
optimizer = optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=1e-3)
def main():
for epoch in range(30):
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(db):
# x: [b, 28, 28] => [b, 784]
# y: [b]
# 对矩阵进行变换
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28 * 28])
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# [b, 784] => [b, 10]
logits = model(x)
# 对真实值进行onehot编码
y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10)
# 均方误差
loss_mse = tf.reduce_mean(tf.losses.MSE(y_onehot, logits))
# 交叉熵损失
loss_ec = tf.reduce_mean(tf.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_onehot, logits, from_logits=True))
grads = tape.gradient(loss_ec, model.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.trainable_variables))
if step % 100 == 0:
print(epoch, step, 'loss: ', float(loss_ec), float(loss_mse))
# test
total_correct = 0
total_num = 0
for x, y in db_test:
# x:[b, 28, 28] => [b, 784]
# y:[b]
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28*28])
# [b, 10]
logits = model(x)
# logits => prob, [b, 10]
prob = tf.nn.softmax(logits, axis=1)
# [b, 10] => [b], int64
pred = tf.argmax(prob, axis=1)
pred = tf.cast(pred, dtype=tf.int32)
correct = tf.equal(pred, y)
correct = tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(correct, dtype=tf.int32))
total_correct += int(correct)
total_num += x.shape[0]
acc = total_correct / total_num
print(epoch, 'test acc:', acc)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
pass
6. Tensorboard可视化
6.1. 工作原理
- Listen logdir
- build summary instance
- fed data into summary instance
6.2. Step1.run listener
6.2. Step2.build summary
6.3. Step3.fed data
- scalar
- single Image

!
- multi image

6.4. Code
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import datasets, layers, optimizers, Sequential, metrics
import datetime
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import io
def preprocess(x, y):
x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.int32)
return x, y
