前情回顾:
上一篇文章讲了ArrayList与顺序表,那么ArrayList有缺陷吗?当然有,由于其底层是一段连续空间,当在ArrayList任意位置插入或者删除元素时,就需要将后序元素整体往前或者往后 搬移,时间复杂度为O(n),效率比较低,因此ArrayList不适合做任意位置插入和删除比较多的场景。
因此,Java集合中又引入了LinkedList,即链表结构。
一、链表
概念:链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的 。
例如:火车可以看成一个链表。

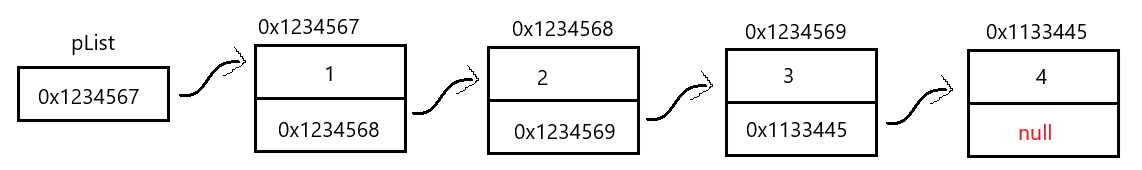
如图所示:
- 链表结构在逻辑上是连续的,但是在物理上不一定连续。
- 现实中的节点一般都是从堆(内容后边都会补上的)上申请出来的。
- 从堆上申请的空间,是按照一定策略分配的,多次申请的空间可能连续也可能不连续。
实际中链表的结构非常多样,例如其中几种:
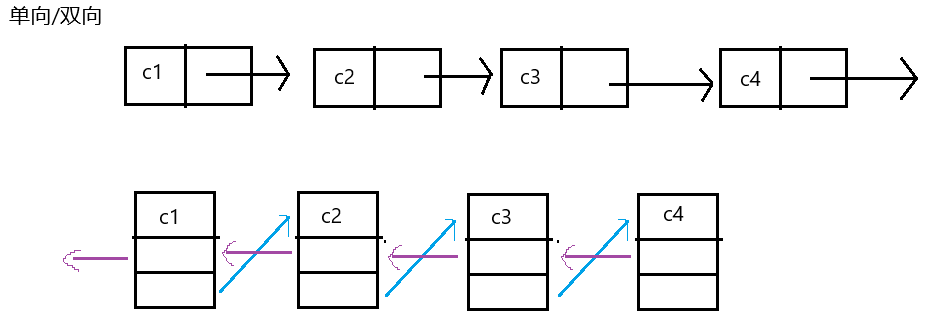
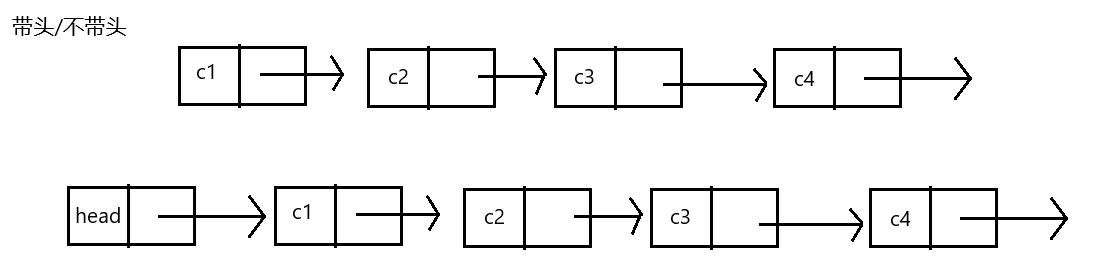
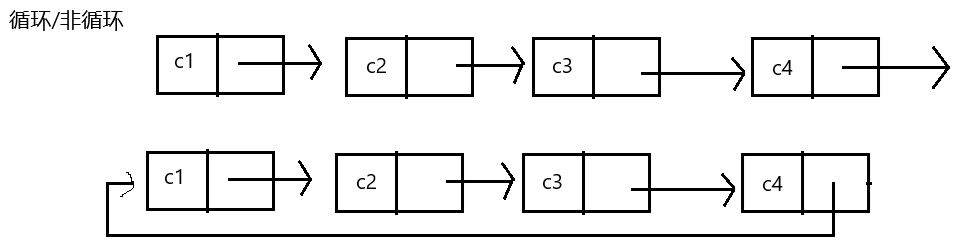
虽然有许多链表结构,但是我们重点掌握两种:
无头单向肺循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如 哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。
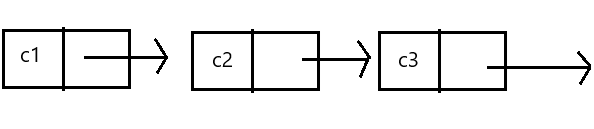
无头双向链表:在Java的集合框架库中LinkedList底层实现就是无头双向循环链表。
在说LinkList之前,先说如何实现链表。
二、链表的实现

