1 ntp 安装查看
1.1 安装命令
apt-get install ntp1.2 查看服务是否启动
service --status-all或者
ps -aux | grep ntp1.3 重启命令
/etc/init.d/ntp restart1.4 查看运行状态
watch ntpq -p
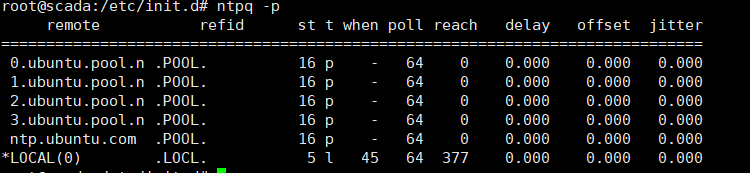
remote - 本机和上层ntp的ip或主机名,“+”表示优先,“*”表示次优先
refid - 参考上一层ntp主机地址
st - stratum阶层
when - 多少秒前曾经同步过时间
poll - 下次更新在多少秒后
reach - 已经向上层ntp服务器要求更新的次数
delay - 网络延迟
offset - 时间补偿
jitter - 系统时间与bios时间差
1.5 湖南麒麟系统相关命令
开机启动
systemctl enable ntpd.service
systemctl start ntpd
systemctl status ntpd
2 /etc/ntp.conf 配置详解
#配置文件内容
# /etc/ntp.conf, configuration for ntpd; see ntp.conf(5) for help
driftfile /var/lib/ntp/ntp.drift
# Enable this if you want statistics to be logged.
#statsdir /var/log/ntpstats/
statistics loopstats peerstats clockstats
filegen loopstats file loopstats type day enable
filegen peerstats file peerstats type day enable
filegen clockstats file clockstats type day enable
# Specify one or more NTP servers.
# Use servers from the NTP Pool Project. Approved by Ubuntu Technical Board
# on 2011-02-08 (LP: #104525). See http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html for
# more information.
pool 0.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
pool 1.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
pool 2.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
pool 3.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
# Use Ubuntu's ntp server as a fallback.
pool ntp.ubuntu.com
# Access control configuration; see /usr/share/doc/ntp-doc/html/accopt.html for
# details. The web page <http://support.ntp.org/bin/view/Support/AccessRestrictions>
# might also be helpful.
#
# Note that "restrict" applies to both servers and clients, so a configuration
# that might be intended to block requests from certain clients could also end
# up blocking replies from your own upstream servers.
# By default, exchange time with everybody, but don't allow configuration.
restrict -4 default kod notrap nomodify nopeer noquery limited
restrict -6 default kod notrap nomodify nopeer noquery limited
# Local users may interrogate the ntp server more closely.
restrict 127.0.0.1
restrict ::1
# Needed for adding pool entries
restrict source notrap nomodify noquery
# Clients from this (example!) subnet have unlimited access, but only if
# cryptographically authenticated.
#restrict 192.168.123.0 mask 255.255.255.0 notrust
# If you want to provide time to your local subnet, change the next line.
# (Again, the address is an example only.)
#broadcast 192.168.123.255
# If you want to listen to time broadcasts on your local subnet, de-comment the
# next lines. Please do this only if you trust everybody on the network!
#disable auth
#broadcastclient
#Changes recquired to use pps synchonisation as explained in documentation:
#http://www.ntp.org/ntpfaq/NTP-s-config-adv.htm#AEN3918
#server 127.127.8.1 mode 135 prefer # Meinberg GPS167 with PPS
#fudge 127.127.8.1 time1 0.0042 # relative to PPS for my hardware
#server 127.127.22.1 # ATOM(PPS)
#fudge 127.127.22.1 flag3 1 # enable PPS API2.1 driftfile记录时间差异
设定方式:
driftfile [可以被ntpd写入的目录与档案]因为预设的NTP Server本身的时间计算是依据BIOS的芯片震荡周期频率来计算的,但是这个数值与上层Time Server不见得一致。所以NTP 守护进程(ntpd) 会自动的去计自己主机的频率与上层Time server的频率,并且将两个频率的误差记录下来,记录下来的文件就是在driftfile后面接的完整文件名当中。关于文件名,你必须要知道:
driftfile 后面接的档案需要使用完整路径文件名;
该档案不能是连结档;
该档案需要设定成ntpd这个守护进程可以写入的权限;
该档案所记录的数值单位为:百万分之一秒 (ppm);
driftfile后面接的文件会被ntpd自动更新,所以他的权限一定要能够让ntpd写入才行。
2.2 开启日志
使用statsdir和filegen开启统计分析。
设定方式:
statsdir /var/log/ntpstats/
statistics loopstats peerstats clockstats
filegen loopstats file loopstats type day enable
filegen peerstats file peerstats type day enable
filegen clockstats file clockstats type day enable当打开统计分析时,ntp会在/var/log/ntpstats/目录下产生filegen中所设定的统计文件。
2.3 使用restrict管理权限控制
restrict [address] mask [mask] [parameter]其中parameter的参数主要有下面这些:
ignore: 拒绝所有类型的NTP联机;
nomodify: 客户端不能使用ntpc与ntpq这两个程序来修改服务器的时间参数,但客户端仍可透过这个主机来进行网络校时;
noquery: 客户端不能使用ntpq,ntpc等指令来查询时间服务器,等于不提供NTP的网络校时;
notrap: 不提供trap这个远程事件登录(remote event logging)的功能;notrust: 拒绝没有认证的客户端;
如果你没有在 parameter 的地方加上任何参数的话,这表示该IP或网段不受任何限制。
注意:没有限制需求不要配置restrict,默认是不限制的。
2.4 使用server设定上层NTP服务器
server [address] [options...]在server后面填写服务器地址(可以使IP或主机名),这里最长使用的prefer,表示优先使用的服务器。
3 ntp作为server配置
只需要配置server即可,保证可以提供对时即可。
如果没有服务ip,可以将本地时间作为对外提供时间,可以添加如下配置:
