霍夫曼编码是一种无损数据压缩算法。其思想是为输入字符分配可变长度的代码,分配的代码的长度基于相应字符的频率。
分配给输入字符的可变长度代码是前缀码,这意味着代码(位序列)的分配方式是分配给一个字符的代码不是分配给任何其他字符的代码的前缀。这就是霍夫曼编码确保在解码生成的比特流时没有歧义的方式。
让我们用一个反例来理解前缀码。假设有四个字符 a、b、c 和 d,它们对应的可变长度代码分别为 00、01、0 和 1。这种编码会导致歧义,因为分配给 c 的代码是分配给 a 和 b 的代码的前缀。如果压缩的比特流是 0001,则解压缩的输出可能是“cccd”或“ccb”或“acd”或“ab”。有关霍夫曼编码的应用, 请参阅此处:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Huffman_coding#Applications。霍夫曼编码主要有两个主要部分:
1、根据输入字符构建哈夫曼树。
2、遍历哈夫曼树并为字符分配代码。
算法:
用来构造最佳前缀码的方法称为哈夫曼编码。
该算法以自下而上的方式构建树。我们可以用T来表示这棵树
设 |c| 为叶子的数量
|c| -1 是合并节点所需的操作数。Q 是构建二叉堆时可以使用的优先级队列。
Algorithm Huffman (c)
{
n= |c|
Q = c
for i<-1 to n-1
do
{
temp <- get node ()
left (temp] Get_min (Q) right [temp] Get Min (Q)
a = left [templ b = right [temp]
F [temp]<- f[a] + [b]
insert (Q, temp)
}
return Get_min (0)
}
构建哈夫曼树的步骤
输入是唯一字符的数组及其出现的频率,输出是哈夫曼树。
1、为每个唯一字符创建一个叶节点,并构建所有叶节点的最小堆(最小堆用作优先级队列。频率字段的值用于比较最小堆中的两个节点。最初,最不频繁的字符位于根节点)
2、从最小堆中提取频率最小的两个节点。
3、创建一个新的内部节点,其频率等于两个节点频率之和。将第一个提取的节点作为其左子节点,将另一个提取的节点作为其右子节点。将此节点添加到最小堆中。
4、重复步骤 2 和步骤 3,直到堆只包含一个节点。剩下的节点是根节点,树已完成。
让我们通过一个例子来理解该算法:
字符 频率
a 5
b 9
c 12
d 13
e 16
f 45
步骤 1.构建一个包含 6 个节点的最小堆,其中每个节点代表一棵单节点树的根。
步骤 2.从最小堆中提取两个最小频率节点。添加一个频率为 5 + 9 = 14 的新内部节点。
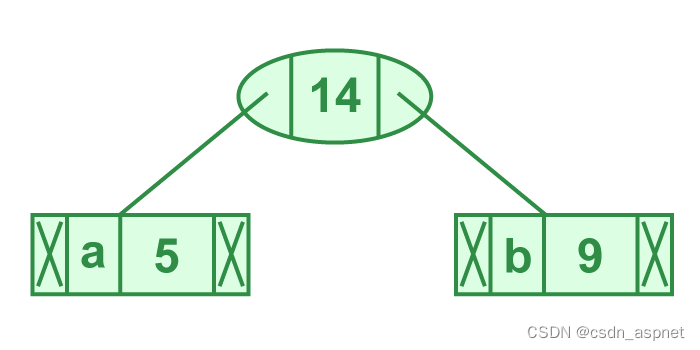
步骤 2 的说明
现在最小堆包含 5 个节点,其中 4 个节点是每个节点只有一个元素的树的根,一个堆节点是具有 3 个元素的树的根
字符 频率
c 12
d 13
内部节点(Internal Node) 14
e 16
f 45
步骤 3.从堆中提取两个最小频率节点。添加一个频率为 12 + 13 = 25 的新内部节点

步骤 3 的说明
现在最小堆包含 4 个节点,其中 2 个节点是每个节点只有一个元素的树的根,另外两个堆节点是具有多个节点的树的根
字符 频率
内部节点(Internal Node) 14
e 16
内部节点(Internal Node) 25
f 45
步骤 4.提取两个最小频率节点。添加一个频率为 14 + 16 = 30 的新内部节点
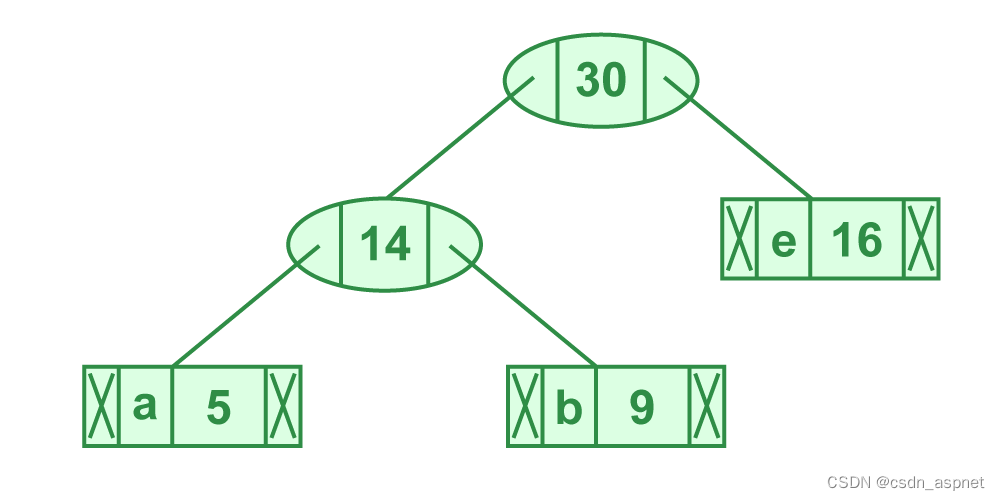
步骤 4 的说明
现在最小堆包含 3 个节点。
字符 频率
内部节点(Internal Node) 25
内部节点(Internal Node) 30
f 45