def plot_to_image(figure):
"""Converts the matplotlib plot specified by 'figure' to a PNG image and
returns it. The supplied figure is closed and inaccessible after this call."""
# Save the plot to a PNG in memory.
buf = io.BytesIO()
plt.savefig(buf, format='png')
# Closing the figure prevents it from being displayed directly inside
# the notebook.
plt.close(figure)
buf.seek(0)
# Convert PNG buffer to TF image
image = tf.image.decode_png(buf.getvalue(), channels=4)
# Add the batch dimension
image = tf.expand_dims(image, 0)
return image
def image_grid(images):
"""Return a 5x5 grid of the MNIST images as a matplotlib figure."""
# Create a figure to contain the plot.
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
for i in range(25):
# Start next subplot.
plt.subplot(5, 5, i + 1, title='name')
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.grid(False)
plt.imshow(images[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary)
return figure
batchsz = 128
(x, y), (x_val, y_val) = datasets.mnist.load_data()
print('datasets:', x.shape, y.shape, x.min(), x.max())
db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x, y))
db = db.map(preprocess).shuffle(60000).batch(batchsz).repeat(10)
ds_val = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_val, y_val))
ds_val = ds_val.map(preprocess).batch(batchsz, drop_remainder=True)
network = Sequential([layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(32, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(10)])
network.build(input_shape=(None, 28 * 28))
network.summary()
optimizer = optimizers.Adam(lr=0.01)
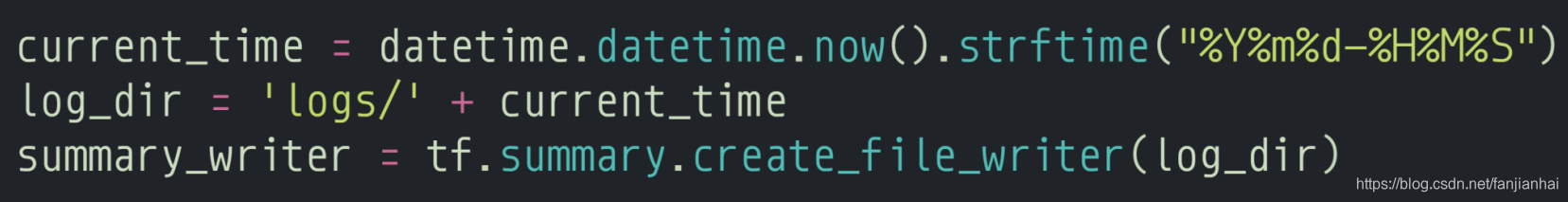
current_time = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S")
log_dir = 'logs/' + current_time
summary_writer = tf.summary.create_file_writer(log_dir)
# get x from (x,y)
sample_img = next(iter(db))[0]
# get first image instance
sample_img = sample_img[0]
sample_img = tf.reshape(sample_img, [1, 28, 28, 1])
with summary_writer.as_default():
