注:FAT16驱动代码不是本人编写的,是从网上下载的,本人只是对该代码进行研读学习,并做下笔记。该FAT16驱动应该是比较老的了,猜测应该在DOS时代比较流行,但放在今天,对于刚刚进阶FAT16的小伙伴来说,还是很适合初学者学习的好资料!笔者也相信,只要小伙伴们静下心来,慢慢读懂该代码,相信很快就能在脑海中形成一张FAT16的总览图了。
笔者对代码进行了简单测试,在STM32平台上对2G SD卡进行了读写TXT操作,没有问题。当然,这个代码功能还是很简单的,只有创建、读、写文件3个操作,而且写操作不能修改文件的大小,即没有追加功能,文件的大小是由CreateFile一开始创建好了的。
以下为源码部分:
//****************************************************************************************************
//文件名:FAT16.c
//来源:网络
//注释:hexiaolong2009(http://blog.csdn.net/hexiaolong2009)
//****************************************************************************************************
#include "stm32f10x.h"
#include "fat16.h"
#include "sd.h"
//****************************************************************************************************
//全局变量定义
u16 BytesPerSector;
u16 ResvdSectors;
u16 RootDirCnt;
u16 SectorsPerFAT;
u16 DirStartSector;
u16 DataStartSector;
u16 DBRStartSector;
u8 SectorsPerClus;
u8 FATCount;
u8 SectorBuf[512];
//读取一个逻辑扇区
static u8 ReadBlock(u16 LBA)
{
return SD_ReadSector(SectorBuf, LBA + DBRStartSector, 1);
}
//写入一个逻辑扇区
static u8 WriteBlock(u16 LBA)
{
return SD_WriteSector(SectorBuf, LBA + DBRStartSector, 1);
}
//将文件名格式化成标准的DOS 8.3格式的文件名
