本文主要分析基于MultiQueue的Linux Block Layer层部分源码内容
!!!为帮助理解,提供了一份整体流程图如下(内容太大模糊了),细致的visio以及pdf版本可在本人的下载资源中下载,地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/g382112762/9691677:
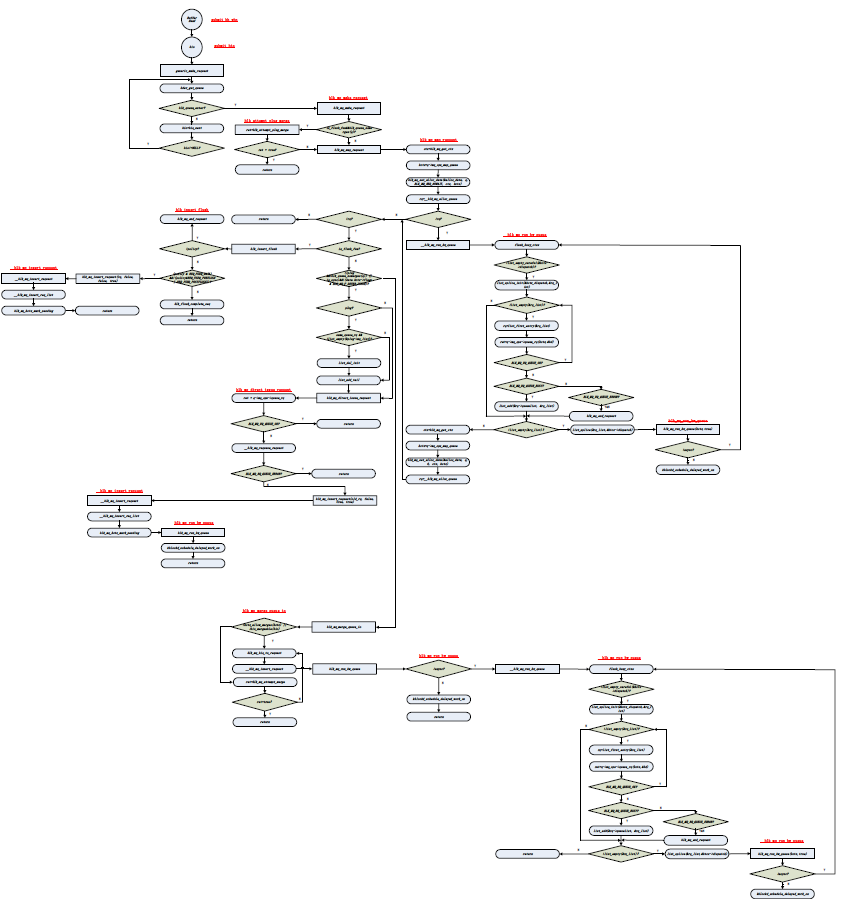
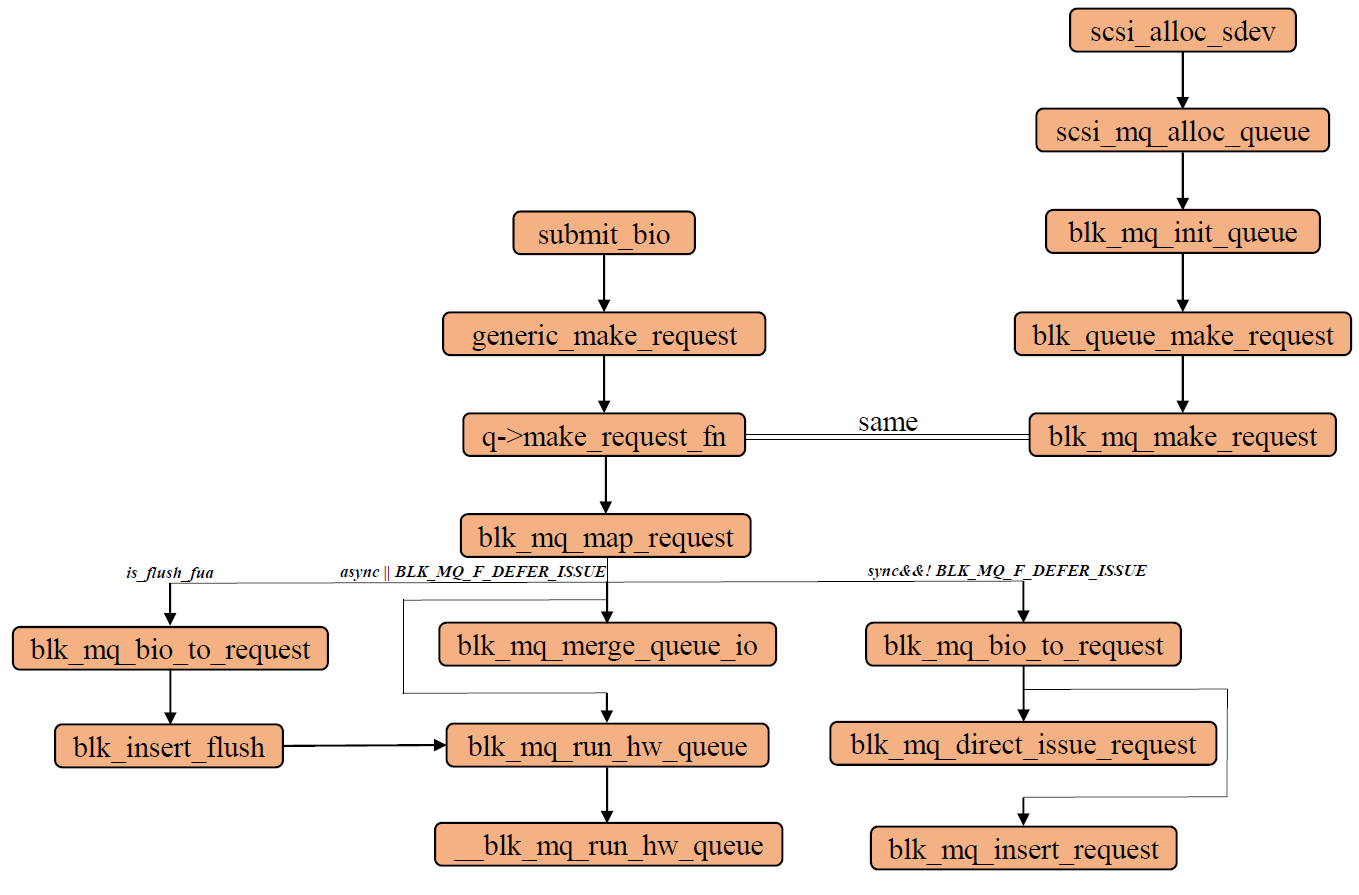
当要写一个page页到底层设备时,需要通过submit_bh进行提交。该函数主要负责对初始化一个bio以及对其进行相关的封装处理。其函数调用主要的流程为:submit_bh -> submit_bh_wbc -> submit_io ->generic_make_request。一旦bio进入generic_make_request则说明其将在块设备层中被进行相关处理工作。
generic_make_request函数如下:
blk_qc_t generic_make_request(struct bio *bio)
{
struct bio_list bio_list_on_stack;
blk_qc_t ret = BLK_QC_T_NONE;
if (!generic_make_request_checks(bio)) //判断当前bio是否有效 gaocm
goto out;
if (current->bio_list) {
bio_list_add(current->bio_list, bio);
goto out;
}
//上述过程要求当前的make_request_fn每次只能被触发一次,因此,通过current->bio_list判断当前是否有bio在其中,若有则将当前这个加入到尾部等待被处理,若没有则可直接处理该bio gaocm
//还有一个值得注意的地方是,通常情况下,current->bio_list是为NULL的,因此,上述if语句将会在进行递归调用generic_make_request时候会执行。而该递归调用的地方即后面的q->make_request_fn函数里面,该函数会判断当前的bio是否超过了最大能处理能力范围,若是则将其拆分,拆分后的剩余bio将会再次被加入到generic_make_request函数中,而此时,current->bio_list中已经包含了原始的超过最大处理能力的bio,为了避免再次出发q->make_request_fn函数,则在上述if语句中先退出,完成拆分后满足处理能力大小的bio。
BUG_ON(bio->bi_next);
bio_list_init(&bio_list_on_stack); //初始化该双向链表 gaocm