emm……咋一看图感觉是挺多的,实际写下来确实很多,让咱来逐个解决。
三、基本操作
必要内容写好
public class SingleLinkedList implements IList{
static class ListNode{
public int val;
public ListNode next;
ListNode(int val){
this.val=val;
}
}
public ListNode head;
}
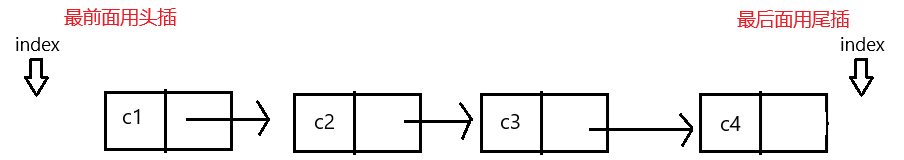
1.头插
写链表不要需要考虑空间是否足够,所以会省略一些处理方式。
头插不需要考虑链表为 null 情况,没有往哪放。
所以直接 new 一个节点 data,让 data 指向头结点,将头结点改为 data 。
代码如下:
public void addFirst(int data){
//new一个节点
ListNode node =new ListNode(data);
node.next=head;
head=node;
}
2.尾插
定义一个变量遍历链表,当变量的 next 为空时,插入 new 的节点。

代码如下:
public void addLast(int data){
ListNode node =new ListNode(data);
//判断链表是否为空
if(head==null){
head=node;
return;
}
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur.next!=null){
cur=cur.next;
}
cur.next=node;
}
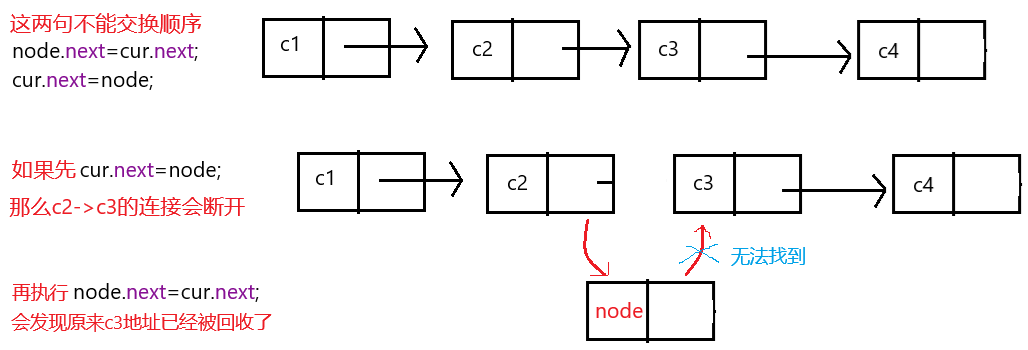
3.任意位置插入
要判断位置是否合法,但不用考虑空间大小问题。
那中间插入怎么操作?
可以这么想,如果 index 为零,就是对应位置,看图:

完整代码如下:
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
int pos=size();
if(index < 0 || index > pos){
System.out.println("index位置不合法");
return;
}
ListNode node=new ListNode(data);
if(index==0){
addFirst(data);
}
if (index==pos){
addLast(data);
}
ListNode cur=head;
while (index-1!=0){
cur=cur.next;
index--;
}
node.next=cur.next;
cur.next=node;
}
4.查找链表关键字
很简单,先判断为空,再遍历链表,查找 key 如果有返回TRUE,否则,返回FALSE。
代码如下:
public boolean contains(int key){
if(head==null){
return false;
}
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur!=null){
if(cur.val==key){
return true;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
return false;
}
5.删除第一个关键节点
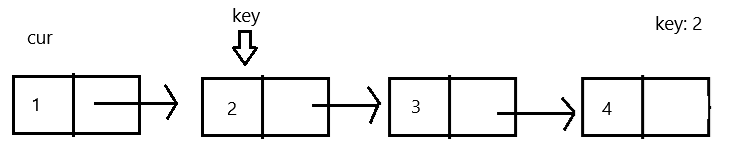
判断 head 为空,再判断 head 是否等于 key ,若等于则让 head=head.next。
if(head==null){
return;
}
if (head.val==key){
head=head.next;
return;
}
接下来是数值在长度范围内情况,怎么找呢?如果 cur != null 遍历,走到 key 值就无法执行操作。

