案例
ansible -i inventory.ini masters -m command -a "systemctl status NetworkManager"
ansible -i inventory.ini masters-shadow -m command -a "systemctl status NetworkManager"
ansible -i inventory.ini slaves -m command -a "systemctl status NetworkManager"
Ansible是一种自动化工具,它通过使用模块来管理和配置远程主机。Ansible模块是Ansible的基本构建块,用于执行各种任务和操作。
模块
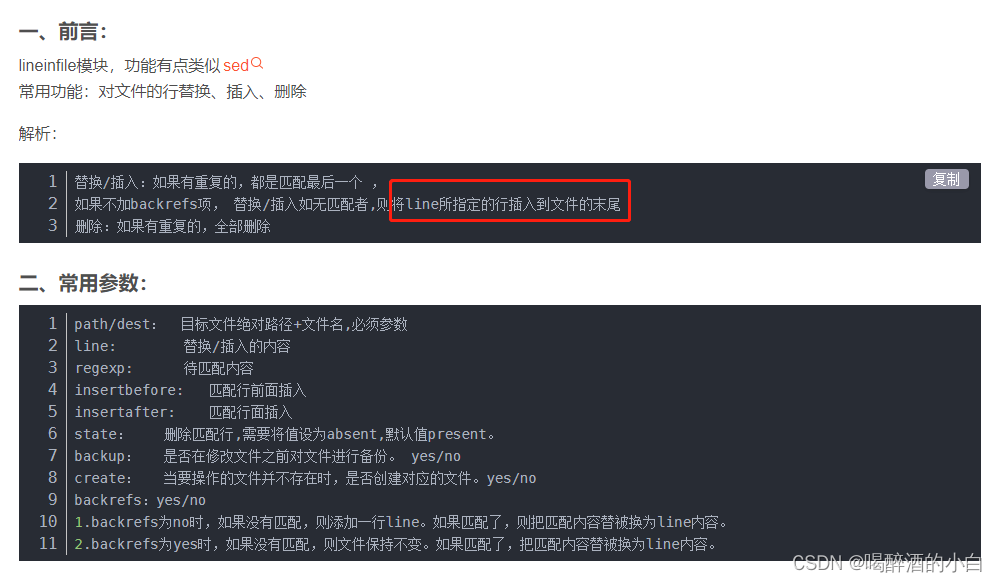
lineinfile
sysctl
sysctl 模块

ansible-doc sysctl
debug
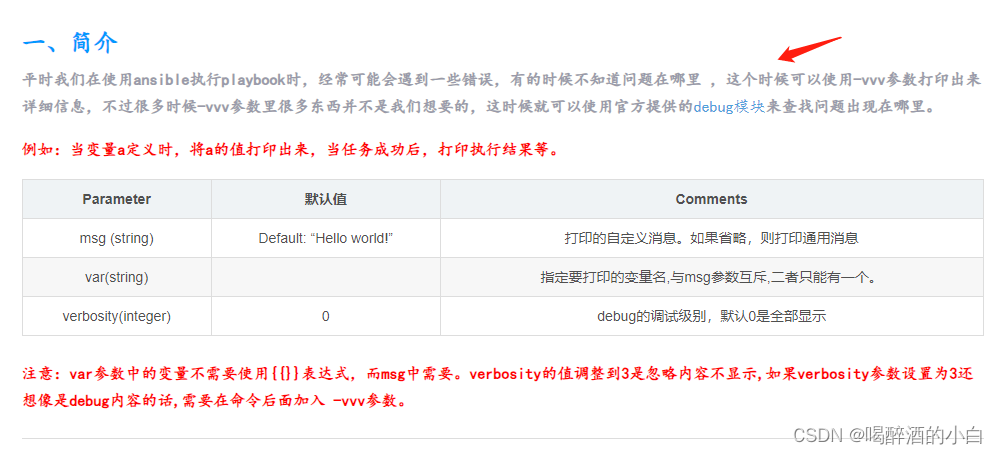
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37814112/article/details/129396441
gather_facts
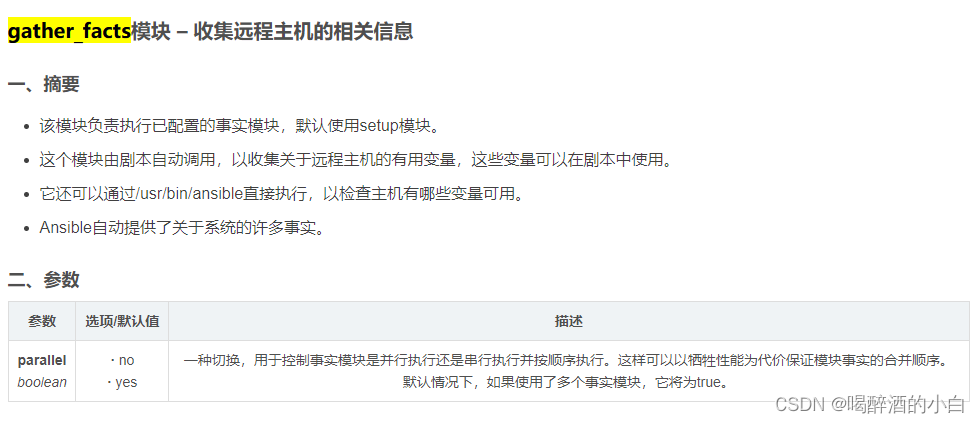
ansible all -m gather_facts --tree /tmp/facts
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44762073/article/details/127448080
整体介绍
Ansible模块可以通过以下几种方式使用:
-
Shell模块:Shell模块允许在远程主机上执行命令或脚本。它通过在远程主机上启动一个shell会话来运行命令,并将输出返回给控制机。
-
Command模块:Command模块与Shell模块类似,用于在远程主机上执行命令。但是,Command模块不会启动一个shell会话,而是直接执行命令。
-
File模块:File模块用于管理远程主机上的文件和目录。它可以创建、修改、删除文件和目录,并设置文件权限和所有权。
-
Package模块:Package模块用于在远程主机上安装、更新和卸载软件包。它可以与不同的软件包管理工具(如apt、yum、dnf等)集成,以实现跨多个操作系统的软件包管理。
-
Service模块:Service模块用于管理远程主机上的系统服务。它可以启动、停止、重新加载和重启服务,并设置服务的启动状态。
除了上述常用模块之外,Ansible还提供了许多其他模块,用于执行各种任务,如用户管理、数据库操作、网络配置等。你可以在Ansible的官方文档中查找并了解更多可用的模块。
通过编写Ansible Playbooks,你可以组合和配置这些模块,以实现自动化的配置管理和部署。Ansible Playbooks使用YAML语法来定义任务和主机组,并指定要在远程主机上执行的模块和参数。
总而言之,Ansible模块是用于在远程主机上执行各种任务和操作的工具,它们是Ansible自动化工具的核心组成部分。
除了常用的模块,Ansible还提供了许多其他模块,用于执行各种不同类型的任务和操作。以下是一些常用的其他Ansible模块:
-
Template模块:Template模块用于根据模板文件生成配置文件。它可以将变量和条件逻辑应用于模板,从而动态生成配置文件,并将其复制到远程主机上。
-
Git模块:Git模块用于在远程主机上执行Git操作,如克隆代码库、拉取更新、检出分支等。
-