static void NameFormat(const char* SrcName, char* DstName)
{
u8 i, j;
//首先用空格初始化目标缓冲区
for(i = 0; i < 11; i++)
*(DstName + i) = 0x20;
//其次拷贝文件名
for(i = 0, j = 0; i < 8; i++, j++)
{
if((*SrcName) == '.')
{
SrcName++;
break;
}
else
{
*(DstName + j) = *SrcName++;
}
}
//最后拷贝扩展名
for(i = 0, j = 8; i < 3; i++, j++)
{
if((*SrcName) == 0) break;
else
{
*(DstName + j) = *SrcName++;
}
}
}
//比较两个缓冲区的前size个字节是否完全相同
static u8 IsEqual(void* Src1, void* Src2, u32 size)
{
u8 *p1, *p2;
p1 = Src1;
p2 = Src2;
for(; size--; )
{
if((*p1++) != (*p2++))
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
//将簇号转换为逻辑扇区号
static u16 Clus2Sector(u16 clus)
{
return (DataStartSector + ((clus - 2) * SectorsPerClus));
}
//读取主引导记录MBR
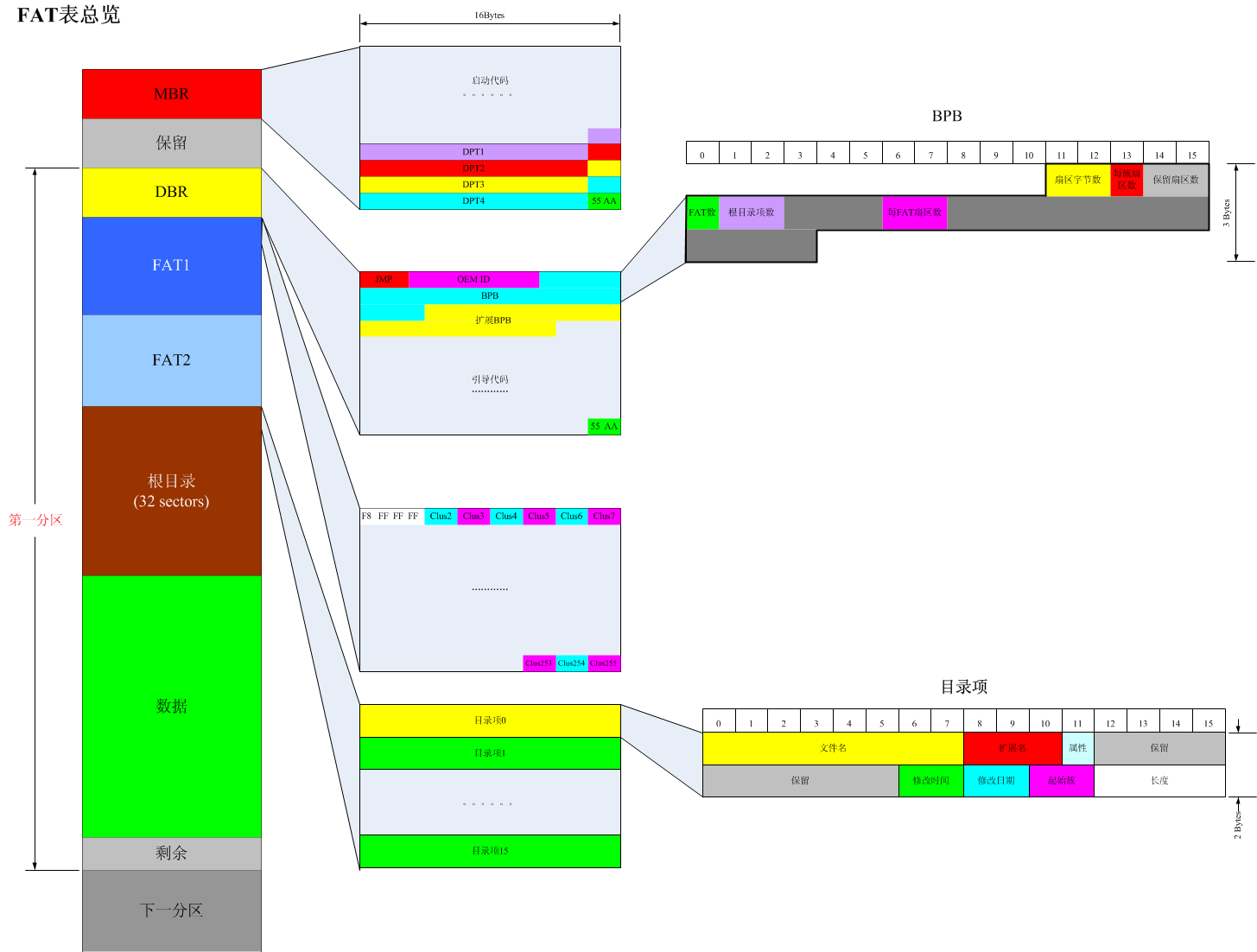
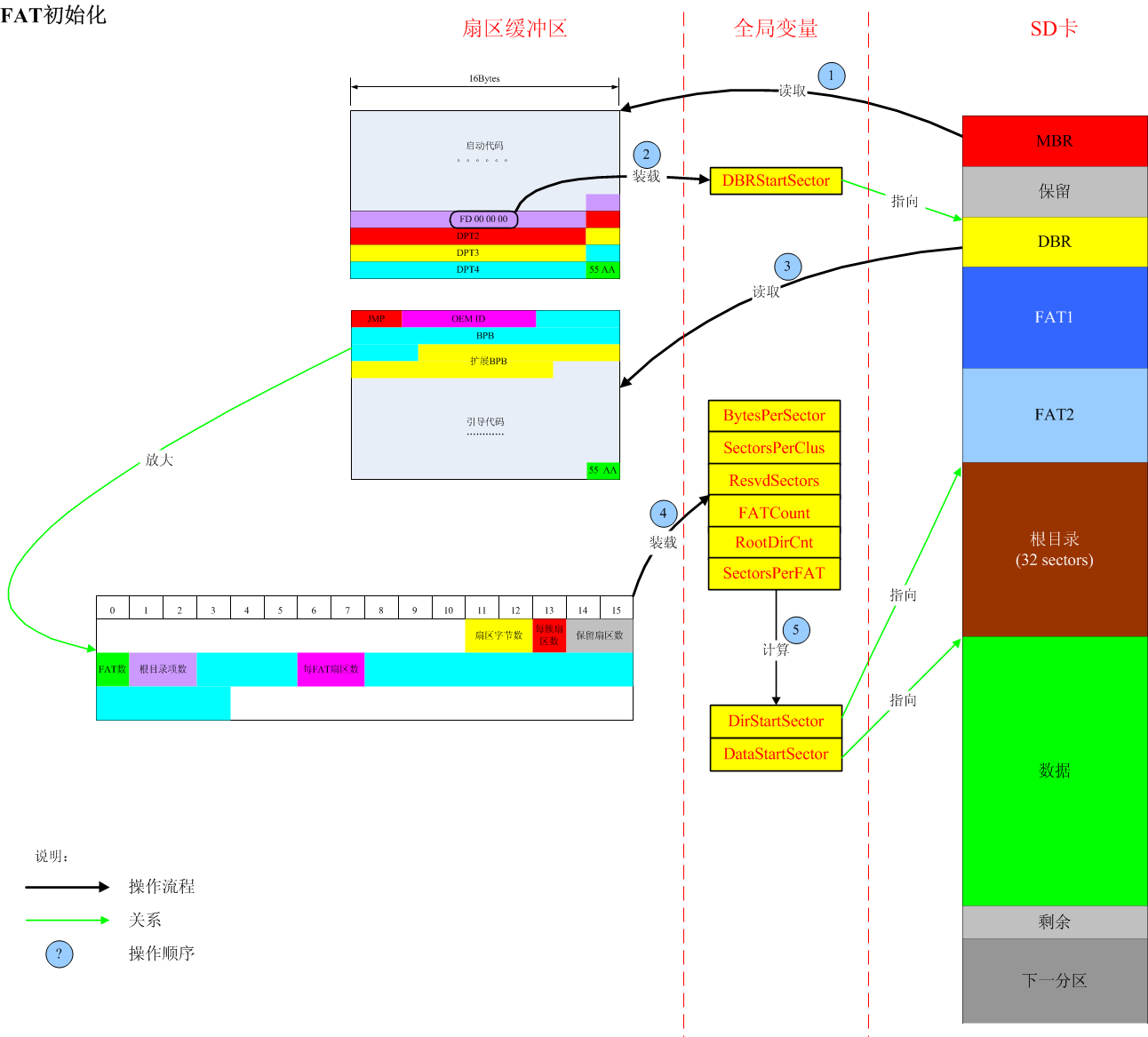
static u8 ReadMBR(void)
{
tMBR *pmbr = (tMBR *)SectorBuf;
//因为此时的DBRStartSector还未被赋值,等于0,所以这里读取的是物理扇区0
if(0 == ReadBlock(0)) return 0;
if(0xAA55 != pmbr->Flag) return 0;
//通过磁盘分区表DPT字段来获取系统引导扇区DBR的扇区偏移量
DBRStartSector = (pmbr->DPT[0].LBAoffest[1] << 16) + pmbr->DPT[0].LBAoffest[0];
return 1;
}
//读取系统引导扇区DBR
static u8 ReadDBR(void)
{
tDBR *pdbr = (tDBR*)SectorBuf;
