应用
选择哪种实现
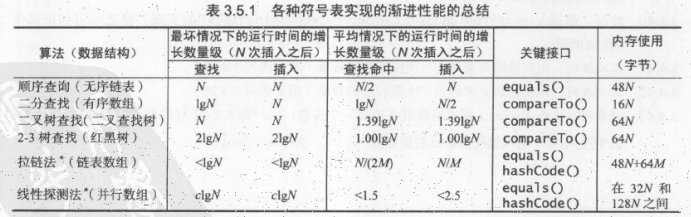
各种实现性能比较:
一般会在散列表和二叉查找树中选择(包括红黑树)。散列表查找更快,红黑树可以保证查找和插入的最坏性能,并且是有序的。一般第一选择是散列表
Java标准库中,TreeMap是基于红黑树实现的,HashMap是基于拉夫链法的符号表实现的
Map到Set的实现:忽略Map中的值或者使用一个简单的类进行封装,就可以将任何一个Map变成Set。实际上Java标准库的Set(TreeSet, HashSet)就是这么干的!
dedup小案例:
dedup就是去重的意思(这里的SET是TreeSet的包装类,直接当成TreeSet就行了):
public class DeDup {
// Do not instantiate.
private DeDup() { }
public static void main(String[] args) {
SET<String> set = new SET<String>();
// read in strings and add to set
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
String key = StdIn.readString();
if (!set.contains(key)) {
set.add(key);
StdOut.println(key);
}
}
}
}白名单黑名单案例:
白名单:文件中的键是好键,根据读入的输入,判断是否为好键,然后控制输出
黑名单类似
白名单代码(这里的SET是TreeSet的包装类,直接当成TreeSet就行了):
public class WhiteFilter {
// Do not instantiate.
private WhiteFilter() { }
public static void main(String[] args) {
SET<String> set = new SET<String>();
// read in strings and add to set
In in = new In(args[0]);
while (!in.isEmpty()) {
String word = in.readString();
set.add(word);
}
// read in string from standard input, printing out all exceptions
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
String word = StdIn.readString();
if (set.contains(word))
StdOut.println(word);
}
}
}字典类用例(略)
索引类(略)
一个键与多个值对应,并且支持反向索引(值->键)
这里ST就是TreeMap
public class LookupIndex {
// Do not instantiate.
private LookupIndex() { }
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filename = args[0];
String separator = args[1];
In in = new In(filename);
ST<String, Queue<String>> st = new ST<String, Queue<String>>();
ST<String, Queue<String>> ts = new ST<String, Queue<String>>();
while (in.hasNextLine()) {
String line = in.readLine();
String[] fields = line.split(separator);
String key = fields[0];//存的键
for (int i = 1; i < fields.length; i++) {
String val = fields[i];
if (!st.contains(key)) st.put(key, new Queue<String>());
if (!ts.contains(val)) ts.put(val, new Queue<String>());
st.get(key).enqueue(val);
ts.get(val).enqueue(key);
}
}
}稀疏向量:
解决稀疏矩阵的乘法问题(常规矩阵相乘是平方级别的)
下面是针对两个向量的点乘操作,这里的向量是稀疏的(这里ST就是HashMap)
public class SparseVector {
private int d; // dimension
private ST<Integer, Double> st; // the vector, represented by index-value pairs
public SparseVector(int d) {
this.d = d;
this.st = new ST<Integer, Double>();
}
public void put(int i, double value) {
if (i < 0 || i >= d) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Illegal index");
if (value == 0.0) st.delete(i);
else st.put(i, value);
}
public double get(int i) {
if (i < 0 || i >= d) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Illegal index");
if (st.contains(i)) return st.get(i);
else return 0.0;
}
public int nnz() {
return st.size();
}
public int dimension() {
return d;
}
public double dot(SparseVector that) {
if (this.d != that.d) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Vector lengths disagree");
double sum = 0.0;
// iterate over the vector with the fewest nonzeros
if (this.st.size() <= that.st.size()) {
for (int i : this.st.keys())
if (that.st.contains(i)) sum += this.get(i) * that.get(i);
}
else {
for (int i : that.st.keys())
if (this.st.contains(i)) sum += this.get(i) * that.get(i);
}
return sum;
}
public double dot(double[] that) {
double sum = 0.0;
for (int i : st.keys())
sum += that[i] * this.get(i);
return sum;
}
public double magnitude() {
return Math.sqrt(this.dot(this));
}
public double norm() {
return Math.sqrt(this.dot(this));
}
public SparseVector scale(double alpha) {
SparseVector c = new SparseVector(d);
for (int i : this.st.keys()) c.put(i, alpha * this.get(i));
return c;
}
public SparseVector plus(SparseVector that) {
if (this.d != that.d) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Vector lengths disagree");
SparseVector c = new SparseVector(d);
for (int i : this.st.keys()) c.put(i, this.get(i)); // c = this
for (int i : that.st.keys()) c.put(i, that.get(i) + c.get(i)); // c = c + that
return c;
}
public String toString() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
for (int i : st.keys()) {
s.append("(" + i + ", " + st.get(i) + ") ");
}
return s.toString();
}





















 298
298

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








