首先来看看构造函数
transient HashMapEntry<K, V>[] table;
public HashMap() {
table = (HashMapEntry<K, V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
threshold = -1; // Forces first put invocation to replace EMPTY_TABLE
}
private static final Entry[] EMPTY_TABLE
= new HashMapEntry[MINIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1];
private static final int MINIMUM_CAPACITY = 4;从上面可以看到创建了一个大小为2的HashMapEntry数组。HashMapEntry是一个链表实体,它里面有四个成员变量。
再来看看它的另外一个构造函数:
public HashMap(int capacity) {
if (capacity < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Capacity: " + capacity);
}
//
if (capacity == 0) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
HashMapEntry<K, V>[] tab = (HashMapEntry<K, V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
table = tab;
threshold = -1; // Forces first put() to replace EMPTY_TABLE
return;
}
if (capacity < MINIMUM_CAPACITY) {
capacity = MINIMUM_CAPACITY;
} else if (capacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
capacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
} else {
capacity = Collections.roundUpToPowerOfTwo(capacity);
}
makeTable(capacity);
}这个构造函数可以指定HashMapEntry数组的大小。当capacity == 0时,跟第一个构造函数相同。我们来看看capacity>0的情况.
1、当capacity < MINIMUM_CAPACITY时,就让capacity = MINIMUM_CAPACITY,也就是说数组大小最小为MINIMUM_CAPACITY。
2、当capacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY时,就让capacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY,也就是说数组大小最大为MAXIMUM_CAPACITY。
private static final int MINIMUM_CAPACITY = 4;
private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;3、当 MINIMUM_CAPACITY < capacity < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY 时,执行Collections.roundUpToPowerOfTwo(capacity),这个函数的作用是得到让capacity转换成2的(capacity-1的二进制位数)次方。也就是说如果capacity为5,它的二进制为101,减1后为100,位数为3,即最终得到的capacity为2的3次方。
具体的实现如下:
public static int roundUpToPowerOfTwo(int i) {