current->bio_list = &bio_list_on_stack; //当前为NULL gaocm
do {
struct request_queue *q = bdev_get_queue(bio->bi_bdev); //获得bio对应的设备队列 gaocm
if (likely(blk_queue_enter(q, false) == 0)) { //判断当前的设备队列是否有效能够响应该请求 gaocm
ret = q->make_request_fn(q, bio); //将bio进行进一步处理,放入块设备层的处理队列中 gaocm
blk_queue_exit(q);
bio = bio_list_pop(current->bio_list);
} else {
struct bio *bio_next = bio_list_pop(current->bio_list);
bio_io_error(bio);
bio = bio_next;
}
} while (bio);
current->bio_list = NULL; /* deactivate */ //clear this bio list and make_request function is avalible again
out:
return ret;
}若当前的设备队列有效,则会调用q->make_request_fn函数处理该bio,将其放入块设备层处理队列中。
q->make_request_fn函数在一开始在blk_queue_make_request函数中被注册为blk_mq_make_request函数或者blk_sq_make_request,其判断标准是当前块设备层支持多个hardware queue还是单个hardware queue。
为了说明该注册q->make_request_fn函数的过程,我们从队列初始化源头开始解释起:
1. 首先在driver\scsi文件夹下的scsi_scan.c文件中,scsi_alloc_sdev函数会判断当前scsi支持的块设备是否支持multiqueue:
if (shost_use_blk_mq(shost)) // multiple queue is enabled gaocm
sdev->request_queue = scsi_mq_alloc_queue(sdev); //scsi定义的MQ队列 gaocm
else
sdev->request_queue = scsi_alloc_queue(sdev);2.若上述设备支持mq则进入scsi_mq_alloc_queue函数,该函数中主要进行设备队列的初始化,blk_mq_init_queue,在blk_mq_init_queue 函数中根据set信息进行与该设备队列相关的信息参数初始化,过程如下:
