递归总要返回上一层,这就符合回溯法的性质。回溯法是暴力解法的一种,时间复杂度高,可用于某些特殊问题。
题目 1:
请设计一个函数,用来判断在一个矩阵中是否存在一条包含某字符串所有字符的路径。路径可以从矩阵中的任意一个格子开始,每一步可以在矩阵中向左,向右,向上,向下移动一个格子。如果一条路径经过了矩阵中的某一个格子,则之后不能再次进入这个格子。


例如 :
a b c e s f c s a d e e 这样的3 X 4 矩阵中包含一条字符串"bcced"的路径,但是矩阵中不包含"abcb"路径,因为字符串的第一个字符b占据了矩阵中的第一行第二个格子之后,路径不能再次进入该格子。
解决思路,类似于图论中深度优先遍历的思想
从任意一个格子开始:hasPath函数做的事情
以任意一个格子为起点,开始回溯:hasPathCore做的事情
例子:
要匹配字母:aba
当前访问的格子中字母为:a
周围的四个字母都没有访问过,为:e b d t
访问a后,访问b
b的周围是:n x j a
由于n x j都不符合下一个字母 a 的要求,a本身又被访问过,因此退回到 a,a的周围 e d t不符和要求,b路走不通,查找失败
import java.util.*;
import java.util.zip.CheckedOutputStream;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] matrix = {'a','b','c','e','s','f','c','s','a','d','e','e'};
int rows = 3;
int cols = 4;
char[] str = {'b','c','c','e','d'};
char[] str2 = {'a','b','c','d'};
System.out.println(hasPath(matrix,rows,cols,str));
}
public static boolean hasPath(char[] matrix, int rows, int cols, char[] str) {
if (matrix == null || rows<1 || cols<1 || str == null){
return false;
}
boolean[] visited = new boolean[rows * cols];// 默认false(Boolean不会被初始化,boolean作为基本类型才会)
int pathLen = 0;
for (int i=0; i<rows; ++i){
for (int j=0; j<cols; ++j){
if (hasPathCore(matrix,visited,str,rows,cols,i,j,pathLen)){
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public static boolean hasPathCore(char[] matrix,boolean[] visited, char[] str,int rows, int cols, int row, int col, int pathLen){
if (pathLen == str.length){
return true;
}
Boolean hasPath = false;
//1:查找当前单元是否去过
//2:判断单元周围是否有可以去的地方
//3:无路退回,返回false
//4:只有在当前单元和当前字符匹配,且周围单元和下一个字符匹配的前提下,才会返回true
System.out.println(row+" "+col+" "+pathLen);
if (row < rows
&& col < cols
&& row >= 0
&& col >=0
&& matrix[row * cols + col] == str[pathLen]
&& !visited[row * cols + col]){
pathLen++;
visited[row * cols + col] = true;
hasPath = hasPathCore(matrix,visited,str,rows,cols,row+1,col,pathLen)
||hasPathCore(matrix,visited,str,rows,cols,row-1,col,pathLen)
||hasPathCore(matrix,visited,str,rows,cols,row,col+1,pathLen)
||hasPathCore(matrix,visited,str,rows,cols,row,col-1,pathLen);
if (hasPath == false){
pathLen--;
visited[row * rows + col] = false;
}
}
return hasPath;
}
}
题目2
地上有一个m行和n列的方格。一个机器人从坐标0,0的格子开始移动,每一次只能向左,右,上,下四个方向移动一格,但是不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于k的格子。 例如,当k为18时,机器人能够进入方格(35,37),因为3+5+3+7 = 18。但是,它不能进入方格(35,38),因为3+5+3+8 = 19。请问该机器人能够达到多少个格子?
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(movingCount(18,50,50));
}
public static int movingCount(int threshold, int rows, int cols){
boolean[] visited = new boolean[rows * cols];
return movingCountCore(threshold,rows,cols,0,0,visited);
}
public static int movingCountCore(int threshold, int rows, int cols, int row, int col, boolean[] visited){
int count = 0;
if (row >= 0 && col >= 0
&& row < rows
&& col < cols
&& calDigitSum(row)+calDigitSum(col) <= threshold
&& visited[row * cols + col]==false){
visited[row * cols + col] = true;
count = 1 + movingCountCore(threshold,rows,cols,row+1,col,visited)
+movingCountCore(threshold,rows,cols,row-1,col,visited)
+movingCountCore(threshold,rows,cols,row,col+1,visited)
+movingCountCore(threshold,rows,cols,row,col-1,visited);
}
return count;
}
//计算一个数字各个位数之和
public static int calDigitSum(int val){
int sum = 0;
while (val > 0){
sum = sum + val % 10;
val = val / 10;
}
return sum;
}
}
LeetCode 17:电话号码的组合
给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。
给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。

