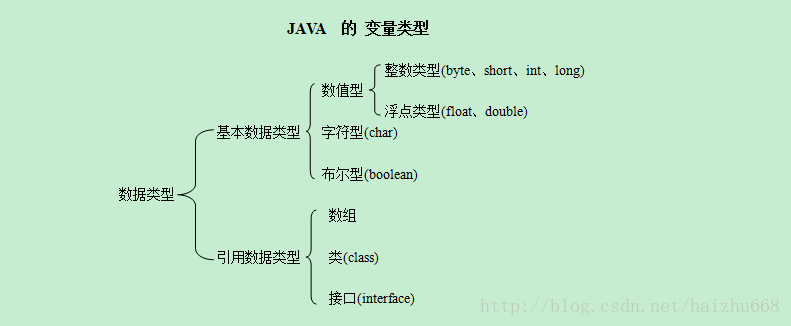
一:数据类型的种类:
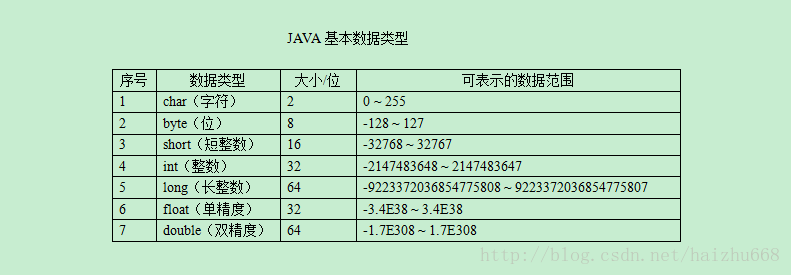
1.1 整数类型:byte,short,int,long
四中类型都有正负值,区别在于存储值的范围。但是在实际应用中,大多数时间都会使用int或者long类型。因为,虽然byte和short类型虽然能够节省一部分内存,但是除非有很多那种类型的值需要存储,否则不要使用,这是由于在计算中使用它们还会增加复杂度,所以除非绝对必要,否则一般不应该使用它们。当然,从某些外部源读取数据时,例如一个硬盘文件,必须让每个数据值的类型与原始类型对应。
1.2 浮点数据类型:float,double
boolean
char
long
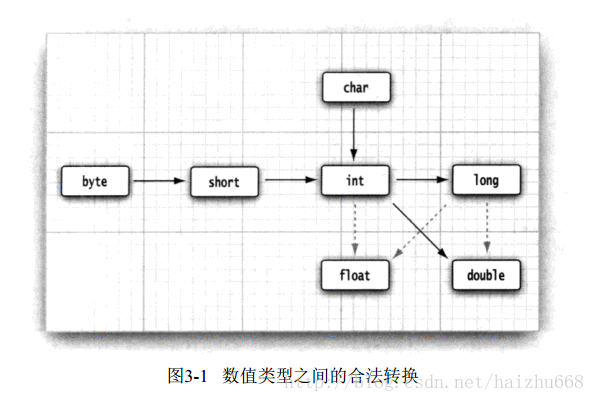
1.3 数据类型转换
二:直接常量
下面例子中定义的i1,l1,f1等等都可以称之为“直接常量”。
另外注意 Integer.toBinaryString() 方法:
package haizhu.com;
public class Caozuofu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i1 = 0x2f;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(i1));
int i2 = 0x2F;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(i2));
int i3 = 0177;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(i3));
char c = 0xffff;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(c));
byte b = 0x7f;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(b));
short s = 0x7fff;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(s));
long l1 = 200;
System.out.println(l1);
long l2 = 200l;
System.out.println(l2);
long l3 = 200L;
System.out.println(l3);
double d1 = 200;
System.out.println(d1);
double d2 = 200d;
System.out.println(d2);
double d3 = 200D;
System.out.println(d3);
float f1 = 200;
System.out.println(f1);
float f2 = 200f;
System.out.println(f2);
float f3 = 200F;
System.out.println(f3);
}
}
101111
101111
1111111
1111111111111111
1111111
111111111111111
200
200
200
200.0
200.0
200.0
200.0
200.0
200.0
三:问题:数据类型的详解,用法,区别





















 1092
1092











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








