门面模式:外部与一个子系统的通信必须通过一个统一的门面对象进行。门面模式提供一个高层次的接口,使得子系统更易于使用。
三大角色:
子系统角色:实现各个子系统的功能。门面角色和客户角色对其是透明的,它没有任何的信息和链接。
门面角色:门面模式的核心。它被客户角色调用,其熟悉子系统的功能,且其内部根据客户角色的各种需求提供了不同的方法。
客户角色:调用门面角色来实现所需的功能。
在什么情况下使用门面模式
1. 为一个复杂子系统提供一个简单接口
2. 提高子系统的独立性
3. 在层次化结构中,可以使用Facade模式定义系统中每一层的入口。
门面模式的类图
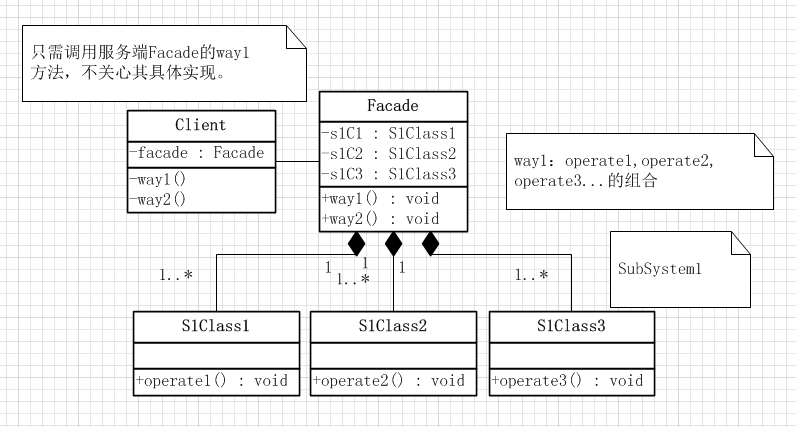
典型案例是寄快递(寄快递的步骤:打包,拿去邮局,填快递单,邮寄),医院看病(挂号,就诊,拿药)。客户端只需调用服务端的一个接口,服务端内部可以有多个操作。这也是迪米特法则的体现。
public class Registration {
public void registerNormal(){
System.out.println("first:registration normal.");
}
public void registerVip(){
System.out.println("first:registration vip.");
}
}public class Doctor {
public void doctorNormal(){
System.out.println("second:look doctor normal.");
}
public void doctorVip(){
System.out.println("second:look doctor vip.");
}
}public class FetchMedicine {
public void fetchMedicineNormal(){
System.out.println("third:fetch medicine normal.");
}
public void fetchMedicineVip(){
System.out.println("third:fetch medicine vip.");
}
}public class FacadeSick {
private static Registration registration = new Registration();
private static Doctor doctor = new Doctor();
private static FetchMedicine fetchMedicine = new FetchMedicine();
public void seeDoctorNormal() {
registration.registerNormal();
doctor.doctorNormal();
fetchMedicine.fetchMedicineNormal();
}
public void seeDoctorVip() {
registration.registerVip();
doctor.doctorVip();
fetchMedicine.fetchMedicineVip();
}
}public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args){
FacadeSick facadeSickNormal = new FacadeSick();
facadeSickNormal.seeDoctorNormal();
FacadeSick facadeSickVip = new FacadeSick();
facadeSickVip.seeDoctorVip();
}
}







 门面模式作为结构型设计模式,用于提供一个统一的接口,使得子系统更易于使用。它包含子系统角色、门面角色和客户角色,其中门面角色协调子系统功能并为客户提供简洁的调用方式。该模式适用于需要为复杂子系统提供简单接口,提高子系统独立性和在层次化结构中定义各层入口的情况。常见应用如寄快递、医院看病流程等,体现了迪米特法则。
门面模式作为结构型设计模式,用于提供一个统一的接口,使得子系统更易于使用。它包含子系统角色、门面角色和客户角色,其中门面角色协调子系统功能并为客户提供简洁的调用方式。该模式适用于需要为复杂子系统提供简单接口,提高子系统独立性和在层次化结构中定义各层入口的情况。常见应用如寄快递、医院看病流程等,体现了迪米特法则。
















 157
157

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