/* mark the queue as mq asap */
q->mq_ops = set->ops; //标记为MQ队列 gaocm
q->queue_ctx = alloc_percpu(struct blk_mq_ctx); //获得percpu的地址 建立software queue环境 gaocm
if (!q->queue_ctx)
goto err_exit;
q->queue_hw_ctx = kzalloc_node(nr_cpu_ids * sizeof(*(q->queue_hw_ctx)),
GFP_KERNEL, set->numa_node); //获得hardware queue上下文环境 gaocm
if (!q->queue_hw_ctx)
goto err_percpu;
q->mq_map = blk_mq_make_queue_map(set); // 建立software queue和hardware queue之间的映射关系 gaocm
if (!q->mq_map)
goto err_map;
blk_mq_realloc_hw_ctxs(set, q);
if (!q->nr_hw_queues)
goto err_hctxs;
INIT_WORK(&q->timeout_work, blk_mq_timeout_work);
blk_queue_rq_timeout(q, set->timeout ? set->timeout : 30 * HZ); //定义scsi设备队列超时设定 gaocm
q->nr_queues = nr_cpu_ids;
q->queue_flags |= QUEUE_FLAG_MQ_DEFAULT;
if (!(set->flags & BLK_MQ_F_SG_MERGE))
q->queue_flags |= 1 << QUEUE_FLAG_NO_SG_MERGE;
q->sg_reserved_size = INT_MAX;
INIT_WORK(&q->requeue_work, blk_mq_requeue_work);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&q->requeue_list);
spin_lock_init(&q->requeue_lock);
if (q->nr_hw_queues > 1)
blk_queue_make_request(q, blk_mq_make_request); //注册q->make_request_fn函数 gaocm
else
blk_queue_make_request(q, blk_sq_make_request);
/*
* Do this after blk_queue_make_request() overrides it...