if(0 == ReadBlock(0)) return 0;
if(0xAA55 != pdbr->Flag) return 0;
//通过系统引导扇区中的BPB字段,计算磁盘的相关参数
BytesPerSector = (pdbr->BPB.BytesPerSector[1] << 8) + pdbr->BPB.BytesPerSector[0];
SectorsPerClus = pdbr->BPB.SectorsPerClus;
ResvdSectors = (pdbr->BPB.ResvdSectors[1] << 8) + pdbr->BPB.ResvdSectors[0];
FATCount = pdbr->BPB.FATCount;
RootDirCnt = (pdbr->BPB.DirCount[1] << 8) + pdbr->BPB.DirCount[0];
SectorsPerFAT = (pdbr->BPB.SectorsPerFAT[1] << 8) + pdbr->BPB.SectorsPerFAT[0];
DirStartSector = ResvdSectors + SectorsPerFAT * FATCount;
DataStartSector = DirStartSector + 32;
return 1;
}
//读取FAT表项的值
static u16 ReadFAT(u16 Index)
{
u16 *pItem = (u16*)&SectorBuf[0];
//因为1扇区 = 256个FAT表项,所以Index >> 8表示从FAT开始的扇区偏移
if(0 == ReadBlock((Index >> 8) + ResvdSectors)) return 0;
//Index % 256 表示扇区内的字偏移
return *(pItem + (Index % 256));
}
//写入某一FAT表项的值
static u16 WriteFAT(u16 Index, u16 val)
{
u16 *pItem = (u16*)&SectorBuf[0];
//计算Index所在的逻辑扇区号
u16 sector = (Index >> 8) + ResvdSectors;
if(0 == ReadBlock(sector)) return 0;
//Index % 256 表示扇区内的字偏移
*(pItem + (Index % 256)) = val;
if(0 == WriteBlock(sector)) return 0;
return 1;
}
//将FAT1的某一扇区拷贝到FAT2所对应的扇区
//sector表示从FAT1开始的扇区偏移
static u8 CopyFAT(u16 sector)