#b本地时间对外对时
server 127.127.1.0
fudge 127.127.1.0 stratum 5server配置
# /etc/ntp.conf, configuration for ntpd; see ntp.conf(5) for help
driftfile /var/lib/ntp/ntp.drift
# Leap seconds definition provided by tzdata
leapfile /usr/share/zoneinfo/leap-seconds.list
# Enable this if you want statistics to be logged.
statsdir /var/log/ntpstats/
statistics loopstats peerstats clockstats
filegen loopstats file loopstats type day enable
filegen peerstats file peerstats type day enable
filegen clockstats file clockstats type day enable
# Specify one or more NTP servers.
# Use servers from the NTP Pool Project. Approved by Ubuntu Technical Board
# on 2011-02-08 (LP: #104525). See http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html for
# more information.
#pool 0.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
#pool 1.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
#pool 2.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
#pool 3.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
# Use Ubuntu's ntp server as a fallback.
#pool ntp.ubuntu.com
# Access control configuration; see /usr/share/doc/ntp-doc/html/accopt.html for
# details. The web page <http://support.ntp.org/bin/view/Support/AccessRestrictions>
# might also be helpful.
#
# Note that "restrict" applies to both servers and clients, so a configuration
# that might be intended to block requests from certain clients could also end
# up blocking replies from your own upstream servers.
# By default, exchange time with everybody, but don't allow configuration.
# limited
restrict -4 default kod notrap nomodify nopeer noquery limited
restrict -6 default kod notrap nomodify nopeer noquery limited
# Local users may interrogate the ntp server more closely.
restrict 127.0.0.1
restrict ::1
# Needed for adding pool entries
#restrict source notrap nomodify noquery
# Clients from this (example!) subnet have unlimited access, but only if
# cryptographically authenticated.
#restrict 192.168.123.0 mask 255.255.255.0 notrust
# If you want to provide time to your local subnet, change the next line.
# (Again, the address is an example only.)
#broadcast 10.21.80.221
# If you want to listen to time broadcasts on your local subnet, de-comment the
# next lines. Please do this only if you trust everybody on the network!
#disable auth
#broadcastclient
#Changes recquired to use pps synchonisation as explained in documentation:
#http://www.ntp.org/ntpfaq/NTP-s-config-adv.htm#AEN3918
server 10.231.80.1 prefer
#b本地时间对外对时
server 127.127.1.0
fudge 127.127.1.0 stratum 5
#server 127.127.8.1 mode 135 prefer # Meinberg GPS167 with PPS
#fudge 127.127.8.1 time1 0.0042 # relative to PPS for my hardware
#server 127.127.22.1 # ATOM(PPS)
#fudge 127.127.22.1 flag3 1 # enable PPS 4 ntp作为client配置
把默认的server ip/域名全部注释掉,配置
server ip地址 如下所示:
server ntp.ntsc.ac.cn
# /etc/ntp.conf, configuration for ntpd; see ntp.conf(5) for help
driftfile /var/lib/ntp/ntp.drift