*/
q->nr_requests = set->queue_depth;
if (set->ops->complete)
blk_queue_softirq_done(q, set->ops->complete);
blk_mq_init_cpu_queues(q, set->nr_hw_queues);
get_online_cpus();
mutex_lock(&all_q_mutex);
list_add_tail(&q->all_q_node, &all_q_list);
blk_mq_add_queue_tag_set(set, q);
blk_mq_map_swqueue(q, cpu_online_mask);
mutex_unlock(&all_q_mutex);
put_online_cpus();
return q;
err_hctxs:
kfree(q->mq_map);
err_map:
kfree(q->queue_hw_ctx);
err_percpu:
free_percpu(q->queue_ctx);
err_exit:
q->mq_ops = NULL;
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
}通过上述函数我们可以发现,当目前支持多个hardware queue时,则在blk_queue_make_request中将q->make_request_fn注册为blk_mq_make_request。(本文先仅讨论多hardware queue情况)
现在我们回到blk_mq_make_request函数,其过程如下:
//多hardware queue的情况下不采用plug queue gaocm
const int is_sync = rw_is_sync(bio->bi_rw); //判断是否为同步 gaocm
const int is_flush_fua = bio->bi_rw & (REQ_FLUSH | REQ_FUA);//判断是否为屏障IO gaocm
struct blk_map_ctx data;
struct request *rq;
unsigned int request_count = 0;
struct blk_plug *plug;
struct request *same_queue_rq = NULL;
blk_qc_t cookie;
blk_queue_bounce(q, &bio); //做DMA时的相关地址限制,可能该bio只能访问低端内存,因此需要将高端内存中的bio数据拷贝到低端内存中 gaocm
if (bio_integrity_enabled(bio) && bio_integrity_prep(bio)) { //bio完整性判断
bio_io_error(bio);
return BLK_QC_T_NONE;
}
blk_queue_split(q, &bio, q->bio_split); //判断当前的bio是否超过了预设最大处理大小,若是则进行拆分,拆分后会进行generic_make_request函数调用 gaocm
if (!is_flush_fua && !blk_queue_nomerges(q) &&
blk_attempt_plug_merge(q, bio, &request_count, &same_queue_rq)) //若非屏障IO并且设备队列支持合并且plug队列中可进行合并则进行合并工作 gaocm
return BLK_QC_T_NONE;
rq = blk_mq_map_request(q, bio, &data); //在mq中注册一个request gaocm
if (unlikely(!rq))
return BLK_QC_T_NONE;
cookie = blk_tag_to_qc_t(rq->tag, data.hctx->queue_num);
if (unlikely(is_flush_fua)) {
blk_mq_bio_to_request(rq, bio); //将bio转换为request gaocm
blk_insert_flush(rq); //若是屏障IO则将其加入到flush队列中,该队列直接发送至driver gaocm
goto run_queue;
}
plug = current->plug;
/*
* If the driver supports defer issued based on 'last', then
* queue it up like normal since we can potentially save some
* CPU this way.
*/
if (((plug && !blk_queue_nomerges(q)) || is_sync) && //有plug队列,且设备队列支持合并或者改请求是同步请求。。。 gaocm?
!(data.hctx->flags & BLK_MQ_F_DEFER_ISSUE)) { //延迟发送 gaocm
struct request *old_rq = NULL;
blk_mq_bio_to_request(rq, bio); //转化为request gaocm
/*
* We do limited pluging. If the bio can be merged, do that.