其实答案已经在图上了,既然 cur != null 遍历不行,那就用 cur.next != null 遍历,当 next.val 等于key时,返回 cur。
代码如下:
public void remove(int key){
ListNode cur= findKey(key);
if(cur==null) {
return;
}
ListNode del=cur.next;
cur.next=del.next;
}
public ListNode findKey(int key){
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur.next!=null){
if(cur.next.val==key){
return cur;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
return null;
}
6.删除所有关键节点
移除一个都很麻烦了,这个还要全部移除…咱也不是怕事的人,上去解决它。

照例判断 head为空,再用 cur.next != null 遍历即可,那如果是其他情况呢?
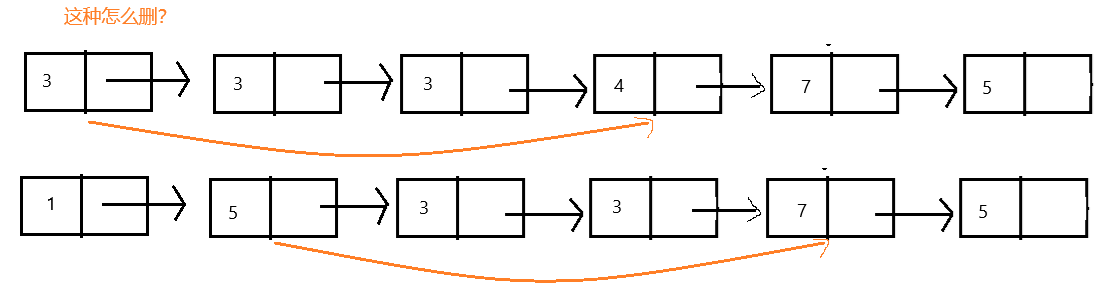
所以不能 cur.next != null 遍历。难道用 cur !=null 遍历?
哎!别说,好像还真行,看图:

