Mediator(中介者)模式
问题
在面向对象系统的设计和开发过程中, 对象之间的交互和通信是最为常见的情况, 因为对象间的交互本身就是一种通信。 在系统比较小的时候, 可能对象间的通信不是很多、 对象也比较少, 我们可以直接硬编码到各个对象的方法中。 但是当系统规模变大, 对象的量变引起系统复杂度的急剧增加, 对象间的通信也变得越来越复杂, 这时候我们就要提供一个专门处理对象间交互和通信的类,这个中介者就是 Mediator 模式。 Mediator 模式提供将对象间的交互和通讯封装在一个类中, 各个对象间的通信不必显势去声明和引用, 大大降低了系统的复杂性能(了解一个对象总比深入熟悉 n 个对象要好)。另外 Mediator 模式还带来了系统对象间的松耦合,这些将在讨论中详细给出。
模式选择
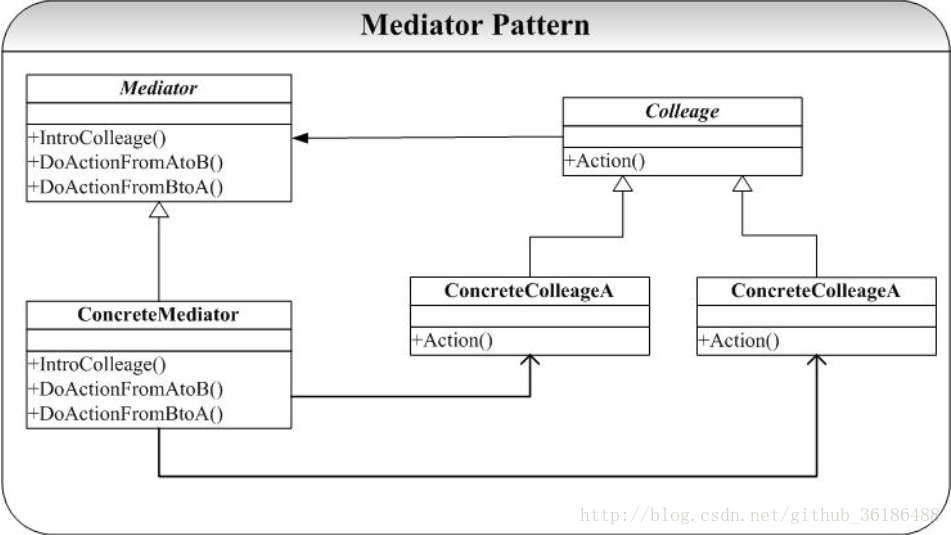
Mediator 模式典型的结构图为:
Mediator 模式中,每个 Colleague 维护一个 Mediator,当要进行交互,例如图中
ConcreteColleagueA 和 ConcreteColleagueB 之间的交互就可以通过ConcreteMediator 提供的DoActionFromAtoB 来处理, ConcreteColleagueA 和 ConcreteColleagueB 不必维护对各自的引用,甚至它们也不知道各个的存在。 Mediator 通过这种方式将多对多的通信简化为了一(Mediator) 对(Colleague)的通信 。
实现
完整代码示例(code)
Mediator 模式实现不是很困难, 这里为了方便初学者的学习和参考, 将给出完整的实现代码。
//Colleage.h
#ifndef _COLLEAGE_H_
#define _COLLEAGE_H_
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Mediator;
class Colleage
{
public:
virtual ~Colleage();
virtual void Aciton() = 0;
virtual void SetState(const string& sdt) = 0;
virtual string GetState() = 0;
protected:
Colleage();
Colleage(Mediator* mdt);
Mediator* _mdt;
private:
};
class ConcreteColleageA:public Colleage
{
public:
ConcreteColleageA();
ConcreteColleageA(Mediator* mdt);
~ConcreteColleageA();
void Aciton();
void SetState(const string& sdt);
string GetState();
protected:
private:
string _sdt;
};
class ConcreteColleageB:public Colleage
{
public:
ConcreteColleageB();
ConcreteColleageB(Mediator* mdt);
~ConcreteColleageB();
void Aciton();
void SetState(const string& sdt);
string GetState();
protected:
private:
string _sdt;
};
#endif //~_COLLEAGE_H_代码片断 2: Colleage.cpp
//Colleage.cpp
include "Mediator.h"
include "Colleage.h"
include <iostream>
using namespace std;
Colleage::Colleage()
{
//_sdt = " ";
}
Colleage::Colleage(Mediator* mdt)
{
this->_mdt = mdt;
//_sdt = " ";
}
Colleage::~Colleage()
{
}
ConcreteColleageA::ConcreteColleageA()
{
}
ConcreteColleageA::~ConcreteColleageA()
{
}
ConcreteColleageA::ConcreteColleageA(Mediator* mdt):Colleage(mdt)
{
}
string ConcreteColleageA::GetState()
{
return _sdt;
}
void ConcreteColleageA::SetState(const string& sdt)
{
_sdt = sdt;
}
void ConcreteColleageA::Aciton()
{
_mdt->DoActionFromAtoB();
cout<<"State of ConcreteColleageB:"<<" "<<this->GetState()<<endl;
}
ConcreteColleageB::ConcreteColleageB()
{
}
ConcreteColleageB::~ConcreteColleageB()
{
}
ConcreteColleageB::ConcreteColleageB(Mediator* mdt):Colleage(mdt)
{
}
void ConcreteColleageB::Aciton()