{
if(!ReadBlock(ResvdSectors + sector)) return 0;
if(!WriteBlock(ResvdSectors + SectorsPerFAT + sector)) return 0;
return 1;
}
//FAT16初始化
u8 FAT_Init(void)
{
//先读取MBR,找到系统引导扇区的位置
if(0 == ReadMBR()) return 0;
//再读取系统引导扇区中的BPB,获取磁盘的相关参数
if(0 == ReadDBR()) return 0;
return 1;
}
//查找根目录下是否存在name所对应的文件,如果存在则将该文件信息存放到dir所指向的结构体中
u8 GetFileDir(const char* name, tDIR *dir)
{
u8 i, j;
tDIR *pDir;
char DOSname[11];
//第一步要将name格式化成标准8.3格式的文件名
NameFormat(name, DOSname);
//因为根目录区总共占32个扇区
for(j = 0; j < 32; j++)
{
if(0 == ReadBlock(DirStartSector + j)) return 0;
//而每个扇区又包含16个目录项
for(i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
//每个目录项又占32个字节,所以这里用i << 5表示目录项在一个扇区中的字节偏移
pDir = (tDIR *)&SectorBuf[i << 5];
//通过文件名来查找文件
if(IsEqual(DOSname, pDir->Name, 11))
{
*dir = *pDir;
return 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
//将文件信息写入Index所指定的目录项中
static u8 WriteDir(u16 Index, tDIR *dir)
{
tDIR *pDir;
//计算Index所在的逻辑扇区偏移,Index / 16表示从目录区开始的扇区偏移量
u16 sector = Index / 16 + DirStartSector;
if(!ReadBlock(sector)) return 0;
pDir = (tDIR*)&SectorBuf[0];
//Index % 16表示1个扇区内的目录项偏移
*(pDir + (Index % 16)) = *dir;
if(!WriteBlock(sector)) return 0;
return 1;
}