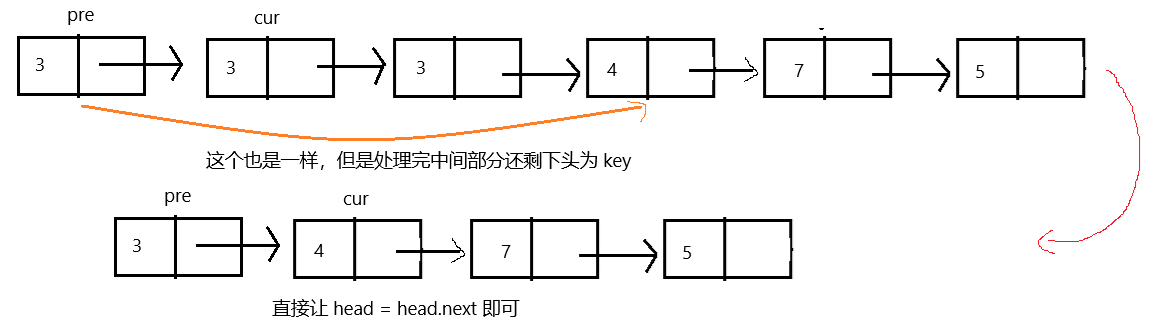
代码如下:
public void removeAllKey(int key){
if(head==null){
return;
}
ListNode pre =head;
ListNode cur= head.next;
while (cur!=null){
if(cur.val==key){
pre.next=cur.next;
cur=cur.next;
}else {
pre=cur;
cur=cur.next;
}
}
if (head.val==key){
head=head.next;
}
}
7.链表长度
剩下几个都比较简单了。
遍历链表,全部加上,返回值。
代码:
public int size(){
int len=0;
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur!=null){
len++;
cur=cur.next;
}
return len;
}
8.遍历链表
遍历然后打印。
代码:
public void display() {
ListNode cur =head;
while (cur!=null){
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur=cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
9.清空链表
遍历,全部置空。
代码:
public void clear(){
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur!=null){
ListNode curN=cur.next;
cur.next=null;
cur=curN;
}
}
无头非循环链表说完了,现在我们对单链表有一些了解,接下来继续说双向链表。
四、LinkedList
概念:LinkedList的底层是双向链表结构,由于链表没有将元素存储在连续的空间中,元素存储在单独的节点中,然后通过引用将节点连接起来了,因此在在任意位置插入或者删除元素时,不需要搬移元素,效率比较高。
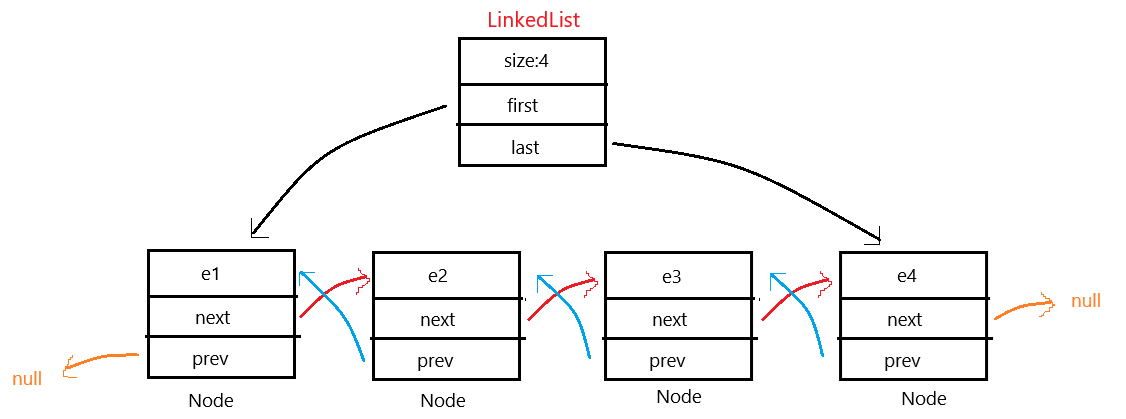
在集合框架中,LinkedList也实现了List接口,底层使用了双向链表,任意位置增删效率较高,时间复杂度为O(1),比较适合任意位置插入的场景,但是不支持随即访问。
1.LinkedList的常用操作
其实和单链表基本是一样的,只是更方便一些,话不多说,上图:

接口 IList 不用管,暂时用不到。
必要内容:
public class MyLinkedList implements IList{
static class ListNode{
public int val;
public ListNode next;
//这个用来记录前一个节点的地址
public ListNode pre;
ListNode(int val){
this.val=val;
}
}
public ListNode head;
public ListNode last;
}
1.头插
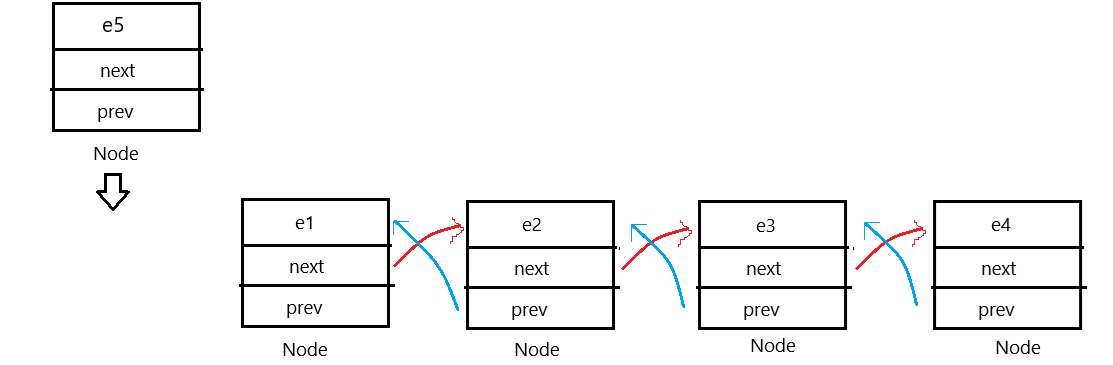
和单链表不一样的地方估计各位已经看出来了,没错,多了 prev 这个位置,用来记录前一个节点的地址,需要注意的是双向链表要判断为空情况,原因很简单,看图:

