1、关于adapter 的
public abstract View getView (int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent)
· 使用convertview来reuse回收view;
· 由于使用findviewbyID消耗太多资源,考虑使用viewholder来缓存view数据;
2、关于background的drawable缩放效率;
· 使用系统自动缩放背景图片非常消耗资源;
· 所以在使用view的图片时可以预先缩放,比如:
originalImage=Bitmap.createScaledBitmap(originalImage,view.getWidth(),
view.getHeight,true)3、关于Window的background(android 1.6以上已优化)
· 在1.5之前的Android 会绘制background消耗资源,所以如果开发全屏应用或者view占满全屏的情况,使用
<style android:name="Theme.nobackground" android:parent="android.theme"/>
;
4、关于invalid;
view的invalidate 绘制会重绘制整个screen,所以最好使用invalid(Rectangle),或者传入坐标去设置绘制区域;
5、
· 使用view hierarchy;
· 使用viewstub 参考:http://blog.csdn.net/hitlion2008/article/details/6737537/
在 开发应用程序的时候,经常会遇到这样的情况,会在运行时动态根据条件来决定显示哪个View或某个布局。那么最通常的想法就是把可能用到的View都写在上面,先把它们的可见性都设为View.GONE,然后在代码中动态的更改它的可见性。这样的做法的优点是逻辑简单而且控制起来比较灵活。但是它的缺点就是,耗费资源。虽然把View的初始可见View.GONE但是在Inflate布局的时候View仍然会被Inflate,也就是说仍然会创建对象,会被实例化,会被设置属性。也就是说,会耗费内存等资源。
推荐的做法是使用android.view.ViewStub,ViewStub是一个轻量级的View,它一个看不见的,不占布局位置,占用资源非常小的控件。可以为ViewStub指定一个布局,在Inflate布局的时候,只有ViewStub会被初始化,然后当ViewStub被设置为可见的时候,或是调用了ViewStub.inflate()的时候,ViewStub所向的布局就会被Inflate和实例化,然后ViewStub的布局属性都会传给它所指向的布局。这样,就可以使用ViewStub来方便的在运行时,要还是不要显示某个布局。
但ViewStub也不是万能的,下面总结下ViewStub能做的事儿和什么时候该用ViewStub,什么时候该用可见性的控制。
首先来说说ViewStub的一些特点:
1. ViewStub只能Inflate一次,之后ViewStub对象会被置为空。按句话说,某个被ViewStub指定的布局被Inflate后,就不会够再通过ViewStub来控制它了。
2. ViewStub只能用来Inflate一个布局文件,而不是某个具体的View,当然也可以把View写在某个布局文件中。
基于以上的特点,那么可以考虑使用ViewStub的情况有:
1. 在程序的运行期间,某个布局在Inflate后,就不会有变化,除非重新启动。
因为ViewStub只能Inflate一次,之后会被置空,所以无法指望后面接着使用ViewStub来控制布局。所以当需要在运行时不止一次的显示和隐藏某个布局,那么ViewStub是做不到的。这时就只能使用View的可见性来控制了。
2. 想要控制显示与隐藏的是一个布局文件,而非某个View。
因为设置给ViewStub的只能是某个布局文件的Id,所以无法让它来控制某个View。
所以,如果想要控制某个View(如Button或TextView)的显示与隐藏,或者想要在运行时不断的显示与隐藏某个布局或View,只能使用View的可见性来控制。
下面来看一个实例
在这个例子中,要显示二种不同的布局,一个是用TextView显示一段文字,另一个则是用ImageView显示一个图片。这二个是在onCreate()时决定是显示哪一个,这里就是应用ViewStub的最佳地点。
先来看看布局,一个是主布局,里面只定义二个ViewStub,一个用来控制TextView一个用来控制ImageView,另外就是一个是为显示文字的做的TextView布局,一个是为ImageView而做的布局:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <LinearLayout
- xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:orientation="vertical"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:gravity="center_horizontal">
- <ViewStub
- android:id="@+id/viewstub_demo_text"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_marginLeft="5dip"
- android:layout_marginRight="5dip"
- android:layout_marginTop="10dip"
- android:layout="@layout/viewstub_demo_text_layout"/>
- <ViewStub
- android:id="@+id/viewstub_demo_image"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_marginLeft="5dip"
- android:layout_marginRight="5dip"
- android:layout="@layout/viewstub_demo_image_layout"/>
- </LinearLayout>
<span style="font-size:12px;color:#ff6666;background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);"><?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:gravity="center_horizontal">
<ViewStub
android:id="@+id/viewstub_demo_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dip"
android:layout_marginRight="5dip"
android:layout_marginTop="10dip"
android:layout="@layout/viewstub_demo_text_layout"/>
<ViewStub
android:id="@+id/viewstub_demo_image"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dip"
android:layout_marginRight="5dip"
android:layout="@layout/viewstub_demo_image_layout"/>
</LinearLayout></span>为TextView的布局:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <LinearLayout
- xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:orientation="vertical"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content">
- <TextView
- android:id="@+id/viewstub_demo_textview"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:background="#aa664411"
- android:textSize="16sp"/>
- </LinearLayout>
