Author: XiangguoSun
E-mail: sunxiangguodut@qq.com
References: Koller, Probabilistic Graphical Models Principles And Techniques
1. I-equivalence
Very different BN structures can actually encode the same set of conditional independence
assertions eg. the three structures below encode
(X⊥Y|Z)
:

Two graph structures 1 and 2 over are I-equivalent if (1)=(2) .
I-equivalence of two graphs implies:
• Any distribution P that can be factorized over one of these graphs can be factorized over other
• There is no intrinsic property of P that would allow us to associate it with one graph rath
Suppose we know that X and Y are correlated in the distrubtion P(X,Y)
We don’t know if the correct structure is:

2. skeleton
The skeleton of a Bayesian network graph over is an undirected graph over that contains an edge {X,Y} for every edge (X,Y) in .
note: we use {X,Y}to represent undirectional edge, (X,Y) for
directional edge.

If two networks have a common skeleton, then the set of trails between two variables is the same in both networks.But having the same trails is not enough for I-equivalence eg.

3. sufficient condition for I-equivalence
Theorem3.7
Let 1 and 2 be two graphs over . If 1 and 2 have the same skeleton and the same set of v-structures then they are I-equivalent.
But there are graphs that are I-equivalent but do not have the same set of v-structures. eg. two complete (fully-connected) graphs have the same skeleton but not the same v-structures.

Can we provide a stronger condition that corresponds to I-Equivalence?
4. immorality
A v-structure
X→Z←Y
is an immorality if there is no direct edge between
X
and

5. necessary and sufficient condition for I-equivalence
Theorem3.8
Let 1 and 2 be two graphs over . Then 1 and 2 have the same skeleton and the same set of immoralities if and only if they are I-equivalent.
6. a final characterization
An edge X→Y in a graph is said to be covered if PaY=PaX∪{X} .
Two graphs and are I-equivalent if and only if there exists a sequence of networks = 1,2,⋯,k=′ that are all I-equivalent to such that the only difference between i and i+1 is a single reversal of a covered edge.

In above figure, there is no any immorality in , neither in ′ , but both have the same skeleton. therefore, according to Theorem3.8, we conclude that and ′ are I-equivalent.
sunxiangguodut@qq.com
http://blog.csdn.net/github_36326955


I devote myself to dive into typical algorithms on machine learning and deep learning, especially the application in the area of computational personality. My research interests include computational personality, user portrait, online social network, computational society, and ML/DL. In fact you can find the internal connection between these concepts:
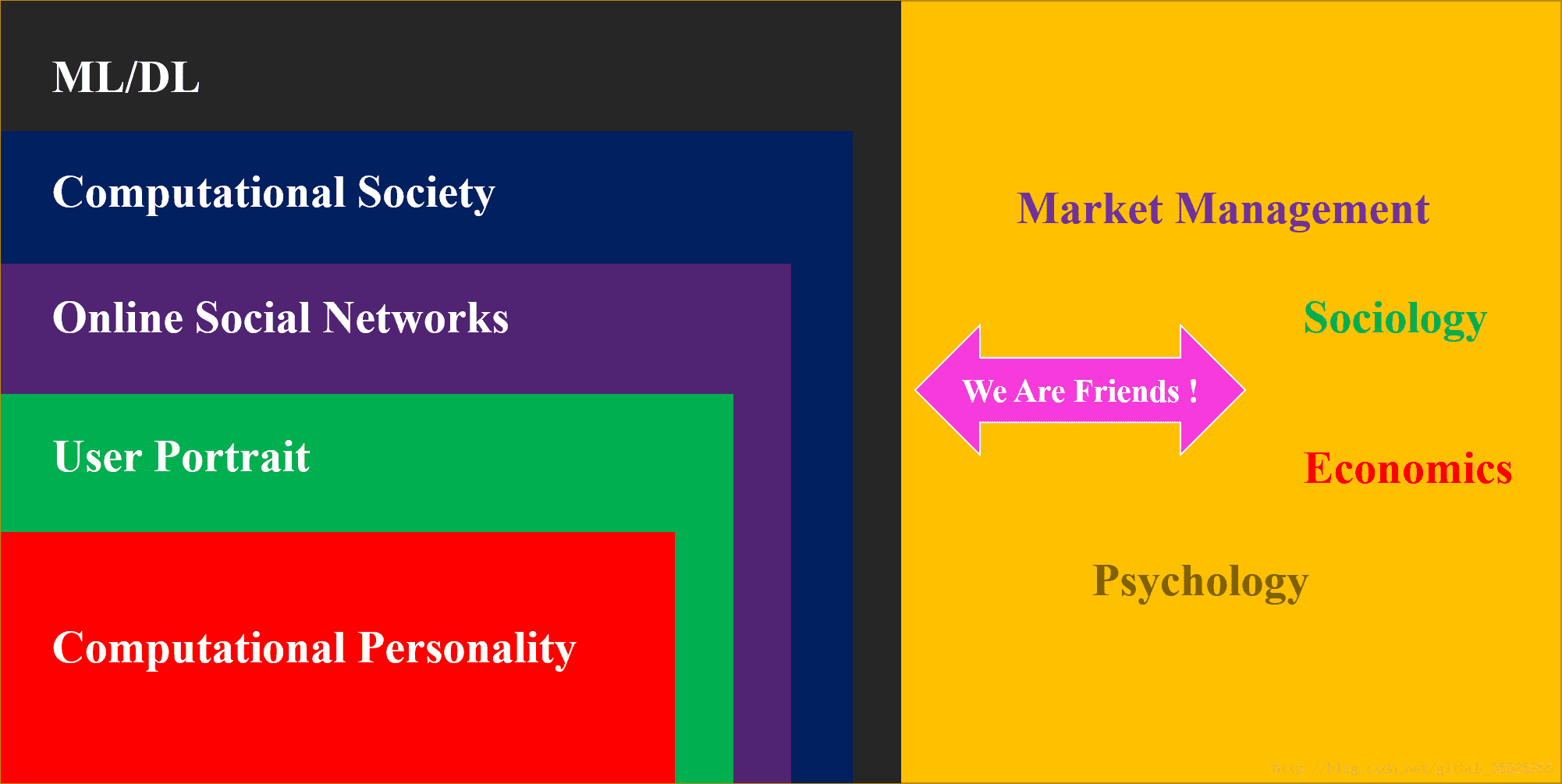
In this blog column, I will introduce some typical algorithms about machine learning and deep learning used in OSNs(Online Social Networks), which means we will include NLP, networks community, information diffusion,and individual recommendation system. Apparently, our ultimate target is to dive into user portrait , especially the issues on your personality analysis.
All essays are created by myself, and copyright will be reserved. You can use them for non-commercical intention and if you are so kind to donate me, you can scan the QR code below. All donation will be used to the library of charity for children in Lhasa.
手机扫一扫,即可:
























 1711
1711

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