//从根目录区中获取一个空的目录项
static u16 GetEmptyDir(void)
{
u8 j, i;
u16 index = 0;
//因为根目录区总共占32个扇区
for(i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
if(!ReadBlock(DirStartSector + i)) return 0xffff;
//而每个扇区又包含16个目录项
for(j = 0; j < 16; j++)
{
//每个目录项又占32个字节,所以这里用j * 32表示目录项在一个扇区中的字节偏移
if(0 == SectorBuf[j * 32])
return index;
index++;
}
}
return 0xffff;
}
//获取一个空的FAT表项,即一个空簇的簇号
static u16 GetEmptyFAT(void)
{
u16 i, j;
u16 *pItem;
//遍历FAT表所占的每个扇区
for(i = 0; i < SectorsPerFAT; i++)
{
if(0 == ReadBlock(i + ResvdSectors)) return 0;
pItem = (u16*)&SectorBuf[0];
//遍历扇区内的每个FAT表项
for(j = 0; j < 256; j++)
{
if(*(pItem + j) == 0) return ((i << 8) + j);
}
}
return 0;
}
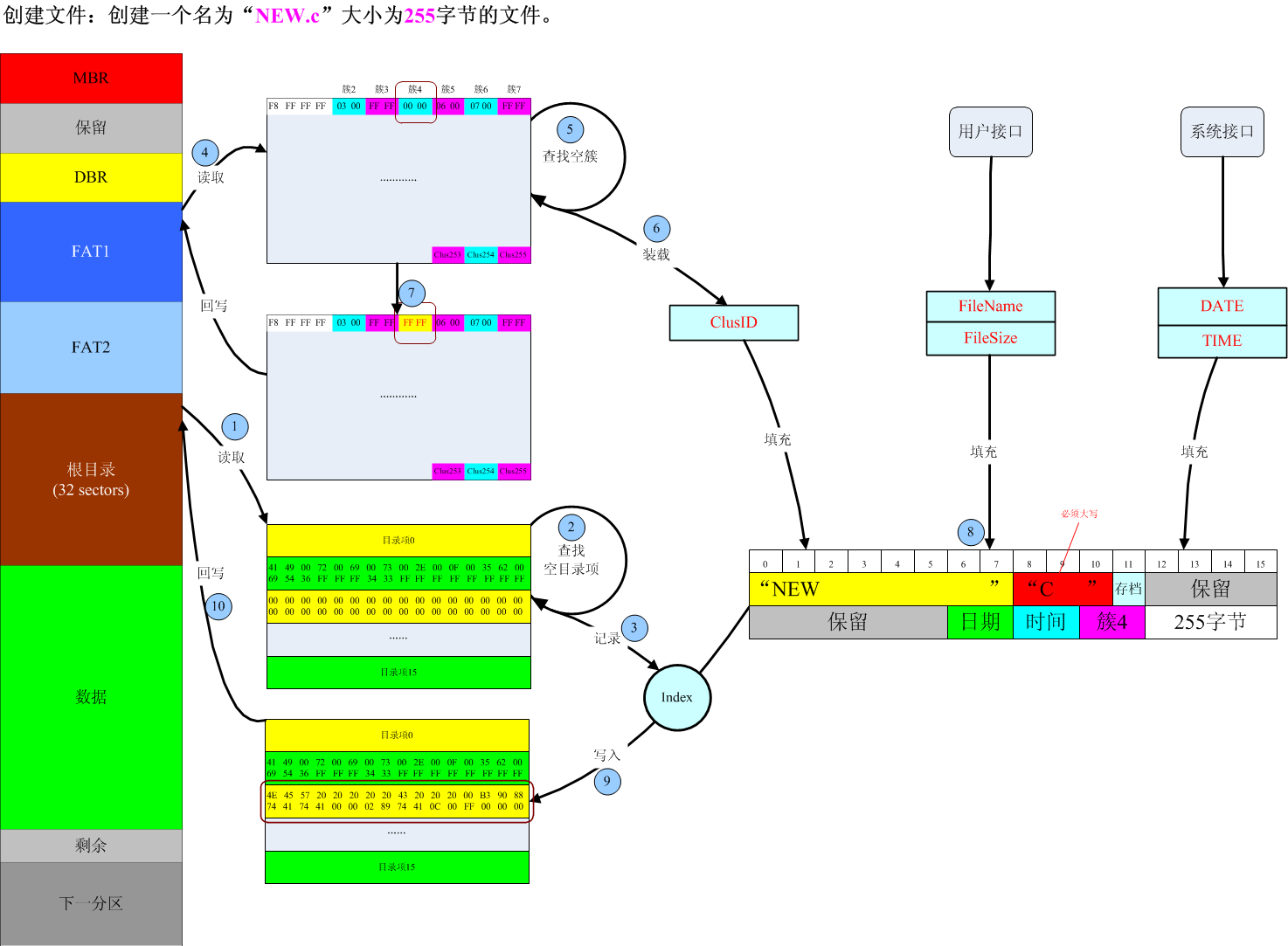
//新建一个文件
//注意:文件的大小已固定为size字节,即使新建的文件没有写任何内容,文件的大小始终为size大小;
// 即使对该文件写入了超过size大小的内容,文件的大小依然不改变
//该函数有待进一步优化,对于大文件的创建,该函数速度非常缓慢
u8 CreateFile(const char* name, u32 size)
{
tDIR dir = {0}; //一定要初始化为0,否则在WINDOWS系统下无法识别文件
u16 ClusID;
u16 i;
u16 FATSector;
//计算一簇所占的字节数
u32 BytesPerClus = BytesPerSector * SectorsPerClus;
//文件已存在,则返回
if(GetFileDir(name, &dir)) return 0;
//首先从根目录区获取一个空的目录项
i = GetEmptyDir();
if(i == 0xffff) return 0;
//从FAT表中获取一个空的FAT表项
ClusID = GetEmptyFAT();