* Otherwise the existing request in the plug list will be
* issued. So the plug list will have one request at most
*/
if (plug) {
/*
* The plug list might get flushed before this. If that
* happens, same_queue_rq is invalid and plug list is
* empty
*/
if (same_queue_rq && !list_empty(&plug->mq_list)) {
old_rq = same_queue_rq;
list_del_init(&old_rq->queuelist); //判断之前是否有能合并或者一样的请求,若有则删除之前的请求 gaocm
}
list_add_tail(&rq->queuelist, &plug->mq_list); //将该请求加入到plug队列中
} else /* is_sync */
old_rq = rq;
blk_mq_put_ctx(data.ctx);
if (!old_rq) //无为处理请求 gaocm
goto done;
if (!blk_mq_direct_issue_request(old_rq, &cookie)) //直接加入到底层scsi层队列中,并发往driver? gaocm
goto done;
blk_mq_insert_request(old_rq, false, true, true); //加入到software queue中 gaocm
goto done;
}
if (!blk_mq_merge_queue_io(data.hctx, data.ctx, rq, bio)) { //底层driver支持延迟发送或者为async请求 gaocm
//能合并则进行合并,否则加入到software queue中 gaocm
/*
* For a SYNC request, send it to the hardware immediately. For
* an ASYNC request, just ensure that we run it later on. The
* latter allows for merging opportunities and more efficient
* dispatching.
*/
run_queue:
blk_mq_run_hw_queue(data.hctx, !is_sync || is_flush_fua); //执行hardware queue gaocm
}
blk_mq_put_ctx(data.ctx);
done:
return cookie;
}上述函数直接说明在多hardware queue的环境下不考虑plug queue,而是直接判断能否发送至driver或者直接加入到software queue中。
为方便大家理解,我将上述函数中的几个重点函数摘抄解释如下:
- blk_mq_map_request 该函数的目的在于在mq中注册一个请求:
static struct request *blk_mq_map_request(struct request_queue *q,
struct bio *bio,
struct blk_map_ctx *data)
{
struct blk_mq_hw_ctx *hctx;
struct blk_mq_ctx *ctx;
struct request *rq;
int rw = bio_data_dir(bio);
struct blk_mq_alloc_data alloc_data;
blk_queue_enter_live(q); //判断设备队列是否有效,对该队列增加一个CPU副本访问 gaocm
ctx = blk_mq_get_ctx(q); //根据CPU获得定义的software queue环境 gaocm
hctx = q->mq_ops->map_queue(q, ctx->cpu); //在映射关系中根据software queue的cpu号确定hardware queue的上下文环境 gaocm
//每个CPU对应一个software queue和hardware queue ? gaocm
if (rw_is_sync(bio->bi_rw))
rw |= REQ_SYNC;
trace_block_getrq(q, bio, rw);
blk_mq_set_alloc_data(&alloc_data, q, BLK_MQ_REQ_NOWAIT, ctx, hctx); //得到关于当前software/hardware queue的相关信息数据 gaocm
rq = __blk_mq_alloc_request(&alloc_data, rw); //分配一个request,该request与当前的software queue和hardware queue相关 gaocm
if (unlikely(!rq)) { //注册该request失败 gaocm
__blk_mq_run_hw_queue(hctx); //执行hardware queue,腾出空间? gaocm
blk_mq_put_ctx(ctx);
trace_block_sleeprq(q, bio, rw);
ctx = blk_mq_get_ctx(q);
hctx = q->mq_ops->map_queue(q, ctx->cpu);
blk_mq_set_alloc_data(&alloc_data, q, 0, ctx, hctx);
rq = __blk_mq_alloc_request(&alloc_data, rw);
ctx = alloc_data.ctx;
hctx = alloc_data.hctx;
}
hctx->queued++; //hardware queue中排队等待的请求加1 gaocm
data->hctx = hctx;
data->ctx = ctx;
return rq;
}- blk_mq_direct_issue_request 将请求直接加入到底层driver中,判断当前scsi设备能否处理该请求:
static int blk_mq_direct_issue_request(struct request *rq, blk_qc_t *cookie)
{
int ret;
struct request_queue *q = rq->q;
struct blk_mq_hw_ctx *hctx = q->mq_ops->map_queue(q,
rq->mq_ctx->cpu);
struct blk_mq_queue_data bd = {
.rq = rq,
.list = NULL,
.last = 1
};
blk_qc_t new_cookie = blk_tag_to_qc_t(rq->tag, hctx->queue_num);
/*
* For OK queue, we are done. For error, kill it. Any other
* error (busy), just add it to our list as we previously
* would have done
*/
