流与FILE对象
1.流的定向:
决定了所读,所写的字符是单字节还是多字节字符集。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <wchar.h>
int fwide(FILE *fp, int mode); //设置流的定向缓冲
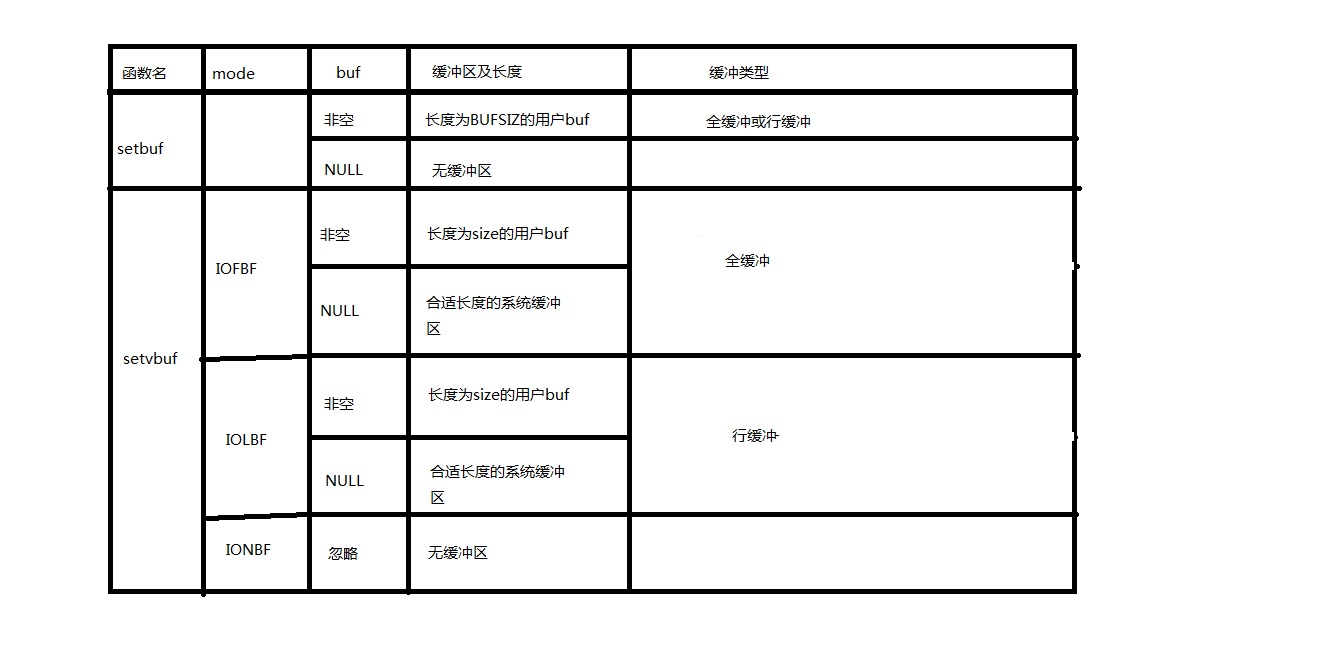
1.全缓冲:在填满标准I/O缓冲区之后才进行实际I/O操作。例如写到文件中时会使用全缓冲。
2.行缓冲:在输入与输出中遇到换行符,标准I/O库执行I/O操作。当流涉及到一个终端(例如标准输入和标准输出),通常使用行缓冲。
3.不带缓冲
#include <stdio.h>
void setbuf(FILE *restrict fp, char *restrict buf);
void setvbuf(FILE *restrict fp, char *restrict buf, int mode,
size_t size);打开流
#include <stdio.h>
FILE *fopen(const char *restrict pathname,
const char *restrict type);
FILE *freopen(const char *restrict pathname,
const char *restrict type,
FILE *restrict fp);
FILE *fdopen(int filedes, cosnt char *type);读和写流
1)字符读写
#include <stdio.h>
int getc(FILE *fp); //宏
int putc(int c, FILE *fp); //宏
int fgetc(FILE* fp);
int fputc(int c, FILE *fp);
int getchar(void);
int putchar(int c);
int ferror(FILE *fp);
int feof(FILE *fp);
void clearerr(FILE *fp);2)可以用下列函数把字符送回流
int ungetc(int c, FILE *fp);一次只能回送一个字符,回送的字符不必一定是上一次读到的字符,不可以回送EOF。但是到达文件尾端时,任然可以回送一个字符。下次读将返回该字符,再次读则返回EOF。
因为ungetc会清除流的文件结束符。
3)一次读写一行
#include <stdio.h>
char *fgets(char *restrict buf,
int n,
FILE *restrict fp);
char *gets(char *buf);
int fputs(cosnt char *restrict str,
FILE *restrict fp);
int puts(const char *str);定位流
格式化I/O
杂记
#include <stdio.h>
int fileno(FILE *fp); //返回与流fp有关的文件的文件描述符






















 565
565

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








