Android布局实验
布局定义用户界面的视觉结构,如Activity或应用小部件的 UI。您可以通过两种方式声明布局:
- 在 XML 中声明 UI 元素。Android 提供了对应于 View 类及其子类的简明 XML 词汇,如用于小部件和布局的词汇;
- 运行时实例化布局元素。您的应用可以通过编程创建 View 对象和 ViewGroup 对象(并操纵其属性)。
Android 框架让您可以灵活地使用以下一种或两种方法来声明和管理应用的 UI。例如,您可以在 XML 中声明应用的默认布局,包括将出现在布局中的屏幕元素及其属性。然后,您可以在应用中添加可在运行时修改屏幕对象(包括那些已在 XML 中声明的对象)状态的代码。
在 XML 中声明 UI 的优点在于,您可以更好地将应用的外观与控制应用行为的代码隔离。您的 UI 描述位于应用代码外部,这意味着您在修改或调整描述时无需修改您的源代码并重新编译。例如,您可以创建适用于不同屏幕方向、不同设备屏幕尺寸和不同语言的 XML 布局。此外,在 XML 中声明布局还能更轻松地显示 UI 的结构,从而简化问题调试过程。因此,本文将侧重于示范如何在 XML 中声明布局。如果您对在运行时实例化 View 对象感兴趣,请参阅 ViewGroup 类和 View 类的参考资料。下面来简单介绍LInearLayout,RelativeLayout,TableLayout布局
1.LinearLayout布局(线性布局)
LinearLayout是一个试图组,用于使所有自试图在单个方向(垂直或水平)保持对齐,可以使用android:orientation属性来指定布局方向
这里需要注意的是LinearLayout中子控件或子布局的属性设置,如果LinearLayout的排列方向是horizontal,内部的控件就绝对不能将宽度指定为match_parent,因为这样的话的单独一个控件就会将整个水平方向占满,其他的控件就没有可放置的位置了。同样的道理,如果LinearLayout的排列方向是vertical,内部的控件就不能将高度指定为match_parent。想对子控件的位置更好的控制,LinearLayout也支持子视图的权重划分android:layout_weight以及android:layout_gravity属性。
- android:layout_weight: 此属性根据视图应在屏幕上占据的控件量向视图分配“重要性的值”,值越大,所占的屏幕空间越大。子视图指定权重值后,系统会按照子视图声明的权重值的比例,将视图组中的剩余空间分配给子视图。默认权重为0。举个例子,如果是在水平的LinearLayout中有三个子空间,他们的权重都为1时,每个空间的width的长度为整个屏幕宽度的三分之一,如果第三个空间的权重为2,那么,它将获得总剩余宽度的一般,其他两个均享剩下的宽度
- android:layout_gravity: 此属性是用来指定控件在布局中的对齐方式,常用的取值有:
| 值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| top | 对象与其容器的顶部对齐, 不改变其大小 |
| bottom | 对象与其容器的底部对齐, 不改变其大小 |
| left | 对象与其容器的左侧对齐, 不改变其大小 |
| right | 对象与其容器的右侧对齐, 不改变其大小 |