ret = q->mq_ops->queue_rq(hctx, &bd); //直接放入scsi队列中,返回是否能够被处理 gaocm
if (ret == BLK_MQ_RQ_QUEUE_OK) {
*cookie = new_cookie;
return 0;
}
__blk_mq_requeue_request(rq); //标记该request的nr_phys_segments减1 gaocm
if (ret == BLK_MQ_RQ_QUEUE_ERROR) {
*cookie = BLK_QC_T_NONE;
rq->errors = -EIO;
blk_mq_end_request(rq, rq->errors);
return 0;
}
return -1;
}- blk_mq_insert_request 将请求加入到software queue队列中:
void blk_mq_insert_request(struct request *rq, bool at_head, bool run_queue,
bool async)
{
struct request_queue *q = rq->q;
struct blk_mq_hw_ctx *hctx;
struct blk_mq_ctx *ctx = rq->mq_ctx, *current_ctx;
current_ctx = blk_mq_get_ctx(q); //获得software queue环境 gacm
if (!cpu_online(ctx->cpu))
rq->mq_ctx = ctx = current_ctx;
hctx = q->mq_ops->map_queue(q, ctx->cpu); //找到对应的hardware queue上下文环境 gaocm
spin_lock(&ctx->lock);
__blk_mq_insert_request(hctx, rq, at_head); //通过rq找到ctx,加入到software queue中 gaocm
spin_unlock(&ctx->lock);
if (run_queue)
blk_mq_run_hw_queue(hctx, async); //运行hardware queue,用异步方式执行 gaocm
blk_mq_put_ctx(current_ctx);
}其中,__blk_mq_insert_request 函数解释如下:
static void __blk_mq_insert_request(struct blk_mq_hw_ctx *hctx,
struct request *rq, bool at_head)
{
struct blk_mq_ctx *ctx = rq->mq_ctx;
__blk_mq_insert_req_list(hctx, ctx, rq, at_head); //加入到software queue gaocm
blk_mq_hctx_mark_pending(hctx, ctx); //标记该software queue中有请求需要被该hardware queue处理 gaocm
}- blk_mq_merge_queue_io 判断能否与当前software queue中的请求进行合并,若不行则加入到software queue中:
static inline bool blk_mq_merge_queue_io(struct blk_mq_hw_ctx *hctx,
struct blk_mq_ctx *ctx,
struct request *rq, struct bio *bio)
{
if (!hctx_allow_merges(hctx) || !bio_mergeable(bio)) { //不允许merge gaocm
blk_mq_bio_to_request(rq, bio);
spin_lock(&ctx->lock);
insert_rq:
__blk_mq_insert_request(hctx, rq, false); //加入到software queue中 gaocm
spin_unlock(&ctx->lock);
return false;
} else {
struct request_queue *q = hctx->queue;
spin_lock(&ctx->lock);
if (!blk_mq_attempt_merge(q, ctx, bio)) { //进行合并尝试 gaocm
blk_mq_bio_to_request(rq, bio); //无法合并则转向加入software queue中 gaocm
goto insert_rq;
}
spin_unlock(&ctx->lock);
__blk_mq_free_request(hctx, ctx, rq); //将刚刚在software queue和hardware queue中注册的request去除,因为请求已经加入到software queue中 gaocm
return true;
}
}- blk_mq_run_hw_queue函数,描述如下:
void blk_mq_run_hw_queue(struct blk_mq_hw_ctx *hctx, bool async)
{
if (unlikely(test_bit(BLK_MQ_S_STOPPED, &hctx->state) ||
!blk_mq_hw_queue_mapped(hctx)))
return;
if (!async) { // false and run gaocm
//若async为flash则说明该处理是同步的,需要马上处理,若是异步则将该操作交由kblocked进行处理 gaocm
int cpu = get_cpu();
if (cpumask_test_cpu(cpu, hctx->cpumask)) { // cpu is set in cpumask gaocm
__blk_mq_run_hw_queue(hctx); //运行hardware queue gaocm
put_cpu();
return;
}
put_cpu();
}
kblockd_schedule_delayed_work_on(blk_mq_hctx_next_cpu(hctx),
&hctx->run_work, 0);
}
其中__blk_mq_run_hw_queue函数描述如下:
static void __blk_mq_run_hw_queue(struct blk_mq_hw_ctx *hctx)
{
struct request_queue *q = hctx->queue;
struct request *rq;
LIST_HEAD(rq_list); //初始化请求list的双向链表 gaocm
LIST_HEAD(driver_list);
struct list_head *dptr;
int queued;
WARN_ON(!cpumask_test_cpu(raw_smp_processor_id(), hctx->cpumask));
if (unlikely(test_bit(BLK_MQ_S_STOPPED, &hctx->state))) //hardware queue状态判断 gaocm
return;
hctx->run++;
/*
* Touch any software queue that has pending entries.