//立即将该空的FAT表项填充为0xFFFF,以免后面再次获取空的FAT表项时错误的分配到同一表项
if(0 == WriteFAT(ClusID, 0xFFFF)) return 0;
//然后给该目录项填充文件信息
NameFormat(name, dir.Name);
dir.Attri = 0;
dir.FirstClus = ClusID;
dir.Length[0] = size;
dir.Length[1] = size >> 16;
//将目录信息回写到目录表中
if(0 == WriteDir(i, &dir)) return 0;
//计算分配到的FAT表项在FAT表中的扇区偏移
FATSector = ClusID / 256;
for(/*文件所占簇个数*/i = size / BytesPerClus; i != 0; i--)
{
u16 NextClus;
//获取下一个空簇的簇号
NextClus = GetEmptyFAT();
if(!NextClus) return 0;
//此部分有待优化
if(0 == WriteFAT(ClusID, NextClus)) return 0;
if(0 == WriteFAT(NextClus, 0xFFFF)) return 0;
//当下一FAT表项所在位置不在当前FAT扇区时,立即将当前FAT1扇区的内容拷贝到对应的FAT2中
if(FATSector != (NextClus / 256))
{
CopyFAT(FATSector);
//并将下一FAT表项所在扇区偏移赋值给FATSector
FATSector = NextClus / 256;
}
ClusID = NextClus;
}
//将最后一扇区拷贝到FAT2中的相应位置
CopyFAT(FATSector);
return 1;
}
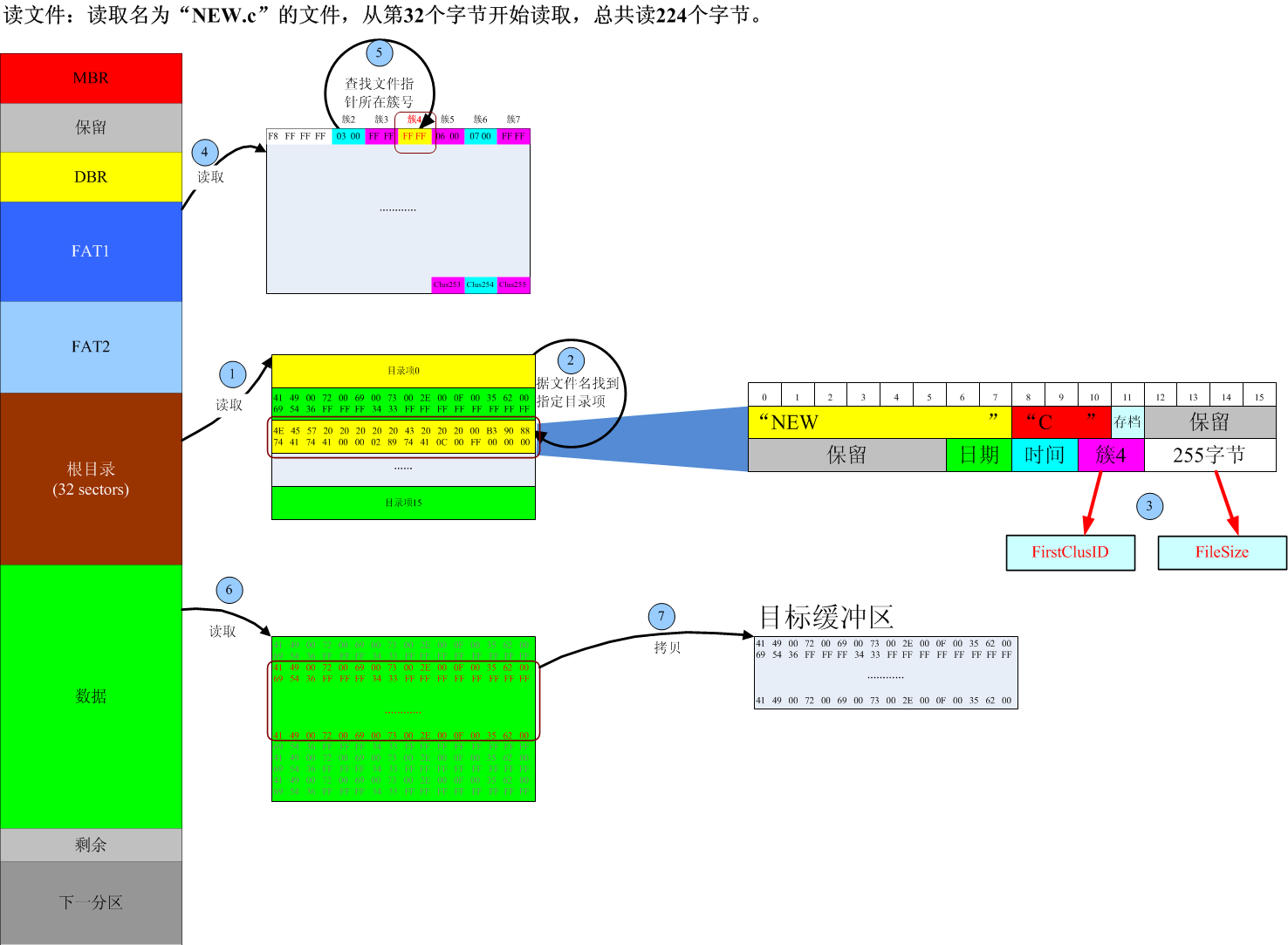
//读取文件
u8 ReadFile(const char* name, u32 offest, void* dst, u32 len)
{
tDIR dir;
u16 ClusID;
u16 StartSector;
u32 FileSize;
u32 PtrByteOffest, PtrSectorOffest, PtrClusOffest;
u16 i;
u8 *pDst = (u8*)dst;
//首先找到文件对应的目录项
if(!GetFileDir(name, &dir)) return 0;
FileSize = (dir.Length[1] << 16) + dir.Length[0];
//文件指针超出文件尾则返回