示例:
输入:"23"
输出:["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"].
说明:
尽管上面的答案是按字典序排列的,但是你可以任意选择答案输出的顺序。



class Solution {
private Map<Character,String> map;
private List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
public void letterCombineCore(String digits,int index,String s){
if (index == digits.length()){
list.add(s);
return;
}
Character c = digits.charAt(index);
String words = this.map.get(c);
for (int i=0; i<words.length(); i++){
letterCombineCore(digits,index+1,s + words.charAt(i));
}
}
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
if (digits.length() == 0){
return new ArrayList<String>();
}
this.map = new HashMap<Character, String>();
this.map.put('2',"abc");
this.map.put('3',"def");
this.map.put('4',"ghi");
this.map.put('5',"jkl");
this.map.put('6',"mno");
this.map.put('7',"pqrs");
this.map.put('8',"tuv");
this.map.put('9',"wxyz");
this.letterCombineCore(digits,0,"");
return this.list;
}
}
LeetCode 51 N皇后问题
n 皇后问题研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
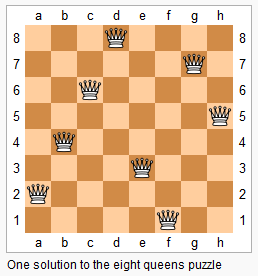
上图为 8 皇后问题的一种解法。
给定一个整数 n,返回所有不同的 n 皇后问题的解决方案。
每一种解法包含一个明确的 n 皇后问题的棋子放置方案,该方案中 ‘Q’ 和 ‘.’ 分别代表了皇后和空位。
示例:
输入: 4
输出: [
[".Q..", // 解法 1
"...Q",
"Q...",
"..Q."],
["..Q.", // 解法 2
"Q...",
"...Q",
".Q.."]
]
解释: 4 皇后问题存在两个不同的解法。
使用回溯法解决这个问题,由于所有皇后间
行不同 :从第0行开始,每次递归,行号+1,这样,每次添加元素,行号都不相同。
列不同 :维持一个数组 colCheck[n], 如果n列放置了元素,就设置为true,下次放元素,先判断 colCheck[n] 是否为true。
正对角线位不同 :正对角线一共有 2n-1条,编号=行号+列号,同样可以维持一个布尔类型的数组,用于表示该对角线是否去过。

反对角线位不同:反对角线一共有 2n-1条,编号=行-列+n-1(也可以是 列-行+n-1),同样可以维持一个布尔类型的数组,用于表示该对角线是否去过。

1:第一行添加一个元素
2:递归到下一行,遍历所有的列,如果存在元素 列 正 逆 对角线都没有访问过,加入元素
3:不断递归,直到行号=n
class Solution {
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
int[][] ans;
boolean[] colCheck;
boolean[] diagnol;
boolean[] diagnolReverse;
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
colCheck = new boolean[n];
diagnol = new boolean[2*n-1];
diagnolReverse = new boolean[2*n-1];
ans = new int[n][n];
this.solveQueensCore(n,0);
return res;
}
private void solveQueensCore(int n,int row){
if (row == n){
ArrayList<String> oneRes = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i=0; i<n; i++){
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
for (int j=0; j<n; j++){
if (ans[i][j] == 0){
builder.append('.');
}else {
builder.append('Q');
}
}
oneRes.add(builder.toString());
}
res.add(oneRes);
}
for (int i=0; i<n; i++){
if (!colCheck[i] && !diagnol[i+row] && !diagnolReverse[i-row+n-1]){
colCheck[i] = true;
diagnol[i+row] = true;
diagnolReverse[i-row+n-1] = true;
ans[row][i] = 1;
solveQueensCore(n,row+1);
colCheck[i] = false;
diagnol[i+row] = false;
diagnolReverse[i-row+n-1] = false;
ans[row][i] = 0;
}
}
return;
}
}```






















 5万+
5万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