Docker模块:Docker模块用于与Docker守护进程进行交互,以管理Docker容器、镜像和网络。它可以启动、停止、删除容器,构建和推送镜像等。
-
Systemd模块:Systemd模块用于与Systemd服务管理器进行交互,以管理系统服务。它可以启动、停止、重启、重新加载和禁用Systemd服务。
-
MySQL模块:MySQL模块提供了与MySQL数据库进行交互的功能。它可以执行SQL查询、创建数据库、用户管理、备份和恢复等操作。
-
AWS模块:AWS模块用于与亚马逊云服务进行交互,执行与EC2实例、S3存储桶、RDS数据库等相关的操作。
-
Azure模块:Azure模块用于与Microsoft Azure云服务进行交互,执行与虚拟机、存储账户、数据库等相关的操作。
-
Slack模块:Slack模块用于与Slack通信平台进行交互,可以发送消息、创建频道、添加用户等。
这只是一小部分其他可用的Ansible模块。Ansible社区不断增加和更新模块,以覆盖更多的任务和操作领域。您可以参考Ansible的官方文档和模块索引,以获取完整的模块列表和详细的说明文档。
请注意,模块的可用性和功能可能与Ansible版本和您使用的目标系统有关。建议在使用之前检查您的Ansible版本和相关模块的要求与限制。
ansible -h
usage: ansible [-h] [--version] [-v] [-b] [--become-method BECOME_METHOD]
[--become-user BECOME_USER] [-K] [-i INVENTORY] [--list-hosts]
[-l SUBSET] [-P POLL_INTERVAL] [-B SECONDS] [-o] [-t TREE] [-k]
[--private-key PRIVATE_KEY_FILE] [-u REMOTE_USER]
[-c CONNECTION] [-T TIMEOUT]
[--ssh-common-args SSH_COMMON_ARGS]
[--sftp-extra-args SFTP_EXTRA_ARGS]
[--scp-extra-args SCP_EXTRA_ARGS]
[--ssh-extra-args SSH_EXTRA_ARGS] [-C] [--syntax-check] [-D]
[-e EXTRA_VARS] [--vault-id VAULT_IDS]
[--ask-vault-pass | --vault-password-file VAULT_PASSWORD_FILES]
[-f FORKS] [-M MODULE_PATH] [--playbook-dir BASEDIR]
[-a MODULE_ARGS] [-m MODULE_NAME]
pattern
Define and run a single task 'playbook' against a set of hosts
positional arguments:
pattern host pattern
optional arguments:
--ask-vault-pass ask for vault password
--list-hosts outputs a list of matching hosts; does not execute
anything else
--playbook-dir BASEDIR
Since this tool does not use playbooks, use this as a
substitute playbook directory.This sets the relative
path for many features including roles/ group_vars/
etc.