if(offest > FileSize) return 0;
//len大于文件长度的情况
if((offest + len) > FileSize)
len = FileSize - offest;
ClusID = dir.FirstClus;
//文件指针相对于文件头的扇区偏移
PtrSectorOffest = offest / BytesPerSector;
//文件指针相对于当前扇区的字节偏移
PtrByteOffest = offest % BytesPerSector;
//文件指针相对于文件头的簇偏移
PtrClusOffest = PtrSectorOffest / SectorsPerClus;
//找到文件指针所在簇号
for(i = 0; i < PtrClusOffest; i++)
ClusID = ReadFAT(ClusID);
//文件指针相对于系统分区的扇区偏移
StartSector = Clus2Sector(ClusID) + PtrSectorOffest;
while(1)
{
//2.从指针所在的扇区开始,遍历文件的每个扇区
for(; PtrSectorOffest < SectorsPerClus; PtrSectorOffest++)
{
if(!ReadBlock(StartSector++)) return 0;
//1.从指针所在扇区的字节偏移开始,遍历扇区的每个字节
for(; PtrByteOffest < BytesPerSector; PtrByteOffest++)
{
*pDst++ = SectorBuf[PtrByteOffest];
len--;
if(0 == len) return 1;
}
PtrByteOffest = 0;
}
//读取下一簇号
ClusID = ReadFAT(ClusID);
//获取下一簇所在的扇区号
StartSector = Clus2Sector(ClusID);
PtrSectorOffest = 0;
}
}
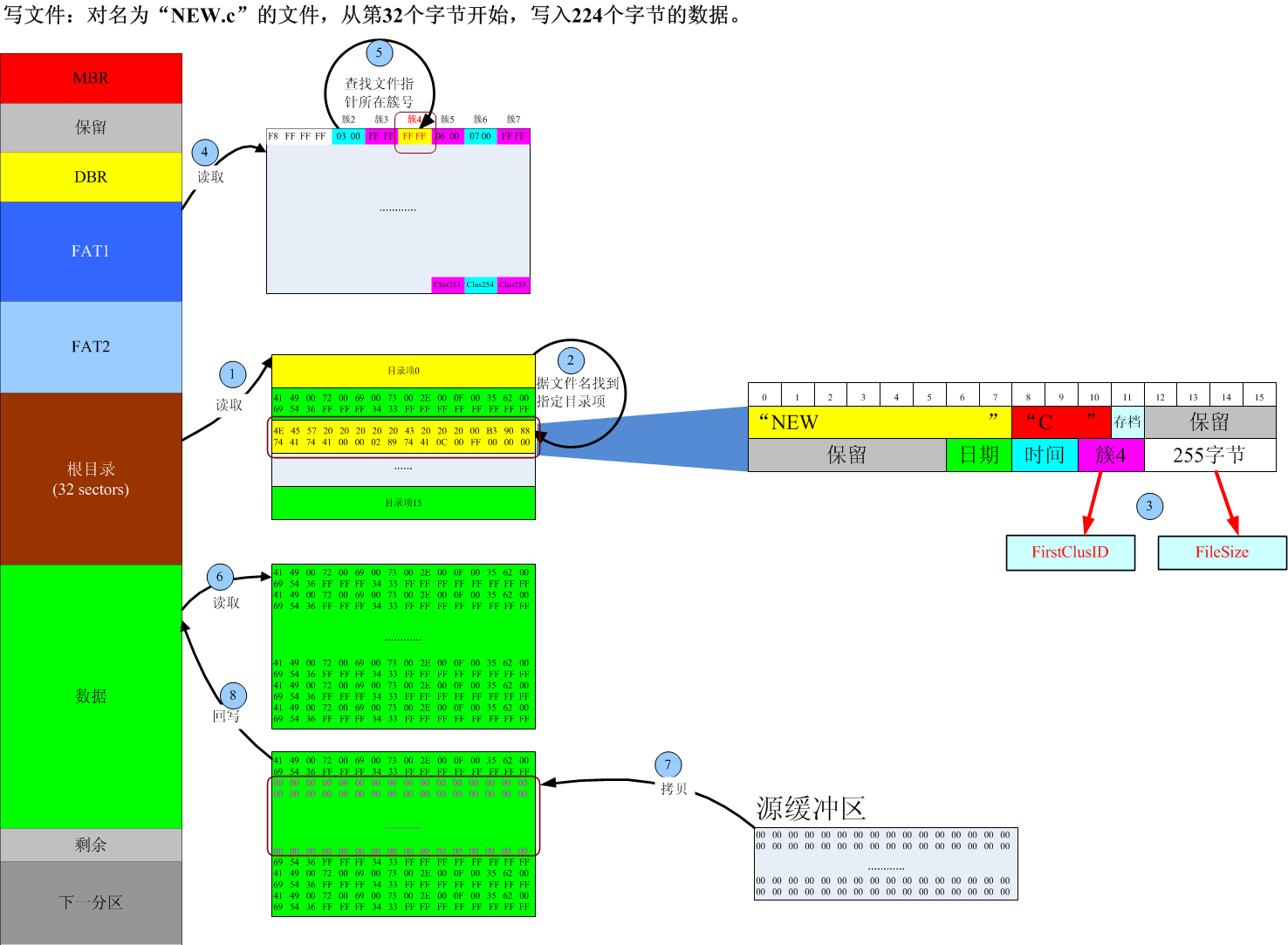
//写文件
u8 WriteFile(const char* name, u32 offest, void* src, u32 len)
{
tDIR dir;
u16 ClusID;
u16 StartSector;
u32 FileSize;
u32 PtrByteOffest, PtrSectorOffest, PtrClusOffest;
u16 i;
u8 *pSrc = (u8*)src;
if(!GetFileDir(name, &dir)) return 0;