<span style="font-size:12px;color:#ff6666;background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);"><?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/viewstub_demo_textview"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#aa664411"
android:textSize="16sp"/>
</LinearLayout></span>为ImageView的布局:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <LinearLayout
- xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:orientation="vertical"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content">
- <ImageView
- android:id="@+id/viewstub_demo_imageview"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
- </LinearLayout>
<span style="font-size:12px;color:#ff6666;background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);"><?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/viewstub_demo_imageview"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout></span>下面来看代码,决定来显示哪一个,只需要找到相应的ViewStub然后调用其infalte()就可以获得相应想要的布局:
- package com.effective;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.view.ViewStub;
- import android.widget.ImageView;
- import android.widget.TextView;
- public class ViewStubDemoActivity extends Activity {
- @Override
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.viewstub_demo_activity);
- if ((((int) (Math.random() * 100)) & 0x01) == 0) {
- // to show text
- // all you have to do is inflate the ViewStub for textview
- ViewStub stub = (ViewStub) findViewById(R.id.viewstub_demo_text);
- stub.inflate();
- TextView text = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.viewstub_demo_textview);
- text.setText("The tree of liberty must be refreshed from time to time" +
- " with the blood of patroits and tyrants! Freedom is nothing but " +
- "a chance to be better!");
- } else {
- // to show image
- // all you have to do is inflate the ViewStub for imageview
- ViewStub stub = (ViewStub) findViewById(R.id.viewstub_demo_image);
- stub.inflate();
- ImageView image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.viewstub_demo_imageview);
- image.setImageResource(R.drawable.happy_running_dog);
- }
- }
- }
<span style="font-size:12px;color:#ff6666;background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">package com.effective;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.ViewStub;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class ViewStubDemoActivity extends Activity {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.viewstub_demo_activity);
if ((((int) (Math.random() * 100)) & 0x01) == 0) {
// to show text
// all you have to do is inflate the ViewStub for textview
ViewStub stub = (ViewStub) findViewById(R.id.viewstub_demo_text);
stub.inflate();
TextView text = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.viewstub_demo_textview);
text.setText("The tree of liberty must be refreshed from time to time" +
" with the blood of patroits and tyrants! Freedom is nothing but " +
"a chance to be better!");
} else {
// to show image
// all you have to do is inflate the ViewStub for imageview
ViewStub stub = (ViewStub) findViewById(R.id.viewstub_demo_image);
stub.inflate();
ImageView image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.viewstub_demo_imageview);
image.setImageResource(R.drawable.happy_running_dog);
}
}
}</span>运行结果:
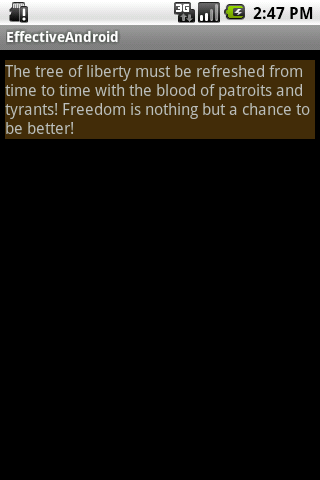

使用的时候的注意事项:
1. 某些布局属性要加在ViewStub而不是实际的布局上面,才会起作用,比如上面用的android:layout_margin*系列属性,如果加在TextView上面,则不会起作用,需要放在它的ViewStub上面才会起作用。而ViewStub的属性在inflate()后会都传给相应的布局。
· 使用<merge>标签,不多说,减少布局层级
6、关于内存分配和回收,内存回收(gc)的时候,界面会卡顿,所有工作都不能进行,所以在绘制界面的时候,
可以使用debug类限制回收和内存分配,最后再释放它。
7、使用DDMS来查看内存分配情况;
8、softReferences和weakReferences
softReferences用于缓存数据,当所有指向对象的指针都是softReferences时,gc会考虑收回对象占用的内存;
假定垃圾回收器确定在某一时间点上某个对象是弱可到达对象。这时,它将自动清除针对此对象的所有弱引用;






















 420
420

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