tf.summary.image("Training sample:", sample_img, step=0)
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(db):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# [b, 28, 28] => [b, 784]
x = tf.reshape(x, (-1, 28 * 28))
# [b, 784] => [b, 10]
out = network(x)
# [b] => [b, 10]
y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10)
# [b]
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_onehot, out, from_logits=True))
grads = tape.gradient(loss, network.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, network.trainable_variables))
if step % 100 == 0:
print(step, 'loss:', float(loss))
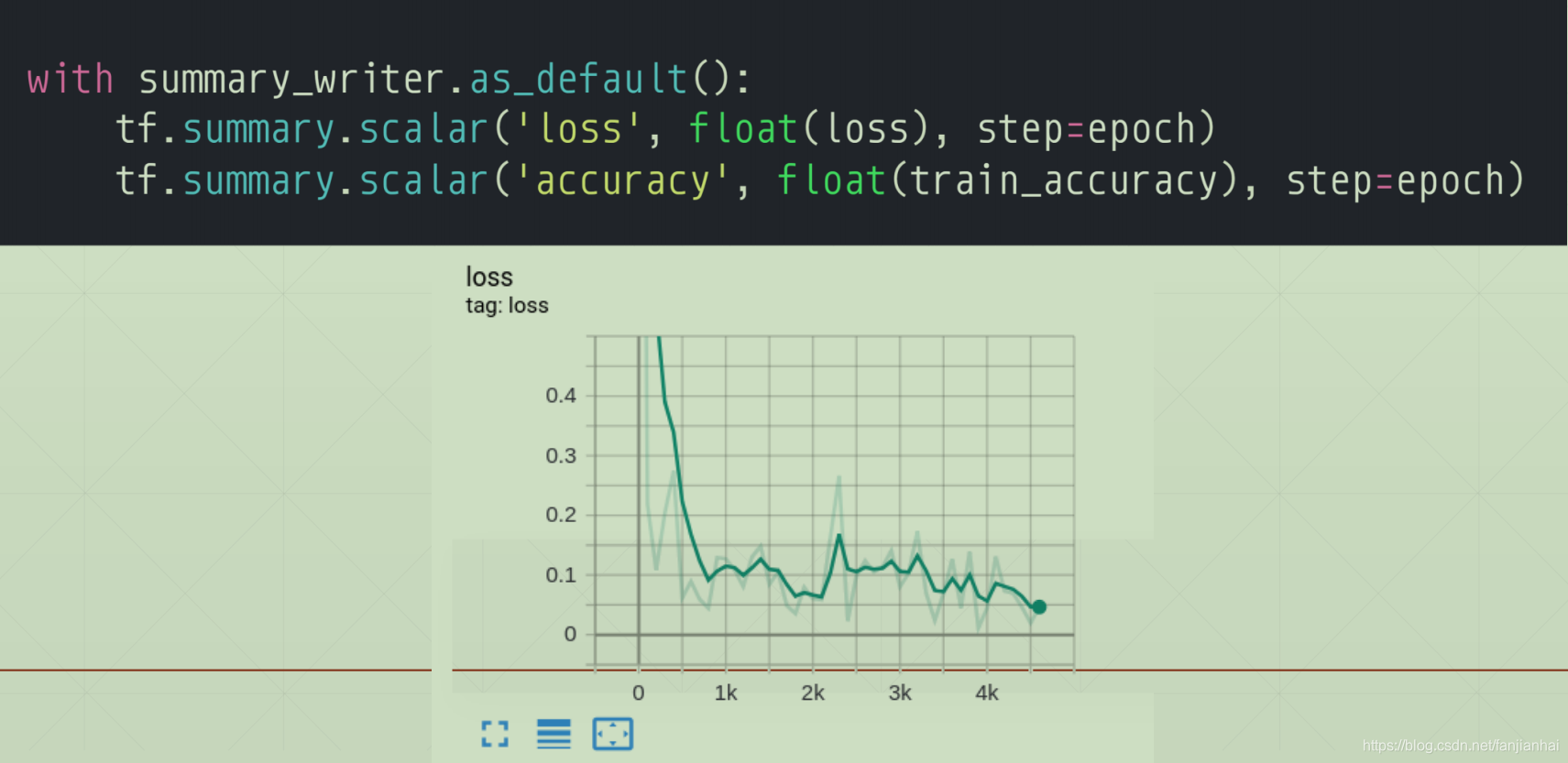
with summary_writer.as_default():
tf.summary.scalar('train-loss', float(loss), step=step)
# evaluate
if step % 500 == 0:
total, total_correct = 0., 0
for _, (x, y) in enumerate(ds_val):
# [b, 28, 28] => [b, 784]
x = tf.reshape(x, (-1, 28 * 28))
# [b, 784] => [b, 10]
out = network(x)
# [b, 10] => [b]
pred = tf.argmax(out, axis=1)
pred = tf.cast(pred, dtype=tf.int32)
# bool type
correct = tf.equal(pred, y)
# bool tensor => int tensor => numpy
total_correct += tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(correct, dtype=tf.int32)).numpy()
total += x.shape[0]
print(step, 'Evaluate Acc:', total_correct / total)
# print(x.shape)
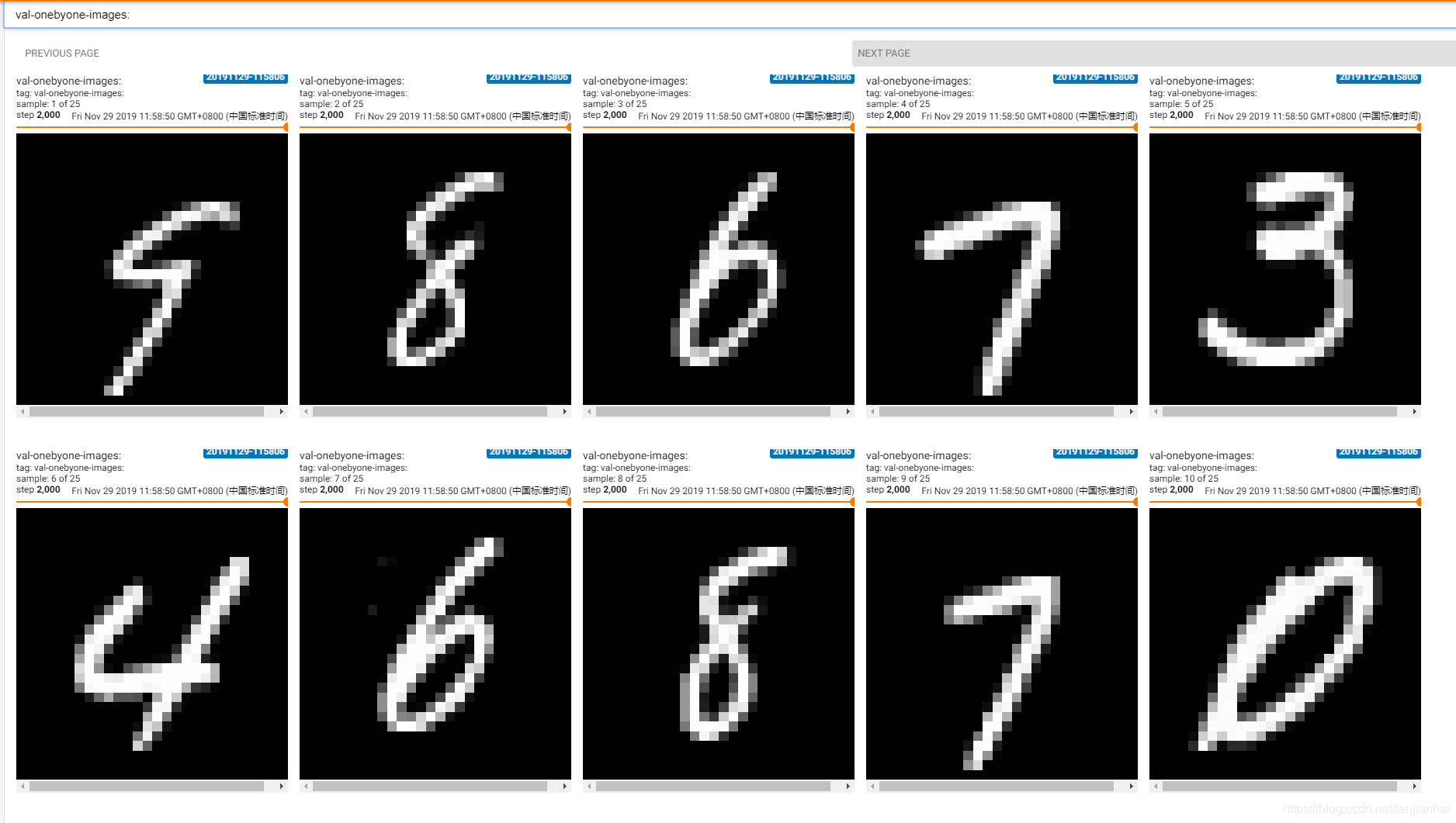
val_images = x[:25]
val_images = tf.reshape(val_images, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
with summary_writer.as_default():
tf.summary.scalar('test-acc', float(total_correct / total), step=step)
tf.summary.image("val-onebyone-images:", val_images, max_outputs=25, step=step)
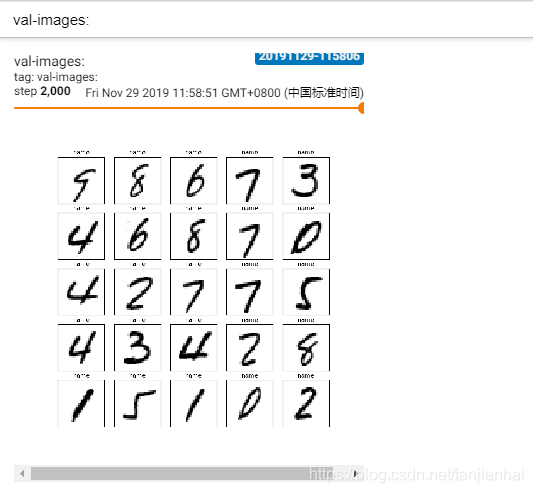
val_images = tf.reshape(val_images, [-1, 28, 28])
figure = image_grid(val_images)
tf.summary.image('val-images:', plot_to_image(figure), step=step)
7. 需要全套课程视频+PPT+代码资源可以私聊我
- 方式1:
CSDN私信我! - 方式2:
QQ邮箱:594042358@qq.com或者直接加我QQ:594042358!





















 160
160











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








