优先队列
一种常见的数据结构,需要支持两种操作:删除最大(最小)元素和插入元素。这种数据类型叫做优先队列。
API
MaxPQ()//创建一个优先队列
MaxPQ(int max)//创建一个最大容量为max的优先队列
MaxPQ(key[] a)//用a[]中的元素创建一个优先队列
void Insert()//向优先队列中插入一个元素
key max()//向优先队列中插入一个元素
key delMax()//删除并返回最大元素
boolean isEmpty()//返回队列是否为空
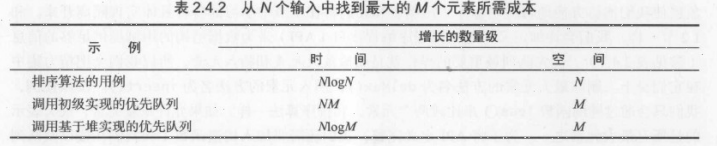
int size()//返回优先队列中的元素个数问题:输入N个字符串,每个字符串都对应着一个整数,你的任务就是从中找出最大的(或者最小的)M个整数(及其关联的字符串)。这些输入可能是金融事务,例如Transaction类。在某些应用场景中,输入量可能非常巨大,甚至可以任务输入是无限的。解决这个问题的一种方法是将输入排序然后从中找出M个最大的元素,但是我们已经说明了输入将会很庞大,另一种方法就是将每个新的输入和已知的M个最大的元素比价,但除非M较小,否则这种比较的代价会非常高昂。只要能够有效地实现insert()和delMin()就能解决这个任务
初级实现
- 数组实现(无序):删的时才找最大的元素
- 有序数组实现:insert的之后就排序
- 链接表示法:基于链表的下压栈,可以选择修改Push或者Pop来实现功能
对比(使用堆是比较理想的,下面将会讨论):
堆得定义
定义:当一棵二叉树的每个结点都大于等于它的两个子节点时,它称为堆有序的
相应地,在堆有序的二叉树中,每个结点都小于等于它的父节点。从任意结点向上,我们都能得到一列非递减的元素;从任意结点向下,我们都能得到一列非递增的元素。特别的:
二叉堆表示法:
二叉堆:就是堆有序的完全二叉树,元素在数组中按照层级存储(一层一层的放入数组中,不用数组的第一个元素)。下面简称堆
堆中:位置K的结点的父节点的位置为k/2,子节点的位置分别是2k和2k+1
一个结论:一棵大小为N的完全二叉树的高度为lgN
堆的算法
堆的有序化:就是使堆有序。一般会遇到两种情况:
当某个节点的优先级上升(或是在堆底加入一个新的元素时),我们需要由下至上的恢复堆的顺序(上浮, 和父节点比较,大就交换)。
相反,我们要由上至下恢复元素(下沉,和子节点中较大的元素交换)。
给出基于堆得有序优先队列代码(注意下沉和上浮操作,不难):
public class MaxPQ<Key> implements Iterable<Key> {
private Key[] pq; // store items at indices 1 to N
private int N; // number of items on priority queue
private Comparator<Key> comparator; // optional Comparator
public MaxPQ(int initCapacity) {
pq = (Key[]) new Object[initCapacity + 1];
N = 0;
}
public MaxPQ() {
this(1);
}
public MaxPQ(int initCapacity, Comparator<Key> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
pq = (Key[]) new Object[initCapacity + 1];
N = 0;
}
public MaxPQ(Comparator<Key> comparator) {
this(1, comparator);
}
public MaxPQ(Key[] keys) {
N = keys.length;
pq = (Key[]) new Object[keys.length + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
pq[i+1] = keys[i];
for (int k = N/2; k >= 1; k--)
sink(k);
assert isMaxHeap();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return N == 0;
}
public int size() {
return N;
}
public Key max() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow");
return pq[1];
}
// helper function to double the size of the heap array
private void resize(int capacity) {
assert capacity > N;
Key[] temp = (Key[]) new Object[capacity];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
temp[i] = pq[i];
}
pq = temp;
}
public void insert(Key x) {
// double size of array if necessary
if (N >= pq.length - 1) resize(2 * pq.length);
// add x, and percolate it up to maintain heap invariant
pq[++N] = x;
swim(N);
assert isMaxHeap();
}
public Key delMax() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow");
Key max = pq[1];
exch(1, N--);
sink(1);
pq[N+1] = null; // to avoid loiterig and help with garbage collection
if ((N > 0) && (N == (pq.length - 1) / 4)) resize(pq.length / 2);
assert isMaxHeap();
return max;
}
private void swim(int k) {
while (k > 1 && less(k/2, k)) {
exch(k, k/2);
k = k/2;
}
}
private void sink(int k) {
while (2*k <= N) {
int j = 2*k;
if (j < N && less(j, j+1)) j++;
if (!less(k, j)) break;
exch(k, j);
k = j;
}
}
private boolean less(int i, int j) {
if (comparator == null) {
return ((Comparable<Key>) pq[i]).compareTo(pq[j]) < 0;
}
else {
return comparator.compare(pq[i], pq[j]) < 0;
}
}
private void exch(int i, int j) {
Key swap = pq[i];
pq[i] = pq[j];
pq[j] = swap;
}
// is pq[1..N] a max heap?