{
_mdt->DoActionFromBtoA();
cout<<"State of ConcreteColleageB:"<<" "<<this->GetState()<<endl;
}
string ConcreteColleageB::GetState()
{
return _sdt;
}
void ConcreteColleageB::SetState(const string& sdt)
{
_sdt = sdt;
}
代码片断 3: Mediator.h
//Mediator.h
ifndef MEDIATOR_H
define MEDIATOR_H
class Colleage;
class Mediator
{
public:
virtual ~Mediator();
virtual void DoActionFromAtoB() = 0;
virtual void DoActionFromBtoA() = 0;
protected:
Mediator();
private:
};
class ConcreteMediator:public Mediator
{
public:
ConcreteMediator();
ConcreteMediator(Colleage* clgA,Colleage* clgB);
~ConcreteMediator();
void SetConcreteColleageA(Colleage* clgA);
void SetConcreteColleageB(Colleage* clgB);
Colleage* GetConcreteColleageA();
Colleage* GetConcreteColleageB();
void IntroColleage(Colleage* clgA,Colleage* clgB);
void DoActionFromAtoB();
void DoActionFromBtoA();
protected:
private:
Colleage* _clgA;
Colleage* _clgB;
};
endif //~MEDIATOR_H代码片断 4: Mediator.cpp
//Mediator.cpp
include "Mediator.h"
include "Colleage.h"
Mediator::Mediator()
{
}
Mediator::~Mediator()
{
}
ConcreteMediator::ConcreteMediator()
{
}
ConcreteMediator::~ConcreteMediator()
{
}
ConcreteMediator::ConcreteMediator(Colleage* clgA,Colleage* clgB)
{
this->_clgA = clgA;
this->_clgB = clgB;
}
void ConcreteMediator::DoActionFromAtoB()
{
clgB->SetState(clgA->GetState());
}
void ConcreteMediator::SetConcreteColleageA(Colleage* clgA)
{
this->_clgA = clgA;
}
void ConcreteMediator::SetConcreteColleageB(Colleage* clgB)
{
this->_clgB = clgB;
}
Colleage* ConcreteMediator::GetConcreteColleageA()
{
return _clgA;
}
Colleage* ConcreteMediator::GetConcreteColleageB()
{
return _clgB;
}
void ConcreteMediator::IntroColleage(Colleage* clgA,Colleage* clgB)
{
this->_clgA = clgA;
this->_clgB = clgB;
}
void ConcreteMediator::DoActionFromBtoA()
{
clgA->SetState(clgB->GetState());
}
代码片断 5: main.cpp
//main.cpp
include "Mediator.h"
include "Colleage.h"
include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
ConcreteMediator* m = new ConcreteMediator();
ConcreteColleageA* c1 = new ConcreteColleageA(m);
ConcreteColleageB* c2 = new ConcreteColleageB(m);
m->IntroColleage(c1,c2);
c1->SetState("old");
c2->SetState("old");
c1->Aciton();
c2->Aciton();
cout<<endl;
c1->SetState("new");
c1->Aciton();
c2->Aciton();
cout<<endl;
c2->SetState("old");
c2->Aciton();
c1->Aciton();
return 0;
}






















 404
404

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