FileSize = (dir.Length[1] << 16) + dir.Length[0];
//文件指针超出文件尾则返回
if(offest > FileSize) return 0;
//len大于文件长度的情况
if((offest + len) > FileSize)
len = FileSize - offest;
ClusID = dir.FirstClus;
//文件指针相对于文件头的扇区偏移
PtrSectorOffest = offest / BytesPerSector;
//文件指针相对于当前扇区的字节偏移
PtrByteOffest = offest % BytesPerSector;
//文件指针相对于文件头的簇偏移
PtrClusOffest = PtrSectorOffest / SectorsPerClus;
//找到文件指针所在簇号
for(i = 0; i < PtrClusOffest; i++)
ClusID = ReadFAT(ClusID);
//文件指针相对于系统分区的扇区偏移
StartSector = Clus2Sector(ClusID) + PtrSectorOffest;
while(1)
{
//2.从指针所在的扇区开始,遍历文件的每个扇区
for(; PtrSectorOffest < SectorsPerClus; PtrSectorOffest++)
{
if(!ReadBlock(StartSector)) return 0;
//1.从指针所在扇区的字节偏移开始,遍历扇区的每个字节
for(; PtrByteOffest < BytesPerSector; PtrByteOffest++)
{
SectorBuf[PtrByteOffest] = *pSrc++;
len--;
if(0 == len)
{
if(!WriteBlock(StartSector)) return 0;
else return 1;
}
}
if(!WriteBlock(StartSector++)) return 0;
PtrByteOffest = 0;
}
//读取下一簇号
ClusID = ReadFAT(ClusID);
//获取下一簇所在的扇区号
StartSector = Clus2Sector(ClusID);
PtrSectorOffest = 0;
}
}
源码下载:  FAT16.zip
FAT16.zip
图文PDF下载:  FAT16模块详解.pdf
FAT16模块详解.pdf

























 1356
1356

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










