查找
这里使用符号表这个词来描述一张抽象的表格,我们会将信息存储在其中(值),然后按照指定的键来搜索并获取这些信息。符号表有时也被称为字典或者索引(说白了就是Map)
符号表
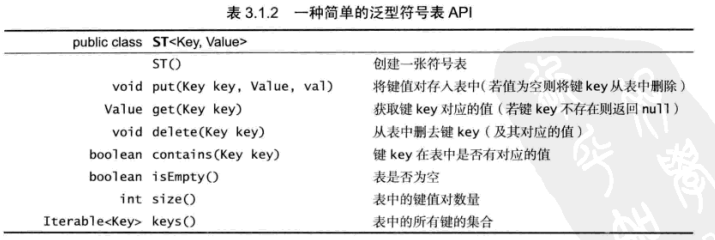
部分API
实现的注意事项:
每个键只对应着一个值;
当插入键值重复时,覆盖旧值;
键不能为空;值不能为空(这条规则可以拿来删除元素,put(key,null))
删除:分为延时删除(如上面的put(key, null))和及时删除(delete())
有序符号表的实现(有序的API会多一点,比如找最大、最小)
按照value排序的表(内部直接使用了TreeMap ,因为标准库的TreeMap是基于红黑树的,性能很好),后面将会讨论怎么一步一步地选择优化到这个ST版本。
public class ST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> implements Iterable<Key> {
private TreeMap<Key, Value> st;
public ST() {
st = new TreeMap<Key, Value>();
}
public Value get(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException("called get() with null key");
return st.get(key);
}
public void put(Key key, Value val) {
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException("called put() with null key");
if (val == null) st.remove(key);
else st.put(key, val);
}
public void delete(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException("called delete() with null key");
st.remove(key);
}
public boolean contains(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException("called contains() with null key");
return st.containsKey(key);
}
public int size() {
return st.size();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
public Iterable<Key> keys() {
return st.keySet();
}
public Iterator<Key> iterator() {
return st.keySet().iterator();
}
public Key min() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("called min() with empty symbol table");
return st.firstKey();
}
public Key max() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("called max() with empty symbol table");
return st.lastKey();
}
public Key ceiling(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException("called ceiling() with null key");
Key k = st.ceilingKey(key);
if (k == null) throw new NoSuchElementException("all keys are less than " + key);
return k;
}
public Key floor(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException("called floor() with null key");
Key k = st.floorKey(key);
if (k == null) throw new NoSuchElementException("all keys are greater than " + key);
return k;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ST<String, Integer> st = new ST<String, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; !StdIn.isEmpty(); i++) {
String key = StdIn.readString();
st.put(key, i);
}
for (String s : st.keys())
StdOut.println(s + " " + st.get(s));
}
}应用
统计某个文件(英文小说)的单词(满足一定长度)出现的频率,输出频率最高的(一个),也是后面其他实现的一个标准评价试验:
public class FrequencyCounter {
// Do not instantiate.
private FrequencyCounter() { }
public static void main(String[] args) {
int distinct = 0, words = 0;
int minlen = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
ST<String, Integer> st = new ST<String, Integer>();
// compute frequency counts
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
String key = StdIn.readString();
if (key.length() < minlen) continue;
words++;
if (st.contains(key)) {
st.put(key, st.get(key) + 1);
}
else {
st.put(key, 1);
distinct++;
}
}
// find a key with the highest frequency count
String max = "";
st.put(max, 0);
for (String word : st.keys()) {
if (st.get(word) > st.get(max))
max = word;
}
StdOut.println(max + " " + st.get(max));
StdOut.println("distinct = " + distinct);
StdOut.println("words = " + words);
}
}基于无序链表中的顺序查找实现
用链表实现符号表,下图是使用案例的轨迹:
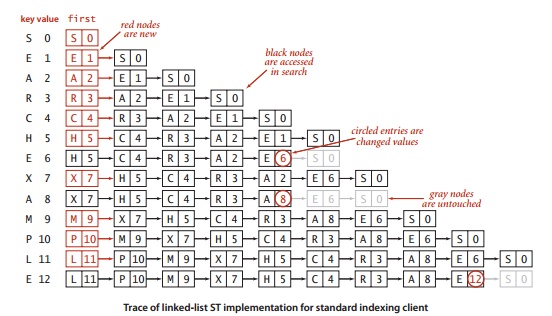
代码(注意理解删除键那里的写法):
public class SequentialSearchST<Key, Value> {
private int N; // number of key-value pairs
private Node first; // the linked list of key-value pairs
// a helper linked list data type
private class Node {
private Key key;
private Value val;
private Node next;
public Node(Key key, Value val, Node next) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