i--; // If input is a power of two, shift its high-order bit right.
// "Smear" the high-order bit all the way to the right.
i |= i >>> 1;
i |= i >>> 2;
i |= i >>> 4;
i |= i >>> 8;
i |= i >>> 16;
return i + 1;
}上面的过程可以动笔来算算。
最后执行makeTable(capacity)函数,来看看具体的实现。
private HashMapEntry<K, V>[] makeTable(int newCapacity) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") HashMapEntry<K, V>[] newTable
= (HashMapEntry<K, V>[]) new HashMapEntry[newCapacity];
table = newTable;
threshold = (newCapacity >> 1) + (newCapacity >> 2); // 3/4 capacity
return newTable;
}它的操作就是创建了一个大小为newCapacity的HashMapEntry数组。阀值为3/4 capacity。
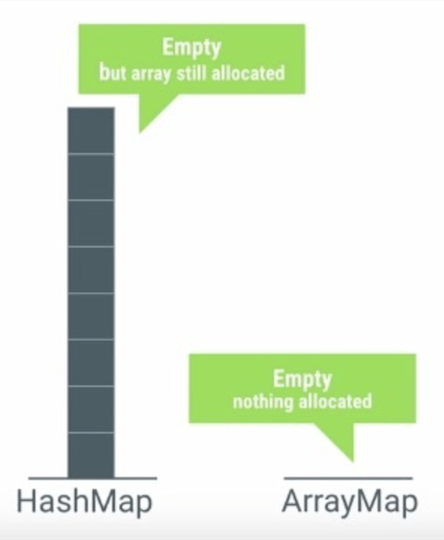
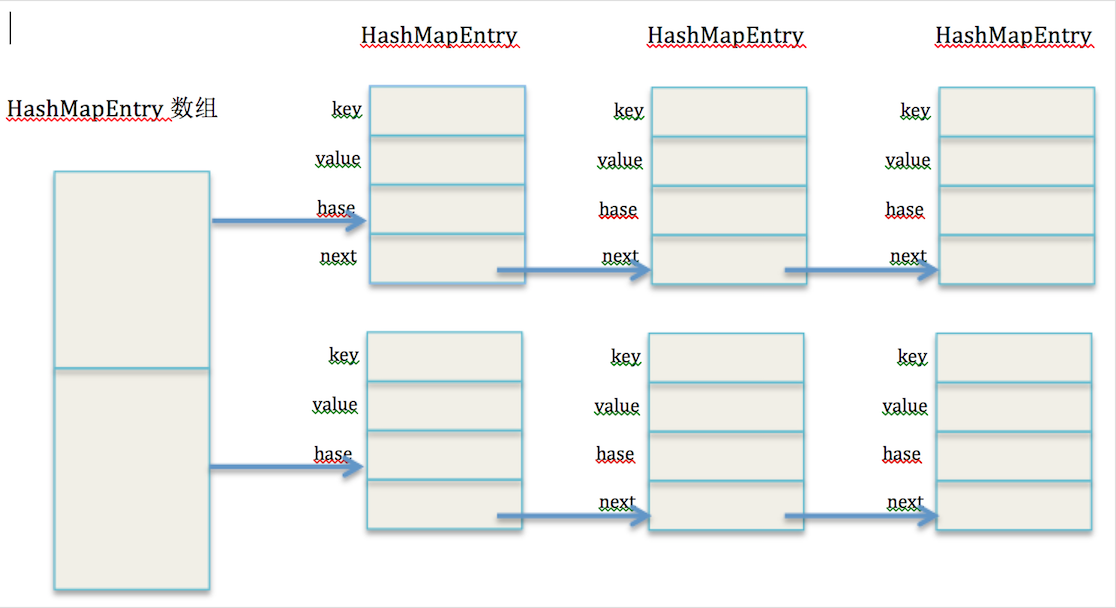
从上面的构造构成可以看到,当我们创建一个HashMap的时候,它内部都会创建一个HashMapEntry数组,如果是无参的构造函数,那么数组的大小为2,如果是有参,则数组的大小会根据参数的值来计算。从这里也可以看到为什么HashMap比ArrayMap的内存占用率高,因为当它们为空的时候,HashMap都会分配空间,但是ArrayMap不会分配空间,从下图也可以看出。
当整个HashMap初始化完毕之后,我们来看看操作函数。
一、put操作
@Override public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null) {
return putValueForNullKey(value);
}
int hash = secondaryHash(key);
HashMapEntry<K, V>[] tab = table;
int index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
for (HashMapEntry<K, V> e = tab[index]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.hash == hash && key.equals(e.key)) {
preModify(e);
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
// No entry for (non-null) key is present; create one
modCount++;
if (size++ > threshold) {
tab = doubleCapacity();
index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
}
addNewEntry(key, value, hash, index);
return null;
}1、如果插入的值的key为null,就会执行putValueForNullKey函数,具体来看看这个函数。
private V putValueForNullKey(V value) {
HashMapEntry<K, V> entry为null,后面就执行 = entryForNullKey;
if (entry == null) {
addNewEntryForNullKey(value);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
} else {
preModify(entry);
V oldValue = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