其他和单链表一样,代码如下:
public void addFirst(int data){
public void addFirst(int data){
ListNode node =new ListNode(data);
if(head==null){
head=last=node;
}
node.next=head;
head.pre=node;
head=node;
}
}
2.尾插
有了 last 节点会方便很多,不需要遍历链表找为空元素,所以思路非常简单,判断为空情况,然后直接用 last 尾插。图示(为空和头插一样):
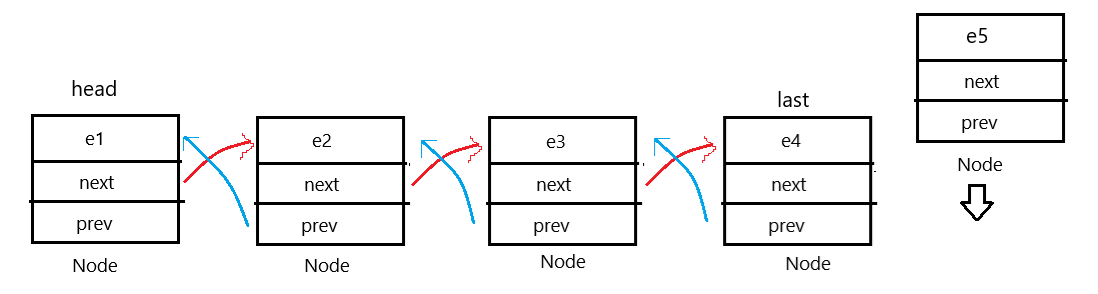
代码如下:
public void addLast(int data){
ListNode node =new ListNode(data);
if (head==null){
head=last=node;
}else {
last.next=node;
node.pre=last;
last=last.next;
}
}
3.任意位置插入
这和单链表完全一样,虽说多了一个记录节点,但还是要遍历一次。
图示:
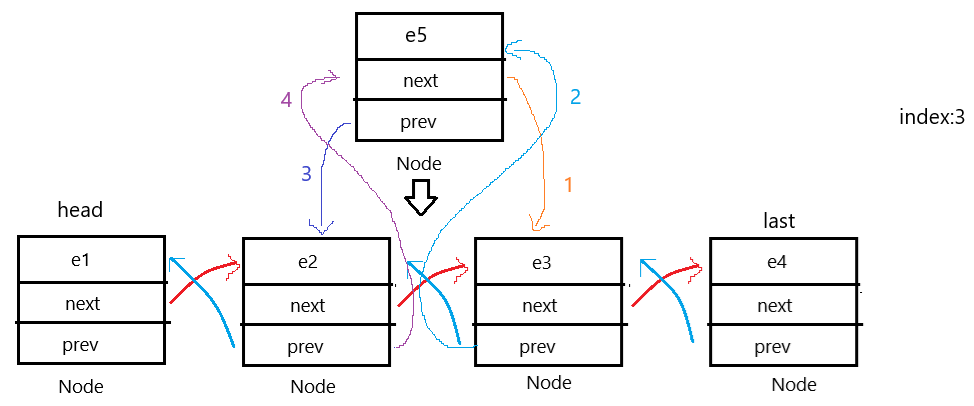
代码如下:
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
int len=size();
if (index<0 || index>len){
System.out.println("index位置不合法");
}
if(index==0){
addFirst(data);
}
if (index==len){
addLast(data);
}
ListNode node =new ListNode(data);
ListNode cur=head;
//查找可以写成一个方法
while (index-1!=0){
cur= cur.next;
index--;
}
node.next=cur;
cur.pre.next=node;
node.pre=cur.pre;
cur.pre=node;
}
4.查找关键字
和单链表一样。代码:
public boolean contains(int key){
if(head==null){
return false;
}
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur!=null){
if(cur.val==key){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
5.删除第一个key节点
直接上图示说明:
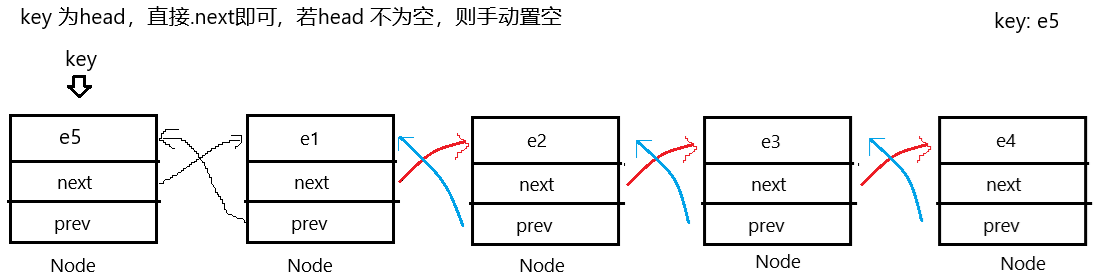
