之前阿里实习二面时,问过这个,我没有看过源码,只知道一个大概的快排,所以就挺僵硬的。现在回来整理一哈,以备不时之需,哈哈。
一、 对基本数据类型数组的排序
1、int类型排序
int[] intArray = new int[]{1,34,5,-9};
Arrays.sort(intArray);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(intArray));
2、 字符串String排序(默认从小到大,可定制排序)
String[] strArray = new String[]{"Z", "a", "D"};
Arrays.sort(strArray); //默认字典序
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strArray));
示例:把数组排成最小的数

class Solution {
public String minNumber(int[] nums) {
String[] strs = new String[nums.length];
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)
strs[i] = String.valueOf(nums[i]);
Arrays.sort(strs, (x, y) -> (x + y).compareTo(y + x));
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for(String s : strs)
res.append(s);
return res.toString();
}
}
字符串排序(忽略大小写) :
Arrays.sort(strArray, String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);逆向排序 :
Arrays.sort(strArray, Collections.reverseOrder());
二、Arrays.sort()源码解析(以int[]为例)
点进sort()方法,得到下面的源码:
public static void sort(int[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
看到DualPivotQuicksort这个类名,是双轴快速排序的含义,继续点进去看:
// Use Quicksort on small arrays
if (right - left < QUICKSORT_THRESHOLD) {
sort(a, left, right, true);
return;
}
其中,QUICKSORT_THRESHOLD代表的数字为286,意味着如果元素个数小于286,使用里面的sort方法,点进去看:
if (length < INSERTION_SORT_THRESHOLD) {
if (leftmost) {
/*
* Traditional (without sentinel) insertion sort,
* optimized for server VM, is used in case of
* the leftmost part.
*/
for (int i = left, j = i; i < right; j = ++i) {
int ai = a[i + 1];
while (ai < a[j]) {
a[j + 1] = a[j];
if (j-- == left) {
break;
}
}
a[j + 1] = ai;
}
} else {
/*
* Skip the longest ascending sequence.
*/
do {
if (left >= right) {
return;
}
} while (a[++left] >= a[left - 1]);
/*
* Every element from adjoining part plays the role
* of sentinel, therefore this allows us to avoid the
* left range check on each iteration. Moreover, we use
* the more optimized algorithm, so called pair insertion
* sort, which is faster (in the context of Quicksort)
* than traditional implementation of insertion sort.
*/
for (int k = left; ++left <= right; k = ++left) {
int a1 = a[k], a2 = a[left];
if (a1 < a2) {
a2 = a1; a1 = a[left];
}
while (a1 < a[--k]) {
a[k + 2] = a[k];
}
a[++k + 1] = a1;
while (a2 < a[--k]) {
a[k + 1] = a[k];
}
a[k + 1] = a2;
}
int last = a[right];
while (last < a[--right]) {
a[right + 1] = a[right];
}
a[right + 1] = last;
}
return;
}
可以看到,当数组长度<INSERTION_SORT_THRESHOLD(47)时,采用插入排序
继续看后面的源码,当数组长度>=INSERTION_SORT_THRESHOLD(47)时,采用快速排序。看一下快速排序的源码:
- 用公式length/8+length/64+1近似计算出数组长度的1/7:
// Inexpensive approximation of length / 7
int seventh = (length >> 3) + (length >> 6) + 1;
- 取5个根据经验得出的等距点 (看注释,这个根据经验得来就很灵性)
/*
* Sort five evenly spaced elements around (and including) the
* center element in the range. These elements will be used for
* pivot selection as described below. The choice for spacing
* these elements was empirically determined to work well on
* a wide variety of inputs.