private boolean isMaxHeap() {
return isMaxHeap(1);
}
// is subtree of pq[1..N] rooted at k a max heap?
private boolean isMaxHeap(int k) {
if (k > N) return true;
int left = 2*k, right = 2*k + 1;
if (left <= N && less(k, left)) return false;
if (right <= N && less(k, right)) return false;
return isMaxHeap(left) && isMaxHeap(right);
}
public Iterator<Key> iterator() {
return new HeapIterator();
}
private class HeapIterator implements Iterator<Key> {
// create a new pq
private MaxPQ<Key> copy;
// add all items to copy of heap
// takes linear time since already in heap order so no keys move
public HeapIterator() {
if (comparator == null) copy = new MaxPQ<Key>(size());
else copy = new MaxPQ<Key>(size(), comparator);
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
copy.insert(pq[i]);
}
public boolean hasNext() { return !copy.isEmpty(); }
public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); }
public Key next() {
if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException();
return copy.delMax();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MaxPQ<String> pq = new MaxPQ<String>();
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
String item = StdIn.readString();
if (!item.equals("-")) pq.insert(item);
else if (!pq.isEmpty()) StdOut.print(pq.delMax() + " ");
}
StdOut.println("(" + pq.size() + " left on pq)");
}
}索引优先队列
能引用已经进入优先队列中的元素。多了change、delete等方法,能够将索引为K的元素设为传进来的item以及删除索引位置的key。代码(这里采用的是MinPQ):
注意理解这个的数组pq和keys的作用(使用qp将不断变化的pq数组的元素和索引挂钩,keys存值,很聪明的想法)
public class IndexMinPQ<Key extends Comparable<Key>> implements Iterable<Integer> {
private int maxN; // maximum number of elements on PQ
private int N; // number of elements on PQ
private int[] pq; // binary heap using 1-based indexing
private int[] qp; // inverse of pq - qp[pq[i]] = pq[qp[i]] = i
private Key[] keys; // keys[i] = priority of i
public IndexMinPQ(int maxN) {
if (maxN < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.maxN = maxN;
keys = (Key[]) new Comparable[maxN + 1]; // make this of length maxN??
pq = new int[maxN + 1];
qp = new int[maxN + 1]; // make this of length maxN??
for (int i = 0; i <= maxN; i++)
qp[i] = -1;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return N == 0;
}
public boolean contains(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
return qp[i] != -1;
}
public int size() {
return N;
}
public void insert(int i, Key key) {
if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
if (contains(i)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("index is already in the priority queue");
N++;
qp[i] = N;
pq[N] = i;
keys[i] = key;
swim(N);
}
public int minIndex() {
if (N == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow");
return pq[1];
}
public Key minKey() {
if (N == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow");
return keys[pq[1]];
}
public int delMin() {
if (N == 0) throw new NoSuchElementException("Priority queue underflow");
int min = pq[1];
exch(1, N--);
sink(1);
assert min == pq[N+1];
qp[min] = -1; // delete
keys[min] = null; // to help with garbage collection
pq[N+1] = -1; // not needed
return min;
}
public Key keyOf(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue");
else return keys[i];
}
public void changeKey(int i, Key key) {
if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue");
keys[i] = key;
swim(qp[i]);
sink(qp[i]);
}
public void change(int i, Key key) {
changeKey(i, key);
}
public void decreaseKey(int i, Key key) {
if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue");
if (keys[i].compareTo(key) <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Calling decreaseKey() with given argument would not strictly decrease the key");
keys[i] = key;
swim(qp[i]);
}
public void increaseKey(int i, Key key) {
if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue");
if (keys[i].compareTo(key) >= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Calling increaseKey() with given argument would not strictly increase the key");
keys[i] = key;
sink(qp[i]);
}
public void delete(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i >= maxN) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
if (!contains(i)) throw new NoSuchElementException("index is not in the priority queue");
int index = qp[i];
exch(index, N--);
swim(index);
sink(index);
keys[i] = null;
qp[i] = -1;
}
private boolean greater(int i, int j) {
return keys[pq[i]].compareTo(keys[pq[j]]) > 0;
}
private void exch(int i, int j) {
int swap = pq[i];
pq[i] = pq[j];
pq[j] = swap;
qp[pq[i]] = i;
qp[pq[j]] = j;
}
private void swim(int k) {
while (k > 1 && greater(k/2, k)) {
exch(k, k/2);
k = k/2;
}
}
private void sink(int k) {
while (2*k <= N) {
int j = 2*k;
if (j < N && greater(j, j+1)) j++;
if (!greater(k, j)) break;
exch(k, j);
k = j;
}
}
public Iterator<Integer> iterator() { return new HeapIterator(); }
private class HeapIterator implements Iterator<Integer> {
// create a new pq
private IndexMinPQ<Key> copy;
// add all elements to copy of heap
// takes linear time since already in heap order so no keys move
public HeapIterator() {
copy = new IndexMinPQ<Key>(pq.length - 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
copy.insert(pq[i], keys[pq[i]]);
}
public boolean hasNext() { return !copy.isEmpty(); }
public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); }
public Integer next() {
if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException();
return copy.delMin();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// insert a bunch of strings
String[] strings = { "it", "was", "the", "best", "of", "times", "it", "was", "the", "worst" };
IndexMinPQ<String> pq = new IndexMinPQ<String>(strings.length);
for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) {
pq.insert(i, strings[i]);
}
// delete and print each key
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int i = pq.delMin();
StdOut.println(i + " " + strings[i]);
}
StdOut.println();
// reinsert the same strings
for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) {
pq.insert(i, strings[i]);
}
// print each key using the iterator
for (int i : pq) {
StdOut.println(i + " " + strings[i]);
}
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
pq.delMin();
}
}
}索引优先队列的使用案例:
多项归并问题:将多个有序的输入流归并成一个有序(按照优先级)的输入流。代码:
public class Multiway {
// This class should not be instantiated.
