作者 水云青
原创作品转载请注明出处
《Linux内核分析》MOOC课程http://mooc.study.163.com/course/USTC-1000029000
首先给出运行程序的源代码:链接地址:
mykernel-master.zip 地址:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1dEsqxe5
linux-3.9.4.tar.xz 地址:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1pKlQDR1
mykernel_for_linux3.9.4sc.patch 地址:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1hqW5L8C
也可以在实验楼中,进行试验https://www.shiyanlou.com/courses/195
在实验楼中进入主文件夹,在终端输入如下命令,来启动程序
- cd LinuxKernel/linux-3.9.4
- qemu -kernel arch/x86/boot/bzImage
1、熟悉、理解Linux内核工作方式
2、尝试编写自己的内核
3、理解多进程时间片轮转的工作方式
试验过程:
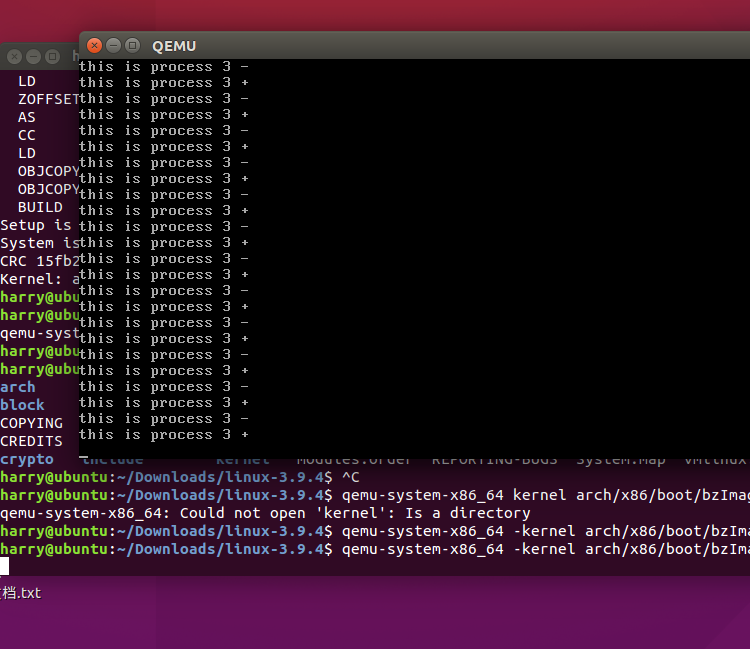
1.编译内核:
。。。。。
具体过程参见word文档
地址:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1pJXD3HT
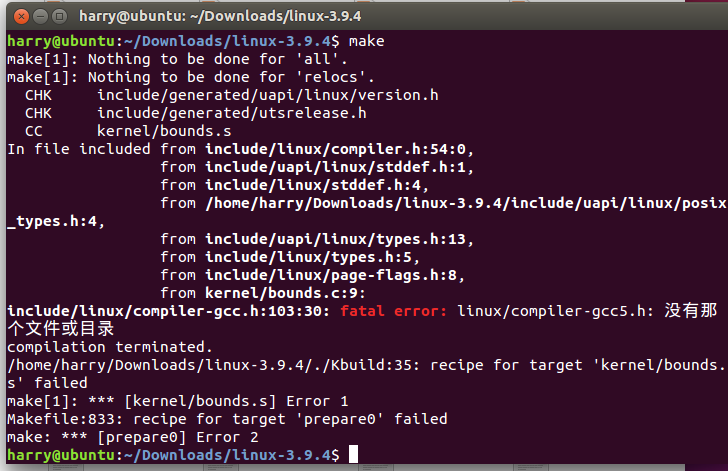
但是笔者在对着文档进行试验时出现了下面的错误
compilation terminated.
这种情况是因为系统太新,手动去网上下一个 compiler-gcc5.h 放你要编译内核模块的内核代码的include/linux下.
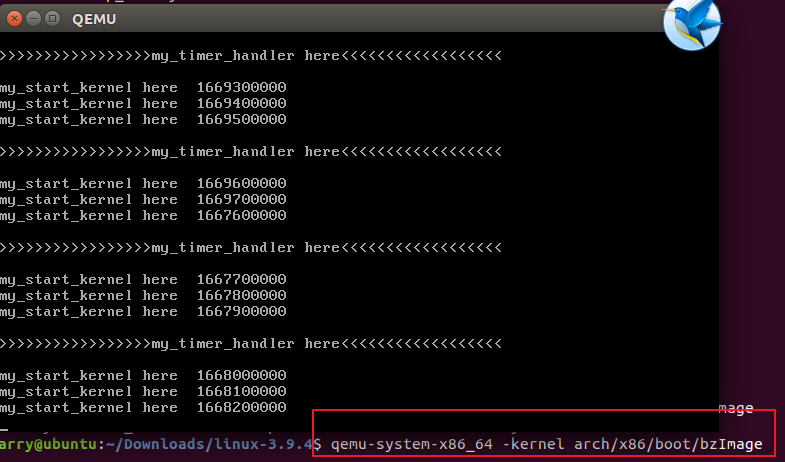
将多进程实践片轮转的mykernel放入linux3.9.4之后,文件下载地址为:
http://pan.baidu.com/s/1kU2nOKB,开始编译,运行,参见word文档。
二、分析
下面对主要代码进行分析
<pre name="code" class="cpp" style="font-size: 13.3333px;">#define MAX_TASK_NUM 4
<pre name="code" class="cpp">#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/ctype.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
#include "mypcb.h"
tPCB task[MAX_TASK_NUM];
tPCB * my_current_task = NULL;
volatile int my_need_sched = 0;
void my_process(void);
void __init my_start_kernel(void)
{
int pid = 0;
int i;
/* Initialize process 0*/
task[pid].pid = pid;
task[pid].state = 0;/* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */
task[pid].task_entry = task[pid].thread.ip = (unsigned long)my_process;
task[pid].thread.sp = (unsigned long)&task[pid].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1];
task[pid].next = &task[pid];
/*fork more process */
for(i=1;i<MAX_TASK_NUM;i++)
{
memcpy(&task[i],&task[0],sizeof(tPCB));
task[i].pid = i;
task[i].state = -1;
task[i].thread.sp = (unsigned long)&task[i].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1];
task[i].next = task[i-1].next;
task[i-1].next = &task[i];
}
/* start process 0 by task[0] */
pid = 0;
my_current_task = &task[pid];
asm volatile(
"movl %1,%%esp\n\t" /* set task[pid].thread.sp to esp */
"pushl %1\n\t" /* push ebp */
"pushl %0\n\t" /* push task[pid].thread.ip */
"ret\n\t" /* pop task[pid].thread.ip to eip */
"popl %%ebp\n\t"
:
: "c" (task[pid].thread.ip),"d" (task[pid].thread.sp) /* input c or d mean %ecx/%edx*/
);
}
void my_process(void)
{
int i = 0;
while(1)
{
i++;
if(i%10000000 == 0)
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE "this is process %d -\n",my_current_task->pid);
if(my_need_sched == 1)
{
my_need_sched = 0;
my_schedule();
}
printk(KERN_NOTICE "this is process %d +\n",my_current_task->pid);
}
}
}void __init my_start_kernel(void)用来初始化和启动线程。
扩充知识:
qemu是一款虚拟化应用程序,可以模拟虚拟机。






















 1589
1589

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








