门
D. The Child and Sequence
time limit per test
4 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite sequence of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers how to repair the sequence. Initially he should create an integer array a[1], a[2], ..., a[n]. Then he should perform a sequence of m operations. An operation can be one of the following:
- Print operation l, r. Picks should write down the value of
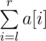 .
. - Modulo operation l, r, x. Picks should perform assignment a[i] = a[i] mod x for each i (l ≤ i ≤ r).
- Set operation k, x. Picks should set the value of a[k] to x (in other words perform an assignment a[k] = x).
Can you help Picks to perform the whole sequence of operations?
Input
The first line of input contains two integer: n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105). The second line contains n integers, separated by space: a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) — initial value of array elements.
Each of the next m lines begins with a number type 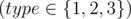 .
.
- If type = 1, there will be two integers more in the line: l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n), which correspond the operation 1.
- If type = 2, there will be three integers more in the line: l, r, x (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 2.
- If type = 3, there will be two integers more in the line: k, x (1 ≤ k ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 3.
Output
For each operation 1, please print a line containing the answer. Notice that the answer may exceed the 32-bit integer.
Examples
input
Copy
5 5 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 5 4 3 3 5 1 2 5 2 1 3 3 1 1 3
output
Copy
8 5
input
Copy
10 10 6 9 6 7 6 1 10 10 9 5 1 3 9 2 7 10 9 2 5 10 8 1 4 7 3 3 7 2 7 9 9 1 2 4 1 6 6 1 5 9 3 1 10
output
Copy
49 15 23 1 9
Note
Consider the first testcase:
- At first, a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}.
- After operation 1, a = {1, 2, 3, 0, 1}.
- After operation 2, a = {1, 2, 5, 0, 1}.
- At operation 3, 2 + 5 + 0 + 1 = 8.
- After operation 4, a = {1, 2, 2, 0, 1}.
- At operation 5, 1 + 2 + 2 = 5.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define lson rt << 1, l, mid
#define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r
#define ll long long
const int MAX = 1e6 + 7;
ll a[MAX << 2], mx[MAX << 2];
void pushup(int rt){
a[rt] = a[rt << 1] + a[rt << 1 | 1];
mx[rt] = max(mx[rt << 1], mx[rt << 1 | 1]);
}
void build(int rt, int l, int r){
if(l == r){
scanf("%lld", &a[rt]);
mx[rt] = a[rt];
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(lson);
build(rson);
pushup(rt);
}
void update(int rt, int l, int r, int pos, int v){
if(l == r){
a[rt] = v;
mx[rt] = v;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(pos <= mid) update(lson, pos, v);
else update(rson, pos, v);
pushup(rt);
}
void update_mod(int rt, int l, int r, int x, int y, int p){
if(mx[rt] < p) return;
if(l == r){
a[rt] %= p, mx[rt] %= p;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(x <= mid) update_mod(lson, x, y, p);
if(mid < y) update_mod(rson, x, y, p);
pushup(rt);
}
ll query(int rt, int l, int r, int x, int y){
if(x <= l && r <= y) return a[rt];
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
ll ans = 0;
if(x <= mid) ans += query(lson, x, y);
if(mid < y) ans += query(rson, x, y);
return ans;
}
int main(){
int n, m;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
build(1, 1, n);
while(m--){
int op, x, y, z;
scanf("%d", &op);
if(op == 1){
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
printf("%lld\n", query(1, 1, n, x, y));
}
else if(op == 2){
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &z);
update_mod(1, 1, n, x, y, z);
}
else{
scanf("%d%d", &x ,&y);
update(1, 1, n, x, y);
}
}
return 0;
}






















 422
422

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