public SequentialSearchST() {
}
public int size() {
return N;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
public boolean contains(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException("argument to contains() is null");
return get(key) != null;
}
public Value get(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException("argument to get() is null");
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (key.equals(x.key))
return x.val;
}
return null;
}
public void put(Key key, Value val) {
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException("first argument to put() is null");
if (val == null) {
delete(key);
return;
}
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (key.equals(x.key)) {
x.val = val;
return;
}
}
first = new Node(key, val, first);
N++;
}
public void delete(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException("argument to delete() is null");
first = delete(first, key);
}
//递归调用,删除那个键
private Node delete(Node x, Key key) {
if (x == null) return null;
if (key.equals(x.key)) {
N--;
return x.next;
}
x.next = delete(x.next, key);
return x;
}
public Iterable<Key> keys() {
Queue<Key> queue = new Queue<Key>();
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
queue.enqueue(x.key);
return queue;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SequentialSearchST<String, Integer> st = new SequentialSearchST<String, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; !StdIn.isEmpty(); i++) {
String key = StdIn.readString();
st.put(key, i);
}
for (String s : st.keys())
StdOut.println(s + " " + st.get(s));
}
}
命中:成功的查找,未命中:失败的查找
因此:基于链表的实现以及顺序查找是非常低效的,无法满足处理庞大输入问题的需求
基于有序数组中的二分查找实现
键和值分别用一个数组来保存(put、delete的时候要移动数组所以消耗大)
注意floor和ceiling的实现
public class BinarySearchST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {
private static final int INIT_CAPACITY = 2;
private Key[] keys;
private Value[] vals;
private int N = 0;
public BinarySearchST() {
this(INIT_CAPACITY);
}
public BinarySearchST(int capacity) {
keys = (Key[]) new Comparable[capacity];
vals = (Value[]) new Object[capacity];
}
// resize the underlying arrays
private void resize(int capacity) {
assert capacity >= N;
Key[] tempk = (Key[]) new Comparable[capacity];
Value[] tempv = (Value[]) new Object[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
tempk[i] = keys[i];
tempv[i] = vals[i];
}
vals = tempv;
keys = tempk;
}
public int size() {
return N;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
public boolean contains(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException("argument to contains() is null");
return get(key) != null;
}
public Value get(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException("argument to get() is null");
if (isEmpty()) return null;
int i = rank(key);
if (i < N && keys[i].compareTo(key) == 0) return vals[i];
return null;
}
//得到严格比key小的键个数
public int rank(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException("argument to rank() is null");
int lo = 0, hi = N-1;
while (lo <= hi) {
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
int cmp = key.compareTo(keys[mid]);
if (cmp < 0) hi = mid - 1;
else if (cmp > 0) lo = mid + 1;
else return mid;
}
return lo;
}
public void put(Key key, Value val) {
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException("first argument to put() is null");
if (val == null) {
delete(key);
return;
}
int i = rank(key);
// key is already in table
if (i < N && keys[i].compareTo(key) == 0) {
vals[i] = val;
return;
}
// insert new key-value pair
if (N == keys.length) resize(2*keys.length);
for (int j = N; j > i; j--) {
keys[j] = keys[j-1];
vals[j] = vals[j-1];
}
keys[i] = key;
vals[i] = val;
N++;
assert check();