*/
int e3 = (left + right) >>> 1; // The midpoint
int e2 = e3 - seventh;
int e1 = e2 - seventh;
int e4 = e3 + seventh;
int e5 = e4 + seventh;
- 将这5个元素进行插入排序
// Sort these elements using insertion sort
if (a[e2] < a[e1]) { int t = a[e2]; a[e2] = a[e1]; a[e1] = t; }
if (a[e3] < a[e2]) { int t = a[e3]; a[e3] = a[e2]; a[e2] = t;
if (t < a[e1]) { a[e2] = a[e1]; a[e1] = t; }
}
if (a[e4] < a[e3]) { int t = a[e4]; a[e4] = a[e3]; a[e3] = t;
if (t < a[e2]) { a[e3] = a[e2]; a[e2] = t;
if (t < a[e1]) { a[e2] = a[e1]; a[e1] = t; }
}
}
if (a[e5] < a[e4]) { int t = a[e5]; a[e5] = a[e4]; a[e4] = t;
if (t < a[e3]) { a[e4] = a[e3]; a[e3] = t;
if (t < a[e2]) { a[e3] = a[e2]; a[e2] = t;
if (t < a[e1]) { a[e2] = a[e1]; a[e1] = t; }
}
}
}
-
如果a[e1] != a[e2] && a[e2] != a[e3] && a[e3] != a[e4] && a[e4] != a[e5],选用双轴快速排序;否则采用单轴快速排序(使用a[e3]作为pivot)(下面看双轴快排)
-
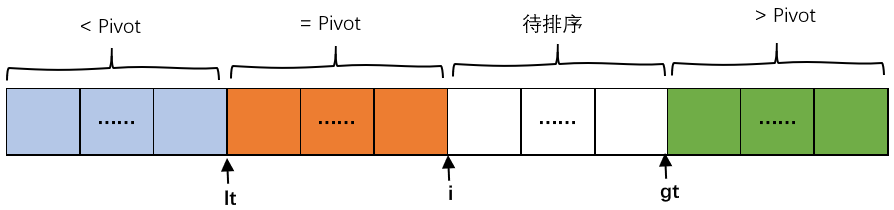
选取a[e2],a[e4]分别作为pivot1,pivot2。由于上一步骤进行了排序,所以必有pivot1 <=pivot2。定义两个指针less和great,less从最左边开始向右遍历,一直找到第一个不小于pivot1的元素;great从右边开始向左遍历,一直找到第一个不大于pivot2的元素。
/* * Use the second and fourth of the five sorted elements as pivots. * These values are inexpensive approximations of the first and * second terciles of the array. Note that pivot1 <= pivot2. */ int pivot1 = a[e2]; int pivot2 = a[e4]; /* * The first and the last elements to be sorted are moved to the * locations formerly occupied by the pivots. When partitioning * is complete, the pivots are swapped back into their final * positions, and excluded from subsequent sorting. */ a[e2] = a[left]; a[e4] = a[right]; /* * Skip elements, which are less or greater than pivot values. */ while (a[++less] < pivot1); while (a[--great] > pivot2); -
接着定义指针k从less-1开始向右遍历至great,把小于pivot1的元素移动到less左边,大于pivot2的元素移动到great右边。这里要注意,我们已知great处的元素小于pivot2,但是它于pivot1的大小关系,还需要进行判断,如果比pivot1还小,需要移动到到less左边,否则只需要交换到k处。
/* * Partitioning: * * left part center part right part * +--------------------------------------------------------------+ * | < pivot1 | pivot1 <= && <= pivot2 | ? | > pivot2 | * +--------------------------------------------------------------+ * ^ ^ ^ * | | | * less k great * * Invariants: * * all in (left, less) < pivot1 * pivot1 <= all in [less, k) <= pivot2 * all in (great, right) > pivot2 * * Pointer k is the first index of ?-part. */ outer: for (int k = less - 1; ++k <= great; ) { int ak = a[k]; if (ak < pivot1) { // Move a[k] to left part a[k] = a[less]; /* * Here and below we use "a[i] = b; i++;" instead * of "a[i++] = b;" due to performance issue. */ a[less] = ak; ++less; } else if (ak > pivot2) { // Move a[k] to right part while (a[great] > pivot2) { if (great-- == k) { break outer; } } if (a[great] < pivot1) { // a[great] <= pivot2 a[k] = a[less]; a[less] = a[great]; ++less; } else { // pivot1 <= a[great] <= pivot2 a[k] = a[great]; } /* * Here and below we use "a[i] = b; i--;" instead * of "a[i--] = b;" due to performance issue. */ a[great] = ak; --great; } } -
将less-1处的元素移动到队头,great+1处的元素移动到队尾,并把pivot1和pivot2分别放到less-1和great+1处
// Swap pivots into their final positions a[left] = a[less - 1]; a[less - 1] = pivot1; a[right] = a[great + 1]; a[great + 1] = pivot2; -
至此,less左边的元素都小于pivot1,great右边的元素都大于pivot2,分别对两部分进行同样的递归排序。
// Sort left and right parts recursively, excluding known pivots
sort(a, left, less - 2, leftmost);
sort(a, great + 2, right, false);
- 对于中间的部分,如果大于4/7的数组长度,很可能是因为重复元素的存在,所以把less向右移动到第一个不等于pivot1的地方,把great向左移动到第一个不等于pivot2的地方,然后再对less和great之间的部分进行递归排序
/*
* If center part is too large (comprises > 4/7 of the array),
* swap internal pivot values to ends.