| center_vertical | 垂直对其方式:垂直方向上居中对齐, 不改变其大小 |
| center_horizontal | 水平对其方式:水平方向上居中对齐, 不改变其大小 |
| center | 对象横纵居中, 不改变其大小 |
| fill_vertical | 必要的时候增加对象的纵向大小,以完全充满其容器. 垂直方向填充 |
| fill_horizontal | 必要的时候增加对象的纵向大小,以完全充满其容器. 垂直方向填充 |
| fill | 必要的时候增加对象的横纵向大小,以完全充满容器 |
下面贴上实现效果图与代码
效果图为:
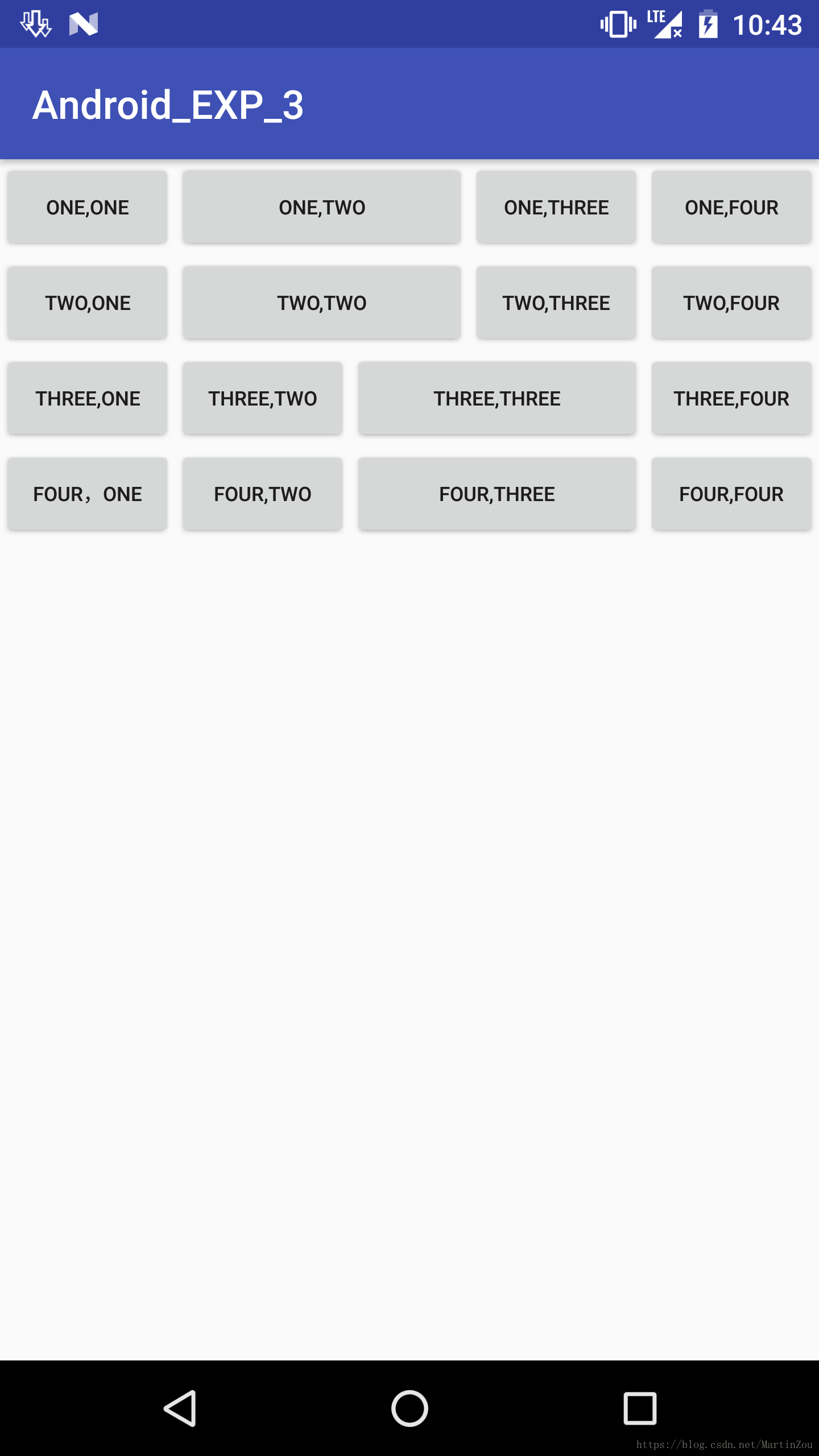
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button
android:textSize="10dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="One,One"
/>
<Button
android:textSize="10dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="One,Two"
/>
<Button
android:textSize="10dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="One,Three"
/>
<Button
android:textSize="10dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="One,Four" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button
android:textSize="10dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Two,One" />
<Button
android:textSize="10dp"








 本文介绍了Android的三种布局方式:LinearLayout(线性布局),RelativeLayout(相对布局)和TableLayout(表格布局)。LinearLayout通过指定方向来排列元素,支持权重分配。RelativeLayout允许元素自由相对定位。TableLayout则按行列组织控件。文章详细讲解了每个布局的特点、关键属性,并附带了示例代码和效果展示。
本文介绍了Android的三种布局方式:LinearLayout(线性布局),RelativeLayout(相对布局)和TableLayout(表格布局)。LinearLayout通过指定方向来排列元素,支持权重分配。RelativeLayout允许元素自由相对定位。TableLayout则按行列组织控件。文章详细讲解了每个布局的特点、关键属性,并附带了示例代码和效果展示。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 691
691

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