}
public void delete(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException("argument to delete() is null");
if (isEmpty()) return;
// compute rank
int i = rank(key);
// key not in table
if (i == N || keys[i].compareTo(key) != 0) {
return;
}
for (int j = i; j < N-1; j++) {
keys[j] = keys[j+1];
vals[j] = vals[j+1];
}
N--;
keys[N] = null; // to avoid loitering
vals[N] = null;
// resize if 1/4 full
if (N > 0 && N == keys.length/4) resize(keys.length/2);
assert check();
}
public void deleteMin() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Symbol table underflow error");
delete(min());
}
public void deleteMax() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("Symbol table underflow error");
delete(max());
}
public Key min() {
if (isEmpty()) return null;
return keys[0];
}
public Key max() {
if (isEmpty()) return null;
return keys[N-1];
}
public Key select(int k) {
if (k < 0 || k >= N) return null;
return keys[k];
}
public Key floor(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException("argument to floor() is null");
int i = rank(key);
if (i < N && key.compareTo(keys[i]) == 0) return keys[i];
if (i == 0) return null;
else return keys[i-1];
}
public Key ceiling(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException("argument to ceiling() is null");
int i = rank(key);
if (i == N) return null;
else return keys[i];
}
public int size(Key lo, Key hi) {
if (lo == null) throw new NullPointerException("first argument to size() is null");
if (hi == null) throw new NullPointerException("second argument to size() is null");
if (lo.compareTo(hi) > 0) return 0;
if (contains(hi)) return rank(hi) - rank(lo) + 1;
else return rank(hi) - rank(lo);
}
public Iterable<Key> keys() {
return keys(min(), max());
}
public Iterable<Key> keys(Key lo, Key hi) {
if (lo == null) throw new NullPointerException("first argument to size() is null");
if (hi == null) throw new NullPointerException("second argument to size() is null");
Queue<Key> queue = new Queue<Key>();
// if (lo == null && hi == null) return queue;
if (lo == null) throw new NullPointerException("lo is null in keys()");
if (hi == null) throw new NullPointerException("hi is null in keys()");
if (lo.compareTo(hi) > 0) return queue;
for (int i = rank(lo); i < rank(hi); i++)
queue.enqueue(keys[i]);
if (contains(hi)) queue.enqueue(keys[rank(hi)]);
return queue;
}
private boolean check() {
return isSorted() && rankCheck();
}
// are the items in the array in ascending order?
private boolean isSorted() {
for (int i = 1; i < size(); i++)
if (keys[i].compareTo(keys[i-1]) < 0) return false;
return true;
}
// check that rank(select(i)) = i
private boolean rankCheck() {
for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++)
if (i != rank(select(i))) return false;
for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++)
if (keys[i].compareTo(select(rank(keys[i]))) != 0) return false;
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinarySearchST<String, Integer> st = new BinarySearchST<String, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; !StdIn.isEmpty(); i++) {
String key = StdIn.readString();
st.put(key, i);
}
for (String s : st.keys())
StdOut.println(s + " " + st.get(s));
}
}但是: BinarysearchST仍然无法处理大型的FrequencyCounter的程序处理大型问题。因为它无法改变以下事实:在键是随机排列的情况下,构造一个基于有序数组的符号表所需要的访问数组的次数是数组长度的平方级别(构建符号表的代价太大)。

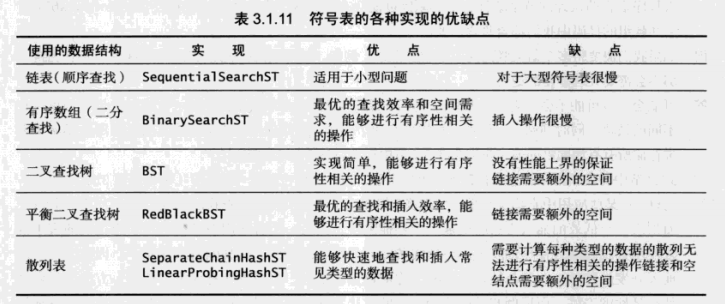
核心问题以及各种Map实现方法优缺点
一般情况下二分查找都比顺序查找快得多,它也是众多实际应用程序的最佳选择。但是二分查找不适合查找和输入时混合进行的以及符号表太大的情况。
下图对于二分查找是数组的访问次数,其他则是比较次数
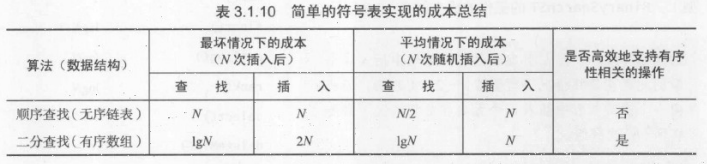
核心的问题是在于我们是否能找到同时保证查找和插入操作都是对数级别的算法和数据结构(也就是二叉查找树,后面将会讨论)。
先给出预览:

























 3398
3398

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