*/
if (less < e1 && e5 < great) {
/*
* Skip elements, which are equal to pivot values.
*/
while (a[less] == pivot1) {
++less;
}
while (a[great] == pivot2) {
--great;
}
}
......
// Sort center part recursively
sort(a, less, great, false);
继续看源码,若是元素个数>=286的话,选用归并排序。不过在归并排序之前,有个小小的优化操作,来判断数组是否接近于排序状态:
int[] run = new int[MAX_RUN_COUNT + 1];
int count = 0; run[0] = left;
// Check if the array is nearly sorted
for (int k = left; k < right; run[count] = k) {
if (a[k] < a[k + 1]) { // ascending
while (++k <= right && a[k - 1] <= a[k]);
} else if (a[k] > a[k + 1]) { // descending
while (++k <= right && a[k - 1] >= a[k]);
for (int lo = run[count] - 1, hi = k; ++lo < --hi; ) {
int t = a[lo]; a[lo] = a[hi]; a[hi] = t;
}
} else { // equal
for (int m = MAX_RUN_LENGTH; ++k <= right && a[k - 1] == a[k]; ) {
if (--m == 0) {
sort(a, left, right, true);
return;
}
}
}
/*
* The array is not highly structured,
* use Quicksort instead of merge sort.
*/
if (++count == MAX_RUN_COUNT) {
sort(a, left, right, true);
return;
}
}
这里主要作用是看这个数组是否具备结构:实际逻辑是分组排序,每降序为一个组,如1,9,8,7,6,8。9到6是降序,为一个组,然后把降序的一组排成升序:1,6,7,8,9,8。然后最后的8后面继续往后面找。
每遇到这样一个降序组,++count,当++count等于MAX_RUN_COUNT(67),被判断为这个数组不具备结构(也就是这数据时而升时而降),此时采用快速排序(The array is not highly structured,use Quicksort instead of merge sort.)。
如果count少于MAX_RUN_COUNT(67)的,说明这个数组还有点结构,就继续往下走下面的归并排序:
// Merging
for (int last; count > 1; count = last) {
for (int k = (last = 0) + 2; k <= count; k += 2) {
int hi = run[k], mi = run[k - 1];
for (int i = run[k - 2], p = i, q = mi; i < hi; ++i) {
if (q >= hi || p < mi && a[p + ao] <= a[q + ao]) {
