【题目来源】
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1100
https://vjudge.net/problem/ZOJ-1062
http://poj.org/problem?id=1095
【题目描述】
We can number binary trees using the following scheme:
The empty tree is numbered 0.
The single-node tree is numbered 1.
All binary trees having m nodes have numbers less than all those having m+1 nodes.
Any binary tree having m nodes with left and right subtrees L and R is numbered n such that all trees having m nodes numbered > n have either Left subtrees numbered higher than L, or A left subtree = L and a right subtree numbered higher than R.
The first 10 binary trees and tree number 20 in this sequence are shown below:
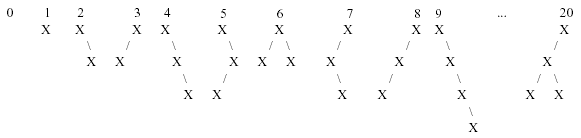
Your job for this problem is to output a binary tree when given its order number.
【输入格式】
Input consists of multiple problem instances. Each instance consists of a single integer n, where 1 <= n <= 500,000,000. A value of n = 0 terminates input. (Note that this means you will never have to output the empty tree.)
【输出格式】
For each problem instance, you should output one line containing the tree corresponding to the order number for that instance. To print out the tree, use the following scheme:
A tree with no children should be output as X.
A tree with left and right subtrees L and R should be output as (L’)X(R’), where L’ and R’ are the representations of L and R.
If L is empty, just output X(R’).
If R is empty, just output (L’)X.
【输入样例】
1
20
31117532
0
【输出样例】
X
((X)X(X))X
(X(X(((X(X))X(X))X(X))))X(((X((X)X((X)X)))X)X)
【算法分析】
● 本题大意:给定一个二叉树的排序规则,之后输入一个序号,然后按格式约定输出这个序号所对应的二叉树。本题给出的二叉树的排序规则如下:
(1)结点个数多的二叉树,序号更“大”;
(2)结点个数一样的二叉树,左子树高度高的二叉树,序号更“大”;
(3)结点个数一样的二叉树,左子树相同,右子数高度高的二叉树,序号更“大”。
● 根据本题题意,若以数对儿的形式表示结点数为 n 的二叉树的左右子树的结点数,则存在多种情形。即:(0, n-1),(1, n-2),…… ,(n-1, 0)
本题中,若设结点数为 n 的二叉树有 h[n] 个,则 h[n]=h[0]∗h[n−1]+h[1]∗h[n−2]+⋯h[n−1]∗h[0],(n⩾2),且 h[0]=h[1]=1。显然,本题与卡特兰数的递推关系及初始值相符。所以,我们得出 h[n] 就是卡特兰数。
● 对于任给的一个编号 idx ,其对应的二叉树的结点数量为:
上面公式,其对应的LaTEX代码为:
node\_num=min \{x|\sum\limits_{i=1}\limits^{x}h[i]\geq idx\}特别要注意,上面公式中的 h[i] 代表结点数为 i 的二叉树的数量,而不是二叉树中的结点数量。对照本题给出的示意图,可以理解此公式的涵义。
● 对于一个编号为 idx ,且有 node_num 个结点的二叉树,其左子树所含结点的个数为:
上面公式,所对应的 LaTEX 代码为:
le\_son\_num=min \{x|\sum\limits_{i=1}\limits^{x}(h[i]*h[node\_num-i-1])\geq idx\_diff\}其中,idx_diff 为相对编号,表示该二叉树在同结点数量的所有二叉树中排第几。
上面公式,所对应的 LaTEX 代码为:
idx\_diff=idx-\sum\limits_{i=1}\limits^{node\_num-1}h[i]根据上面的分析,易知给定的二叉树的右子树所含结点的个数为:
● 若将二叉树的两棵子树也看成如题所述的二叉树,则左子树的相对编号 le_son_idx_diff 为:
上面公式,所对应的 LaTEX 代码为:
le\_son\_idx\_diff=\left \lceil \frac{idx\_diff}{h[ri\_son\_num]} \right \rceil右子树的相对编号 ri_son_idx_diff 为:
上面公式,所对应的 LaTEX 代码为:
ri\_son\_idx\_diff=[(idx\_diff-1)\ mod\ h[ri\_son\_num]]+1然后,按照此法不断递归,便可得到所求。
● 卡特兰数:https://blog.csdn.net/hnjzsyjyj/article/details/129148916
其中,卡特兰数常用的递推式为:
h[n]=1,(n=0,1)
h[n]=h[0]∗h[n−1]+h[1]∗h[n−2]+⋯h[n−1]∗h[0],(n⩾2)
卡特兰数代码如下:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=10001;
int main(){
long long c[maxn],ans,n;
scanf("%d",&n);
c[0]=1;
c[1]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=i-1;j++){
c[i]+=c[j]*c[i-j-1];
}
}
for(int k=0;k<=n;k++){
printf("%d ",c[k]);
}
return 0;
}
/*
in:19
out:1 1 2 5 14 42 132 429 1430 4862 16796 58786 208012 742900 2674440 9694845 35357670 129644790 477638700
*/
【算法代码】
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//int ct[19]= {1,1,2,5,14,42,132,429,1430,4862,16796,58786,208012,742900,2674440,9694845,35357670,129644790,477638700};
int h[25];
void katelan() {
h[0]=1;
h[1]=1;
for(int i=2; i<=20; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<=i-1; j++) {
h[i]+=h[j]*h[i-j-1];
}
}
}
void dfs(int n,int k) { //递归求有k个节点的第n棵树
if(n==1 && k==1) {
printf("X");
return;
}
int le=0,ri=n-1;
while(ri>=0 && k>h[le]*h[ri]) {
k-=h[le]*h[ri];
le++;
ri--;
}
if(le!=0) {
printf("(");
dfs(le,k%h[ri]==0?k/h[ri]:k/h[ri]+1);
printf(")");
}
printf("X");
if(ri!=0) {
printf("(");
dfs(ri,k%h[ri]==0?h[ri]:k%h[ri]);
printf(")");
}
}
int main() {
katelan();
int n;
while(cin>>n) {
if(n==0) break;
int t=1;
while(n>h[t]) {
n-=h[t];
t++;
}
dfs(t,n);
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
/*
in:
1
20
31117532
0
out:
X
((X)X(X))X
(X(X(((X(X))X(X))X(X))))X(((X((X)X((X)X)))X)X)
*/
【参考文献】
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43549984/article/details/90208542
https://blog.csdn.net/ezereal/article/details/50172891
https://blog.csdn.net/iteye_6233/article/details/82125546
https://blog.csdn.net/hnjzsyjyj/article/details/129148916
https://www.cnblogs.com/keam37/p/3637717.html
https://blog.csdn.net/zhousilijames/article/details/46491881
https://blog.csdn.net/welcome_z/article/details/7906507
https://blog.csdn.net/fei____fei/article/details/24410017











 本文介绍了一种生成二叉树的算法,基于给定的排序规则,通过计算卡特兰数和递归方法确定每个节点的子树结构,以输出对应序号的二叉树。算法涉及卡特兰数的递推关系以及如何根据编号找到对应树的结构表示。
本文介绍了一种生成二叉树的算法,基于给定的排序规则,通过计算卡特兰数和递归方法确定每个节点的子树结构,以输出对应序号的二叉树。算法涉及卡特兰数的递推关系以及如何根据编号找到对应树的结构表示。
















 1443
1443

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