*/
flush_busy_ctxs(hctx, &rq_list); //将所有标记了有请求将被该hardware queue处理的software queue的请求数据加入到rq_list中 gaocm
/*
* If we have previous entries on our dispatch list, grab them
* and stuff them at the front for more fair dispatch.
*/
if (!list_empty_careful(&hctx->dispatch)) { //若当前的hardware queue不空,即还有先前的请求待处理 gaocm
spin_lock(&hctx->lock);
if (!list_empty(&hctx->dispatch))
list_splice_init(&hctx->dispatch, &rq_list); //将hardware queue中先前未处理完地请求加入到rq_list前部(更公平) gaocm
spin_unlock(&hctx->lock);
}
/*
* Start off with dptr being NULL, so we start the first request
* immediately, even if we have more pending.
*/
dptr = NULL;
/*
* Now process all the entries, sending them to the driver.
*/
queued = 0;
while (!list_empty(&rq_list)) {
struct blk_mq_queue_data bd;
int ret;
rq = list_first_entry(&rq_list, struct request, queuelist); //获得请求 gaocm
list_del_init(&rq->queuelist); //删除该请求 gaocm
bd.rq = rq;
bd.list = dptr; //初始化一个链表 gaocm
bd.last = list_empty(&rq_list);
//初始化mq data,并判断是否还有请求待处理 gaocm
ret = q->mq_ops->queue_rq(hctx, &bd); //将当前请求请求数据加入到scsi queue中并返回相关结果 gaocm
switch (ret) {
case BLK_MQ_RQ_QUEUE_OK:
queued++;
continue;
case BLK_MQ_RQ_QUEUE_BUSY:
list_add(&rq->queuelist, &rq_list); //当前无法加入到hardware queue中则重新放回rq_list gaocm
__blk_mq_requeue_request(rq); //重新设定该请求的某些参数等 gaocm
break;
default:
pr_err("blk-mq: bad return on queue: %d\n", ret);
case BLK_MQ_RQ_QUEUE_ERROR:
rq->errors = -EIO;
blk_mq_end_request(rq, rq->errors);
break;
}
if (ret == BLK_MQ_RQ_QUEUE_BUSY) //说明当前hardware queue正忙,则不再加入请求 gaocm
break;
/*
* We've done the first request. If we have more than 1
* left in the list, set dptr to defer issue.
*/
if (!dptr && rq_list.next != rq_list.prev)
dptr = &driver_list;
}
if (!queued) //没有请求加入hardware queue gaocm
hctx->dispatched[0]++;
else if (queued < (1 << (BLK_MQ_MAX_DISPATCH_ORDER - 1)))
hctx->dispatched[ilog2(queued) + 1]++;
/*
* Any items that need requeuing? Stuff them into hctx->dispatch,
* that is where we will continue on next queue run.
*/
if (!list_empty(&rq_list)) {
spin_lock(&hctx->lock);
list_splice(&rq_list, &hctx->dispatch); //若当前还有请求在rq_list中,则将这些请求重新放回dispatch queue中,等待下次处理并且避免丢失 gaocm
spin_unlock(&hctx->lock);
/*
* the queue is expected stopped with BLK_MQ_RQ_QUEUE_BUSY, but
* it's possible the queue is stopped and restarted again
* before this. Queue restart will dispatch requests. And since
* requests in rq_list aren't added into hctx->dispatch yet,
* the requests in rq_list might get lost.