b[i + bo] = a[p++ + ao];
} else {
b[i + bo] = a[q++ + ao];
}
}
run[++last] = hi;
}
if ((count & 1) != 0) {
for (int i = right, lo = run[count - 1]; --i >= lo;
b[i + bo] = a[i + ao]
);
run[++last] = right;
}
int[] t = a; a = b; b = t;
int o = ao; ao = bo; bo = o;
}
Arrays.sort()对升序数组、降序数组和重复数组的排序效率的提升:
- 对于小数组(小于47)来说,插入排序效率更高,明显提升了性能。
- 双轴快排使用两个pivot,每轮把数组分成3段,在没有明显增加比较次数的情况下巧妙地减少了递归次数。
- pivot的选择上增加了随机性,却没有带来随机数的开销。
- 对重复数据进行了优化处理,避免了不必要交换和递归。
三、Arrays.sort()源码总结(int[])
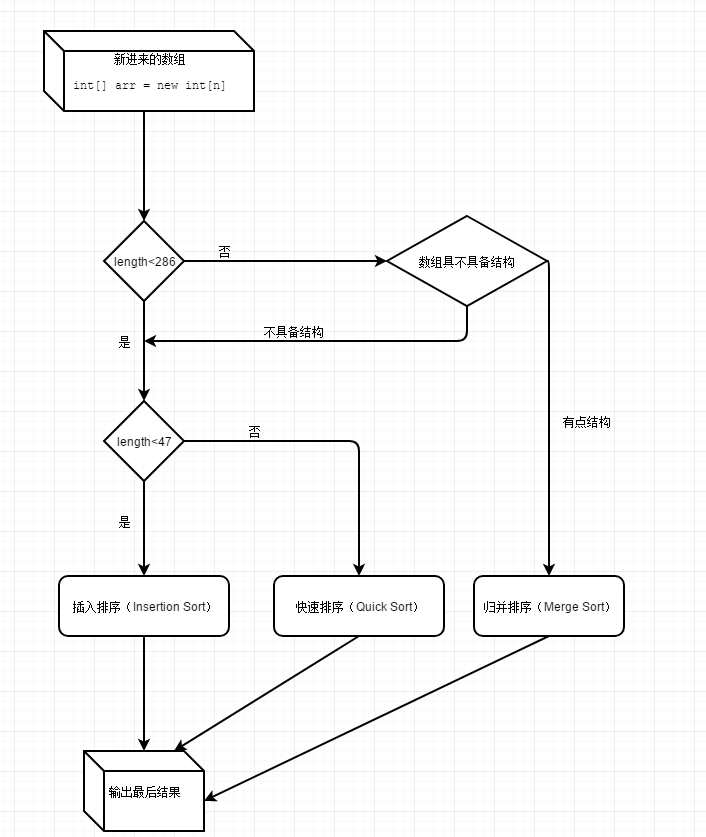
- 首先,对于一个传进来的int[]类型的数组,判断数组的长度length是否<286
- 如果数组长度>=286,检查数组是否具有结构:
- 如果数组具备结构,采用归并排序;
- 如果数组完全不具备结构,采用快速排序。
- 如果数组长度<286,
- 如果数组长度<47,采用插入排序;
- 如果数组长度>=47且<286,根据经验算出5个等距点:
- 如果5个等距点对应的数组值都不相等,采用双轴快速排序;
- 否则,采用单轴快速排序。
快速排序简介:
单轴快速排序:
选取一个基准值(pivot),将待排序数组划分为两部分:>pivot 和<pivot,再对这两部分进行单轴快速排序。可是这种方式对于输入数组中有不少重复元素时效率不太理想。
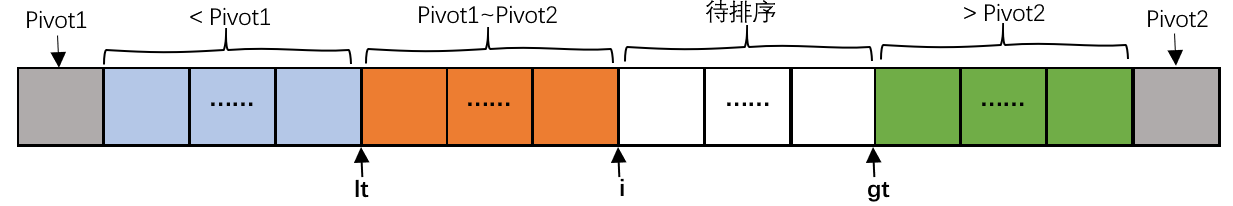
双轴快速排序:
选取两个 基准值pivot1,pivot2,且保证pivot1<=pivot2,其具体实现与三取样切分相似,不过期将待排序数组划分如下三部分:<pivot,介于pivot1与pivot2之间,>pivot2。
四、Arrays.sort()使用归并排序、快速排序的对比
- 使用不同类型的排序算法主要是由于快速排序是不稳定的,而归并排序是稳定的。**这里的稳定是指比较相等的数据在排序之后仍然按照排序之前的前后顺序排列。**对于基本数据类型,稳定性没有意义,而对于对象类型,稳定性是比较重要的,因为对象相等的判断可能只是判断关键属性,最好保持相等对象的非关键属性的顺序与排序前一致;
- 另外一个原因是由于归并排序相对而言比较次数比快速排序少,移动(对象引用的移动)次数比快速排序多,而对于对象来说,比较一般比移动耗时。
假定在待排序的记录序列中,存在多个具备相同的关键字的记录,若通过排序,这些记录的相对次序保持不变,即在原序列中,r[i] = r[j],且 r[i] 在 r[j] 以前,而在排序后的序列中,r[i] 仍在 r[j] 以前,则称这种排序算法是稳定的;不然称为不稳定的
**例子:**咱们要对一组商品排序,商品存在两个属性:价格和销量。当咱们按照价格从高到低排序后,要再按照销量对其排序,这时,若是要保证销量相同的商品仍保持价格从高到低的顺序,就必须使用稳定性算法。





















 1758
1758











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