--syntax-check perform a syntax check on the playbook, but do not
execute it
--vault-id VAULT_IDS the vault identity to use
--vault-password-file VAULT_PASSWORD_FILES
vault password file
--version show program's version number, config file location,
configured module search path, module location,
executable location and exit
-B SECONDS, --background SECONDS
run asynchronously, failing after X seconds
(default=N/A)
-C, --check don't make any changes; instead, try to predict some
of the changes that may occur
-D, --diff when changing (small) files and templates, show the
differences in those files; works great with --check
-M MODULE_PATH, --module-path MODULE_PATH
prepend colon-separated path(s) to module library (def
ault=~/.ansible/plugins/modules:/usr/share/ansible/plu
gins/modules)
-P POLL_INTERVAL, --poll POLL_INTERVAL
set the poll interval if using -B (default=15)
-a MODULE_ARGS, --args MODULE_ARGS
module arguments
-e EXTRA_VARS, --extra-vars EXTRA_VARS
set additional variables as key=value or YAML/JSON, if
filename prepend with @
-f FORKS, --forks FORKS
specify number of parallel processes to use
(default=5)
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INVENTORY, --inventory INVENTORY, --inventory-file INVENTORY
specify inventory host path or comma separated host
list. --inventory-file is deprecated
-l SUBSET, --limit SUBSET
further limit selected hosts to an additional pattern
-m MODULE_NAME, --module-name MODULE_NAME
module name to execute (default=command)
-o, --one-line condense output
-t TREE, --tree TREE log output to this directory
-v, --verbose verbose mode (-vvv for more, -vvvv to enable
connection debugging)
Privilege Escalation Options:
control how and which user you become as on target hosts
--become-method BECOME_METHOD
privilege escalation method to use (default=sudo), use
`ansible-doc -t become -l` to list valid choices.
--become-user BECOME_USER
run operations as this user (default=root)
-K, --ask-become-pass
ask for privilege escalation password
-b, --become run operations with become (does not imply password
prompting)
Connection Options:
control as whom and how to connect to hosts
--private-key PRIVATE_KEY_FILE, --key-file PRIVATE_KEY_FILE
use this file to authenticate the connection
--scp-extra-args SCP_EXTRA_ARGS
specify extra arguments to pass to scp only (e.g. -l)
--sftp-extra-args SFTP_EXTRA_ARGS
specify extra arguments to pass to sftp only (e.g. -f,
-l)
--ssh-common-args SSH_COMMON_ARGS
specify common arguments to pass to sftp/scp/ssh (e.g.
ProxyCommand)
--ssh-extra-args SSH_EXTRA_ARGS
specify extra arguments to pass to ssh only (e.g. -R)
-T TIMEOUT, --timeout TIMEOUT
override the connection timeout in seconds
(default=10)
-c CONNECTION, --connection CONNECTION
connection type to use (default=smart)
-k, --ask-pass ask for connection password
-u REMOTE_USER, --user REMOTE_USER
connect as this user (default=None)
Some modules do not make sense in Ad-Hoc (include, meta, etc)





















 813
813











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