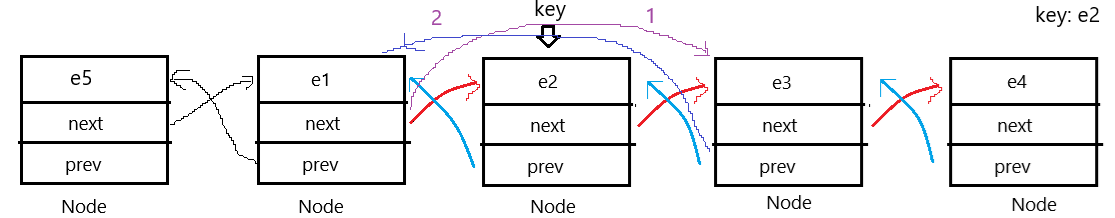
代码如下:
public void remove(int key){
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur!=null){
if(cur.val==key){
//开始删除
if(cur==head){
head=head.next;
if (head!=null){
head.pre=null;
}
else {
cur.pre.next=cur.next;
if(cur.next==null){
last=last.pre;
}else {
cur.next.pre=cur.pre;
}
}
return;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
}
}
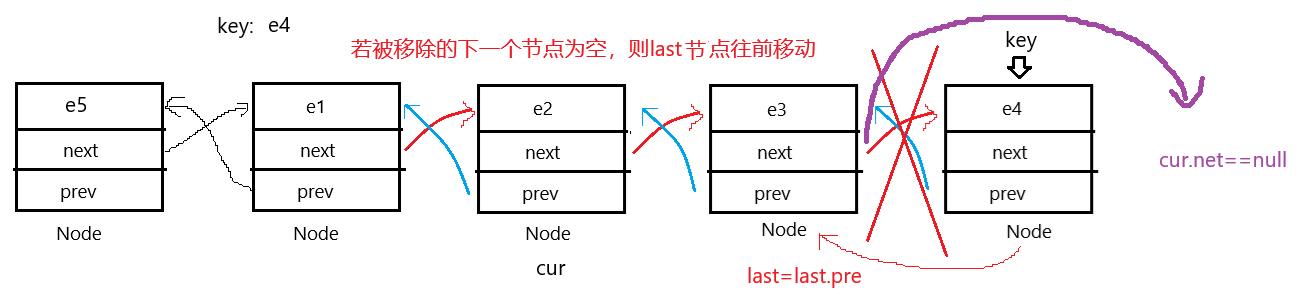
6.移除所有key节点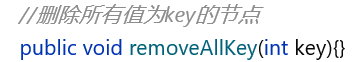
和上边的代码完全一样,思路也完全一样,跟着图走一遍就理解了。
7.链表长度和有效元素
和单链表完全一样。
代码:
public int size(){
int len=0;
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur!=null){
len++;
cur=cur.next;
}
return len;
}
public void display(){
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur!=null){
System.out.println(cur.val+" ");
cur=cur.next;
}
}
8.清除链表元素
遍历链表全部置空,记录节点也得置空。代码:
public void clear(){
ListNode cur =head;
while (cur!=null){
ListNode curN=cur.next;
cur.pre=null;
cur.next=null;
cur=curN;
}
head=last=null;
}
到这就全部完成了,是不是感觉双向链表更好用,需要考虑的限制没有单链表那么多,不过实际用起来各有利弊,后续有内容再补充。
---------------------------------------------------------------完---------------------------------------------------------------





















 1687
1687

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