# Leap seconds definition provided by tzdata
leapfile /usr/share/zoneinfo/leap-seconds.list
# Enable this if you want statistics to be logged.
statsdir /var/log/ntpstats/
statistics loopstats peerstats clockstats
filegen loopstats file loopstats type day enable
filegen peerstats file peerstats type day enable
filegen clockstats file clockstats type day enable
# Specify one or more NTP servers.
# Use servers from the NTP Pool Project. Approved by Ubuntu Technical Board
# on 2011-02-08 (LP: #104525). See http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html for
# more information.
#pool 0.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
#pool 1.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
#pool 2.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
#pool 3.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
# Use Ubuntu's ntp server as a fallback.
#pool ntp.ubuntu.com
# Access control configuration; see /usr/share/doc/ntp-doc/html/accopt.html for
# details. The web page <http://support.ntp.org/bin/view/Support/AccessRestrictions>
# might also be helpful.
#
# Note that "restrict" applies to both servers and clients, so a configuration
# that might be intended to block requests from certain clients could also end
# up blocking replies from your own upstream servers.
# By default, exchange time with everybody, but don't allow configuration.
# limited
restrict -4 default kod notrap nomodify nopeer noquery limited
restrict -6 default kod notrap nomodify nopeer noquery limited
# Local users may interrogate the ntp server more closely.
restrict 127.0.0.1
restrict ::1
# Needed for adding pool entries
#restrict source notrap nomodify noquery
# Clients from this (example!) subnet have unlimited access, but only if
# cryptographically authenticated.
#restrict 192.168.123.0 mask 255.255.255.0 notrust
# If you want to provide time to your local subnet, change the next line.
# (Again, the address is an example only.)
#broadcast 10.21.80.221
# If you want to listen to time broadcasts on your local subnet, de-comment the
# next lines. Please do this only if you trust everybody on the network!
#disable auth
#broadcastclient
#Changes recquired to use pps synchonisation as explained in documentation:
#http://www.ntp.org/ntpfaq/NTP-s-config-adv.htm#AEN3918
server ntp.ntsc.ac.cn
#b本地时间对外对时
#server 127.127.1.0
#fudge 127.127.1.0 stratum 5
#server 127.127.8.1 mode 135 prefer # Meinberg GPS167 with PPS
#fudge 127.127.8.1 time1 0.0042 # relative to PPS for my hardware
#server 127.127.22.1 # ATOM(PPS)
#fudge 127.127.22.1 flag3 1 # enable PPS 5 ntp客户端手动对时
ntp.conf配置好后,服务端重启等待几分钟后,再使用
ntpdate 服务ip进行对时。
注意首先需要把client的ntp停止。
/etc/init.d/ntp stop手动对时只会对一次时间,如果配置server启动ntp会定时对时。








 本文介绍NTP的安装与配置方法,包括服务启动、重启、状态查看等命令,详细解析配置文件ntp.conf的各项设置,并演示如何手动对时。
本文介绍NTP的安装与配置方法,包括服务启动、重启、状态查看等命令,详细解析配置文件ntp.conf的各项设置,并演示如何手动对时。

















 5109
5109

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