}刚开始的时候entryForNullKey==null,所以entry为null,后面就执行addNewEntryForNullKey(value);
void addNewEntryForNullKey(V value) {
entryForNullKey = new HashMapEntry<K, V>(null, value, 0, null);
}它就创建了一个HashMapEntry对象被entryForNullKey进行引用,如果下次进来,entryForNullKey不为空,这样就可以直接修改这个对象里面的value值就可以,也就是对value进行更新。
2、如果key不为null,我们把上面的执行代码放下来分析分析。
//得到key值对应的hash值
int hash = secondaryHash(key);
HashMapEntry<K, V>[] tab = table;
//计算出这个key对应的索引值
int index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
//通过index找到数组中对应的实体对象,然后遍历这个对象后面的链表,查找是否存在在对象
//如果找到,那就只需要对对应的value值进行更新
for (HashMapEntry<K, V> e = tab[index]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.hash == hash && key.equals(e.key)) {
preModify(e);
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
//如果没有找到,那么就需要创建一个,然后插入进去
modCount++;
//threshold是一个阀值,如果当前size个数比这个阀值要大,就需要把数组的大小加倍
//加倍之后,就需要重新计算index索引值了
if (size++ > threshold) {
tab = doubleCapacity();
index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
}
//最后就会把对应的键值对插入到对应的index处
addNewEntry(key, value, hash, index);整个添加过程是怎样的,我们也来进行分析分析,进入addNewEntry函数:
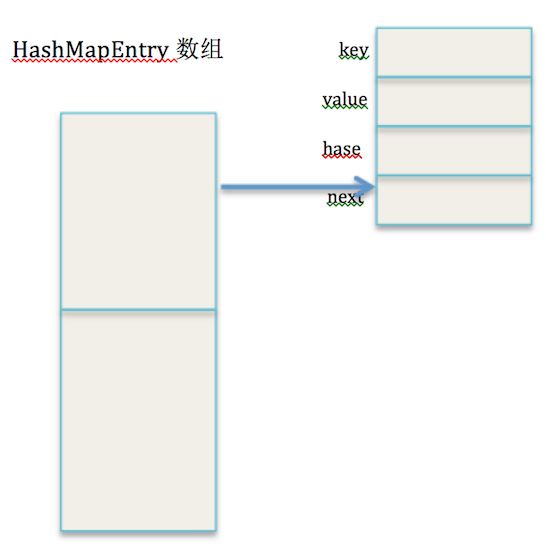
void addNewEntry(K key, V value, int hash, int index) {
table[index] = new HashMapEntry<K, V>(key, value, hash, table[index]);
}假如在index位置第一次添加一个实体,如图所示:
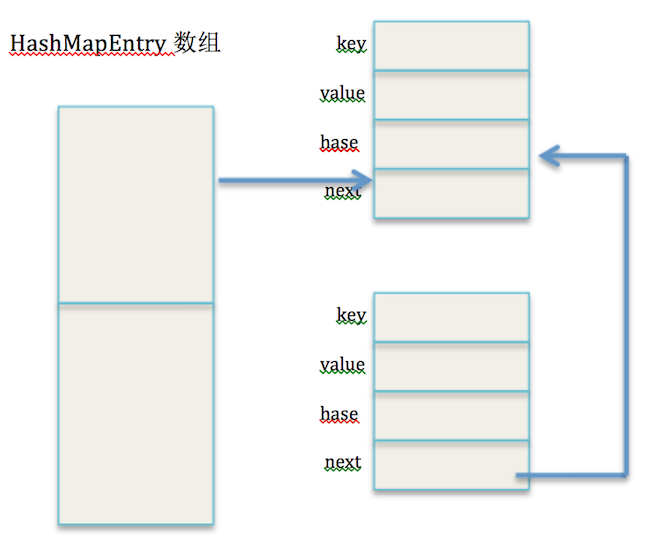
第二次在index位置添加一个实体,分为下面几步:
new HashMapEntry<K, V>(key, value, hash, table[index]);1、在构造函数中会将table[index]赋值给next引用,这样next也会引用到上一个实体对象,效果如下图所示:
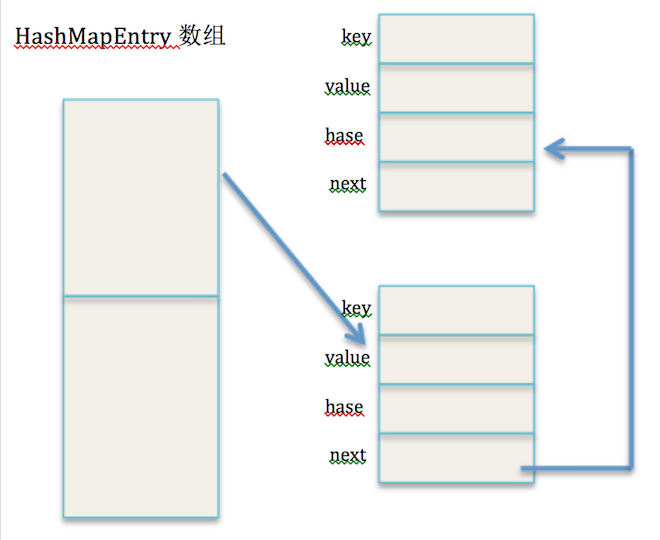
table[index] = new HashMapEntry<K, V>(key, value, hash, table[index])2、把新创建的实体对象赋值给table[index],这样table[index]引用到新创建的这个实体,效果如下图所示:
当进行了很多次插入操作之后,效果图如下所示:
二、get操作
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null) {
HashMapEntry<K, V> e = entryForNullKey;
return e == null ? null : e.value;
}
// Doug Lea's supplemental secondaryHash function (inlined).
