1) I/O
读写流,一定是Blocking的。
效率较好的用法是,使用Buffer。例如BufferReader,每次先读取指定大小的内容到Buffer中,而不是每次读取一个字节
读取文件代码例:
String line = null;
try(BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("filename"))) {
;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
// do something
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
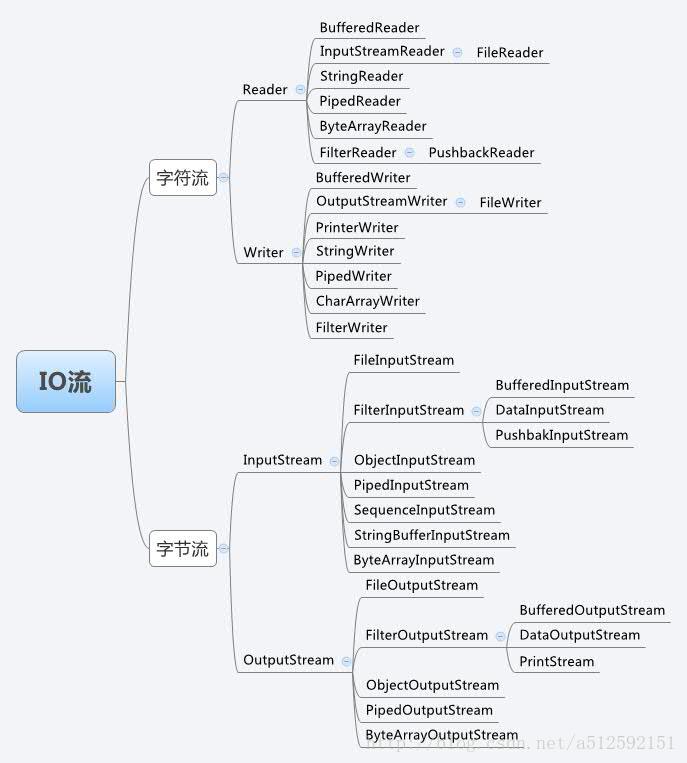
} Stream的家族十分庞大,下图是搜索到的一个较全的概括
另附PrintWriter和Filewriter的对比:
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/5759925/printwriter-vs-filewriter-in-java
2)NIO
※使用FileChannel读取文件,无法按行读取,但是可以获取/指定当前位置(Position)
RandomAccessFile aFile = new RandomAccessFile("filename", "r");
FileChannel inChannel = aFile.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while(inChannel.read(buffer) > 0)
{
// 转换到读取模式
buffer.flip();
// 处理Buffer
// clear或者compact
buffer.clear();
}
inChannel.close();
aFile.close();与read对应的Write方法负责写入
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
buf.clear();
buf.put(newData.getBytes());
buf.flip();
while(buf.hasRemaining()) {
channel.write(buf);
}※读取大文件,可以使用内存映射的MapperedByteBuffer,内存映射不直接将文件读入物理内存
RandomAccessFile aFile = new RandomAccessFile("filename", "r");
FileChannel inChannel = aFile.getChannel();
MappedByteBuffer buffer = inChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, inChannel.size());
buffer.load();
// Do Something
buffer.clear();
inChannel.close();
aFile.close();
※NIO提供Path接口代替File类,并且提供Paths、Files工具类方便操作
例如,读取小文件的所有内容,只需以下步骤:
Path path = Paths.get("filepath");
new String(Files.readAllBytes(path), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
fileChannel.read方法返回一个Future,在执行完成后operation.isDone()将会返回true
AsynchronousFileChannel fileChannel =
AsynchronousFileChannel.open(path, StandardOpenOption.READ);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
long position = 0;
Future<Integer> operation = fileChannel.read(buffer, position);
while(!operation.isDone());
buffer.flip();
byte[] data = new byte[buffer.limit()];
buffer.get(data);
System.out.println(new String(data));
buffer.clear();
fileChannel.read(buffer, position, buffer, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
System.out.println("result = " + result);
attachment.flip();
byte[] data = new byte[attachment.limit()];
attachment.get(data);
System.out.println(new String(data));
attachment.clear();
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
}
});参考文章:
http://blog.csdn.net/yczz/article/details/38761237
http://www.cnblogs.com/xubenben/p/4424398.html
http://tutorials.jenkov.com/java-nio/index.html






















 829
829

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