步骤 5.提取两个最小频率节点。添加一个频率为 25 + 30 = 55 的新内部节点
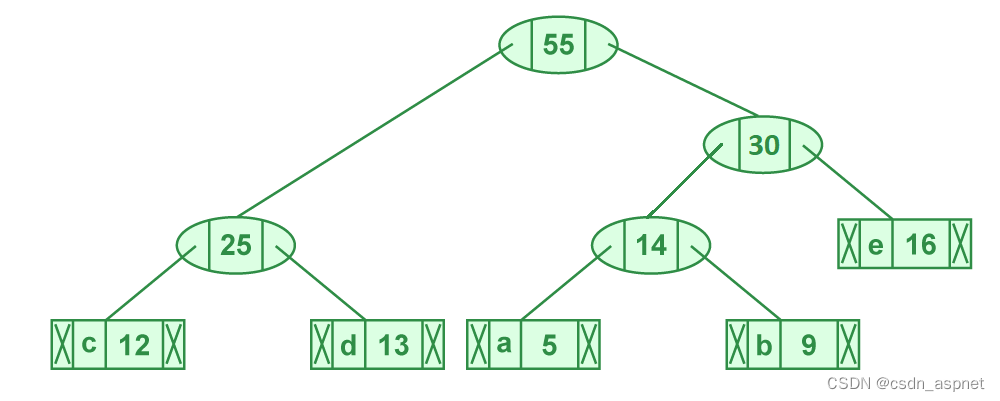
步骤 5 的图示
现在最小堆包含 2 个节点。
字符 频率
f 45
内部节点(Internal Node) 55
步骤 6.提取两个最小频率节点。添加一个频率为 45 + 55 = 100 的新内部节点

步骤 6 的图示
现在最小堆仅包含一个节点。
字符 频率
内部节点(Internal Node) 100
由于堆仅包含一个节点,因此算法在此停止。
打印哈夫曼树代码的步骤:
从根节点开始遍历形成的树。维护一个辅助数组。在移动到左孩子时,将 0 写入数组。在移动到右孩子时,将 1 写入数组。遇到叶子节点时打印数组。
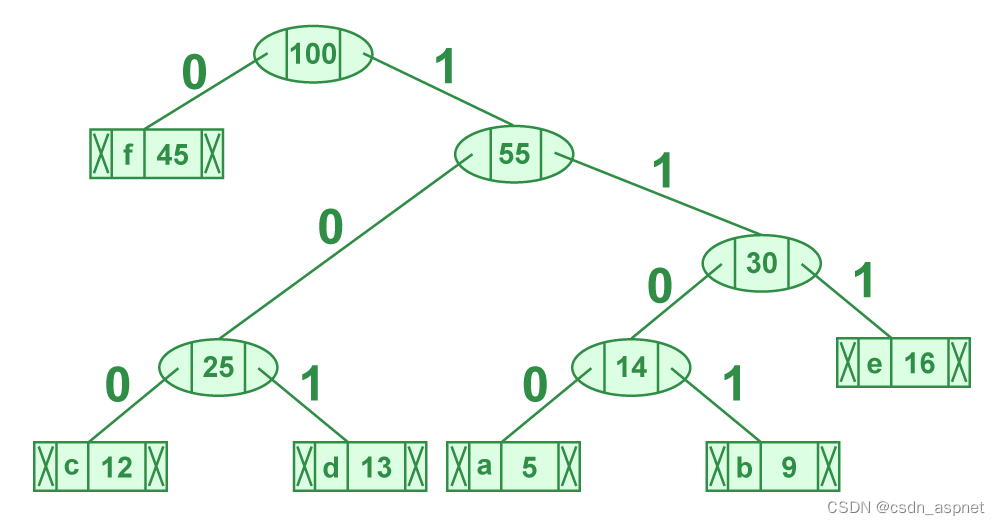
从 HuffmanTree 打印代码的步骤
代码如下:
字符 代码字
f 0
c 100
d 101
a 1100
b 1101
e 111
以下是上述方法的实现:
// node class is the basic structure
// of each node present in the Huffman - tree.
class HuffmanNode
{
constructor()
{
this.data = 0;
this.c = '';
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
// recursive function to print the
// huffman-code through the tree traversal.
// Here s is the huffman - code generated.
function printCode(root,s)
{
// base case; if the left and right are null
// then its a leaf node and we print
// the code s generated by traversing the tree.
if (root.left == null
&& root.right == null
&& (root.c).toLowerCase() != (root.c).toUpperCase()) {
// c is the character in the node
document.write(root.c + ":" + s+"<br>");
return;
}
// if we go to left then add "0" to the code.
// if we go to the right add"1" to the code.
// recursive calls for left and
// right sub-tree of the generated tree.
printCode(root.left, s + "0");
printCode(root.right, s + "1");
}
// main function
// number of characters.
let n = 6;
let charArray = [ 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f' ];
let charfreq = [ 5, 9, 12, 13, 16, 45 ];
// creating a priority queue q.
// makes a min-priority queue(min-heap).
let q = [];
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// creating a Huffman node object