private Multiway() { }
// merge together the sorted input streams and write the sorted result to standard output
private static void merge(In[] streams) {
int N = streams.length;
IndexMinPQ<String> pq = new IndexMinPQ<String>(N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
if (!streams[i].isEmpty())
pq.insert(i, streams[i].readString());
// Extract and print min and read next from its stream.
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
StdOut.print(pq.minKey() + " ");
int i = pq.delMin();
if (!streams[i].isEmpty())
pq.insert(i, streams[i].readString());
}
StdOut.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = args.length;
In[] streams = new In[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
streams[i] = new In(args[i]);
merge(streams);
}
} 堆排序
可以把任意优先队列变成一种排序方法。将所有元素插入一个查找最小元素的优先队列,然后再重复调用删除最小元素的操作来讲它们按顺序删去。用无序数组实现优先队列这么做相当于进行一次插入排序。下面讨论堆排序。
堆的构造:从中间点到左边扫描数组(如下图中的5开始),并调用sink函数(不要从左到右,因为后半元素都是叶子节点,还调用sink效率不高。)
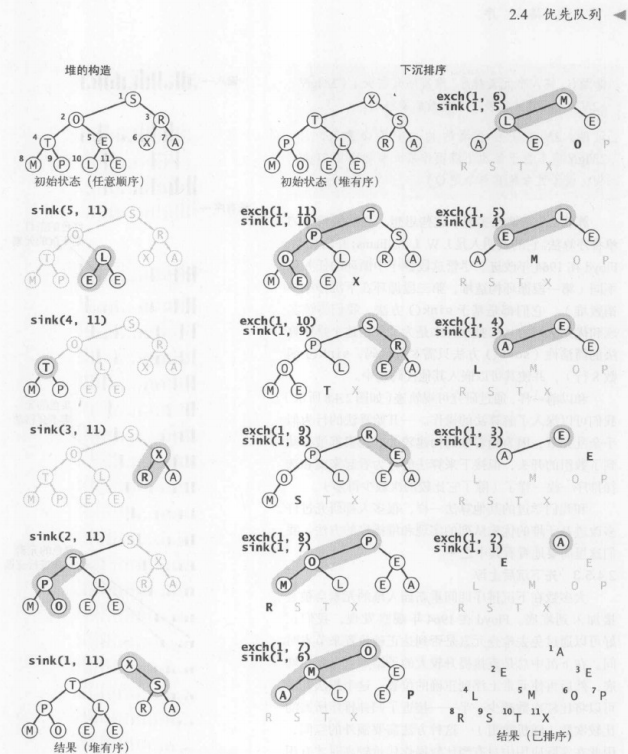

代码:
public class HeapSort {
public static void sort(int[] a){
int N = a.length;
int[] keys = new int[N+1];
//注意,堆的数据结构是从1开始的,0不用
for (int i = 1; i < keys.length; i++) {
keys[i] = a[i-1];
}
// //构造堆,使得堆是有序的
for(int k = N/2;k>=1;k--) sink(keys,k,N);
//排序,相当于毁掉堆
while(N>1){
exch(keys,1,N--);
sink(keys,1,N);
}
//重新写回数组
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
a[i] = keys[i+1];
}
}
private static void sink(int[] a, int k, int N) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
while(2*k<=N){
int j = 2*k;
if (j < N && less(a[j], a[j+1])) j++;
if (less(a[j], a[k])) break;
exch(a, k, j);
k = j;
}
}
private static boolean less(int k, int j) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (k<j) return true;
return false;
}
private static void exch(int[] a, int i, int n) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[n];
a[n] = temp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {2,4,7,8,2,1,0,9};
HeapSort.sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}




























 999
999

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