// Replace with Collections.secondaryHash when the VM is fast enough (http://b/8290590).
int hash = key.hashCode();
hash ^= (hash >>> 20) ^ (hash >>> 12);
hash ^= (hash >>> 7) ^ (hash >>> 4);
HashMapEntry<K, V>[] tab = table;
for (HashMapEntry<K, V> e = tab[hash & (tab.length - 1)];
e != null; e = e.next) {
K eKey = e.key;
if (eKey == key || (e.hash == hash && key.equals(eKey))) {
return e.value;
}
}
return null;
}把上面的弄懂之后,这个get操作就比较好理解了。
从上面我们指定,对于键值key为null的实体,它被单独存放在entryForNullKey中,所以:
1、当key == null
直接就可以获取entryForNullKey中的value值。
2、当key != null
得到key的hash值,然后通过hash找到对应的索引index,这样就可以在数组中找到找到对应的链表表头,进行遍历查找,找到之后,返回它的value值就可以。
三、remove操作
@Override public V remove(Object key) {
if (key == null) {
return removeNullKey();
}
int hash = secondaryHash(key);
HashMapEntry<K, V>[] tab = table;
int index = hash & (tab.length - 1);
for (HashMapEntry<K, V> e = tab[index], prev = null;
e != null; prev = e, e = e.next) {
if (e.hash == hash && key.equals(e.key)) {
if (prev == null) {
tab[index] = e.next;
} else {
prev.next = e.next;
}
modCount++;
size--;
postRemove(e);
return e.value;
}
}
return null;
}同样分两种情况:
1、key == null
这个时候它会执行removeNullKey,我们来看看这个函数:
private V removeNullKey() {
HashMapEntry<K, V> e = entryForNullKey;
if (e == null) {
return null;
}
entryForNullKey = null;
modCount++;
size--;
postRemove(e);
return e.value;
}很简单,它直接把entryForNullKey置位了null.
2、key != null
它执行的就是链表的删除操作。
四、遍历操作
首先我们给出一种遍历方式:
Map map = new HashMap();
Iterator it = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) it.next();
Object key = entry.getKey();
Object val = entry.getValue();
}下面来从源码看看它的过程:
首先我们来看看map.entrySet();
public Set<Entry<K, V>> entrySet() {
Set<Entry<K, V>> es = entrySet;
return (es != null) ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySet());
}
如果entrySet存在,就直接返回这个对象,否则就创建一个EntrySet对象,它是HashMap里面的一个内部类。
我们来看看EntrySet的iterator函数:
public Iterator<V> iterator() {
return newValueIterator();
}
Iterator<Entry<K, V>> newEntryIterator() {
return new EntryIterator();
}它创建了一个EntryIterator对象。
private final class EntryIterator extends HashIterator
implements Iterator<Entry<K, V>> {
public Entry<K, V> next() { return nextEntry(); }
}可以看到它里面只有一个next函数,我们现在来看看它的父类HashIterator的构造函数:
private abstract class HashIterator {
int nextIndex;
HashMapEntry<K, V> nextEntry = entryForNullKey;
HashMapEntry<K, V> lastEntryReturned;
int expectedModCount = modCount;
//在这个构造函数里面得到数组里面的第一个非空的值
HashIterator() {
if (nextEntry == null) {
HashMapEntry<K, V>[] tab = table;
HashMapEntry<K, V> next = null;
while (next == null && nextIndex < tab.length) {
next = tab[nextIndex++];
}
nextEntry = next;
}
}
}下面我们看看EntryIterator里面的next函数,它里面执行的是nextEntry函数:
HashMapEntry<K, V> nextEntry() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
if (nextEntry == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
// 一项一项的遍历链表,如果链表遍历完毕,next就为null,它就会去找下一个非空的数组项
HashMapEntry<K, V> entryToReturn = nextEntry;
HashMapEntry<K, V>[] tab = table;
HashMapEntry<K, V> next = entryToReturn.next;
while (next == null && nextIndex < tab.length) {
next = tab[nextIndex++];
}
nextEntry = next;
return lastEntryReturned = entryToReturn;
}下面来看看hasNext函数:
public boolean hasNext() {
return nextEntry != null;
}
这个很简单,就是看nextEntry是否为空。






















 3184
3184

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