// and add it to the priority queue.
let hn = new HuffmanNode();
hn.c = charArray[i];
hn.data = charfreq[i];
hn.left = null;
hn.right = null;
// add functions adds
// the huffman node to the queue.
q.push(hn);
}
// create a root node
let root = null;
q.sort(function(a,b){return a.data-b.data;});
// Here we will extract the two minimum value
// from the heap each time until
// its size reduces to 1, extract until
// all the nodes are extracted.
while (q.length > 1) {
// first min extract.
let x = q[0];
q.shift();
// second min extract.
let y = q[0];
q.shift();
// new node f which is equal
let f = new HuffmanNode();
// to the sum of the frequency of the two nodes
// assigning values to the f node.
f.data = x.data + y.data;
f.c = '-';
// first extracted node as left child.
f.left = x;
// second extracted node as the right child.
f.right = y;
// marking the f node as the root node.
root = f;
// add this node to the priority-queue.
q.push(f);
q.sort(function(a,b){return a.data-b.data;});
}
// print the codes by traversing the tree
printCode(root, "");
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
输出
f: 0
c: 100
d: 101
a: 1100
b: 1101
e: 111
时间复杂度: O(nlogn),其中 n 是唯一字符的数量。如果有 n 个节点,则 extractMin() 被调用 2*(n – 1) 次。extractMin() 需要 O(logn) 时间,因为它会调用 minHeapify()。因此,总体复杂度为 O(nlogn)。
如果输入数组已排序,则存在线性时间算法。我们将在下一篇文章中讨论这个问题。
空间复杂度:O(N)
霍夫曼编码的应用:
1、它们用于传输传真和文本。
2、它们被传统的压缩格式如PKZIP、GZIP等所使用。
3、JPEG、PNG 和 MP3 等多媒体编解码器使用 Huffman 编码(更准确地说是前缀代码)。
在存在一系列经常出现的字符的情况下它很有用。
参考:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Huffman_coding























 288
288











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