*
* blk_mq_run_hw_queue() already checks the STOPPED bit
**/
blk_mq_run_hw_queue(hctx, true); //说明当前hardware queue正忙,则调用该函数进行异步处理,交由kblocked处理 gaocm
}
}经过上述过程,请求已经接下来将进入到scsi层中,而该blk_mq_ops中的queue_rq函数在drivers/scsi中被注册为scsi_queue_rq:
static struct blk_mq_ops scsi_mq_ops = {
.map_queue = blk_mq_map_queue,
.queue_rq = scsi_queue_rq, //注册queue_rq为scsi_queue_rq gaocm
.complete = scsi_softirq_done,
.timeout = scsi_timeout,
.init_request = scsi_init_request,
.exit_request = scsi_exit_request,
};在scsi_queue_rq函数中,请求将会被转化为scsi command,然后进一步发送到底层driver中。
scsi_queue_rq函数描述如下:
static int scsi_queue_rq(struct blk_mq_hw_ctx *hctx,
const struct blk_mq_queue_data *bd) //在scsi这层中进行处理来自于hardware queue中的请求 gaocm
{
struct request *req = bd->rq;
struct request_queue *q = req->q;
struct scsi_device *sdev = q->queuedata;
struct Scsi_Host *shost = sdev->host;
struct scsi_cmnd *cmd = blk_mq_rq_to_pdu(req);
int ret;
int reason;
ret = prep_to_mq(scsi_prep_state_check(sdev, req)); //判断当前scsi支持的设备是否有效能够处理请求 gaocm
if (ret)
goto out;
ret = BLK_MQ_RQ_QUEUE_BUSY;
if (!get_device(&sdev->sdev_gendev))
goto out;
if (!scsi_dev_queue_ready(q, sdev))
goto out_put_device;
if (!scsi_target_queue_ready(shost, sdev))
goto out_dec_device_busy;
if (!scsi_host_queue_ready(q, shost, sdev))
goto out_dec_target_busy;
if (!(req->cmd_flags & REQ_DONTPREP)) {
ret = prep_to_mq(scsi_mq_prep_fn(req));
if (ret)
goto out_dec_host_busy;
req->cmd_flags |= REQ_DONTPREP;
} else {
blk_mq_start_request(req);
}
if (sdev->simple_tags)
cmd->flags |= SCMD_TAGGED;
else
cmd->flags &= ~SCMD_TAGGED;
scsi_init_cmd_errh(cmd); //错误处理 gaocm
cmd->scsi_done = scsi_mq_done;
reason = scsi_dispatch_cmd(cmd); //发送cmd到底层driver gaocm
if (reason) {
scsi_set_blocked(cmd, reason);
ret = BLK_MQ_RQ_QUEUE_BUSY;
goto out_dec_host_busy;
}
return BLK_MQ_RQ_QUEUE_OK;
out_dec_host_busy:
atomic_dec(&shost->host_busy);
out_dec_target_busy:
if (scsi_target(sdev)->can_queue > 0)
atomic_dec(&scsi_target(sdev)->target_busy);
out_dec_device_busy:
atomic_dec(&sdev->device_busy);
out_put_device:
put_device(&sdev->sdev_gendev);
out:
switch (ret) {
case BLK_MQ_RQ_QUEUE_BUSY:
blk_mq_stop_hw_queue(hctx); //若当前设备正忙,则停止hardware queue的下发工作 gaocm
if (atomic_read(&sdev->device_busy) == 0 &&
!scsi_device_blocked(sdev))
blk_mq_delay_queue(hctx, SCSI_QUEUE_DELAY);
break;
case BLK_MQ_RQ_QUEUE_ERROR:
/*
* Make sure to release all allocated ressources when
* we hit an error, as we will never see this command
* again.
*/
if (req->cmd_flags & REQ_DONTPREP)
scsi_mq_uninit_cmd(cmd);
break;
default:
break;
}
return ret;
}大致源码结构如下图所示:
可能上述注释分析部分存在不准确的地方,还望指正!






















 415
415

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








