Description:
Given a singly linked list where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST.
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#define Elementype int
using namespace std;
using iter_int = vector<int>::iterator;
int index = 0;
//链表结点
typedef struct Node
{
int val;
Node* next;
Node(int x) :val(x), next(nullptr){}
}*List;
typedef struct TreeNode //树结点
{
Elementype val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(Elementype x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
} *Tree;
Tree SortedListToBinarySearchTree(List &head, int first, int last) //自底向上构建
{
if (first > last || head == nullptr)
return nullptr;
const auto length = last - first;
int mid = first + length / 2;
Tree leftChild = SortedListToBinarySearchTree(head, first, mid - 1);
Tree root = new TreeNode(head->val);
root->left = leftChild;
head = head->next;
root->right = SortedListToBinarySearchTree(head, mid + 1, last);
return root;
}
//先序遍历
void preOrderTraversal(Tree root)
{
stack<Tree> sk;
Tree p = root;
if (p)
sk.push(p);
while (!sk.empty())
{
p = sk.top();
cout << p->val<<" ";
sk.pop();
if (p->right)
sk.push(p->right);
if (p->left)
sk.push(p->left);
}
}
int main()
{
Tree root = nullptr; //根结点
List linklist = new Node(-1); //头结点
List head = linklist;
int array[8] = { 1, 3, 4, 7, 11, 15, 20, 25 };
for (int i = 0; i < 8;i++) //创建链表
{
List node = new Node(array[i]);
linklist->next = node;
linklist = linklist->next;
}
root = SortedListToBinarySearchTree(head->next, 0, 7);
cout << "先序遍历: ";
preOrderTraversal(root);
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
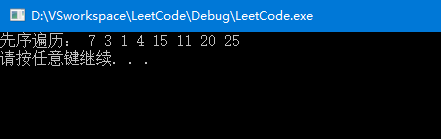
}测试:






















 110
110

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








