Kakuro Extension
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 1268 Accepted Submission(s): 439
Special Judge
Problem Description
If you solved problem like this, forget it.Because you need to use a completely different algorithm to solve the following one.
Kakuro puzzle is played on a grid of "black" and "white" cells. Apart from the top row and leftmost column which are entirely black, the grid has some amount of white cells which form "runs" and some amount of black cells. "Run" is a vertical or horizontal maximal one-lined block of adjacent white cells. Each row and column of the puzzle can contain more than one "run". Every white cell belongs to exactly two runs — one horizontal and one vertical run. Each horizontal "run" always has a number in the black half-cell to its immediate left, and each vertical "run" always has a number in the black half-cell immediately above it. These numbers are located in "black" cells and are called "clues".The rules of the puzzle are simple:
1.place a single digit from 1 to 9 in each "white" cell
2.for all runs, the sum of all digits in a "run" must match the clue associated with the "run"
Given the grid, your task is to find a solution for the puzzle.

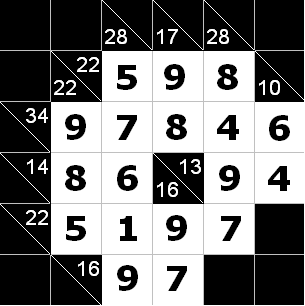
Picture of the first sample input Picture of the first sample output
Kakuro puzzle is played on a grid of "black" and "white" cells. Apart from the top row and leftmost column which are entirely black, the grid has some amount of white cells which form "runs" and some amount of black cells. "Run" is a vertical or horizontal maximal one-lined block of adjacent white cells. Each row and column of the puzzle can contain more than one "run". Every white cell belongs to exactly two runs — one horizontal and one vertical run. Each horizontal "run" always has a number in the black half-cell to its immediate left, and each vertical "run" always has a number in the black half-cell immediately above it. These numbers are located in "black" cells and are called "clues".The rules of the puzzle are simple:
1.place a single digit from 1 to 9 in each "white" cell
2.for all runs, the sum of all digits in a "run" must match the clue associated with the "run"
Given the grid, your task is to find a solution for the puzzle.


Picture of the first sample input Picture of the first sample output
Input
The first line of input contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n,m ≤ 100) — the number of rows and columns correspondingly. Each of the next n lines contains descriptions of m cells. Each cell description is one of the following 7-character strings:
.......— "white" cell;
XXXXXXX— "black" cell with no clues;
AAA\BBB— "black" cell with one or two clues. AAA is either a 3-digit clue for the corresponding vertical run, or XXX if there is no associated vertical run. BBB is either a 3-digit clue for the corresponding horizontal run, or XXX if there is no associated horizontal run.
The first row and the first column of the grid will never have any white cells. The given grid will have at least one "white" cell.It is guaranteed that the given puzzle has at least one solution.
.......— "white" cell;
XXXXXXX— "black" cell with no clues;
AAA\BBB— "black" cell with one or two clues. AAA is either a 3-digit clue for the corresponding vertical run, or XXX if there is no associated vertical run. BBB is either a 3-digit clue for the corresponding horizontal run, or XXX if there is no associated horizontal run.
The first row and the first column of the grid will never have any white cells. The given grid will have at least one "white" cell.It is guaranteed that the given puzzle has at least one solution.
Output
Print n lines to the output with m cells in each line. For every "black" cell print '_' (underscore), for every "white" cell print the corresponding digit from the solution. Delimit cells with a single space, so that each row consists of 2m-1 characters.If there are many solutions, you may output any of them.
Sample Input
6 6 XXXXXXX XXXXXXX 028\XXX 017\XXX 028\XXX XXXXXXX XXXXXXX 022\022 ....... ....... ....... 010\XXX XXX\034 ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... XXX\014 ....... ....... 016\013 ....... ....... XXX\022 ....... ....... ....... ....... XXXXXXX XXXXXXX XXX\016 ....... ....... XXXXXXX XXXXXXX 5 8 XXXXXXX 001\XXX 020\XXX 027\XXX 021\XXX 028\XXX 014\XXX 024\XXX XXX\035 ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... XXXXXXX 007\034 ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... XXX\043 ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... XXX\030 ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... ....... XXXXXXX
Sample Output
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 5 8 9 _ _ 7 6 9 8 4 _ 6 8 _ 7 6 _ 9 2 7 4 _ _ _ 7 9 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 1 9 9 1 1 8 6 _ _ 1 7 7 9 1 9 _ 1 3 9 9 9 3 9 _ 6 7 2 4 9 2 _
Author
NotOnlySuccess@HDU
Source
Recommend
一个数等于若干个数的和,可以看做一条入流分解为若干条出流,入流量等于总的出流量。每个格子(i,j)可以由行和列两个坐标确定,所以要在建立行的点和列的点,代表i行的点向代表j列的点连接一条边(容量范围【1,9】)就是代表(i,j)这个格子。黑格子的总和,可以分表表示为流入行点的总流量和跟流出列点的总流量和。某些行(列)可能有多个约束总和,我们可以将每个总和都看做单独一行(列),所以实际的行数和列数并不一定等于原图的。还要记录每个格子对应那一条边,最后流过那条边的总流量就是要填的数字。
每个格子范围是[1,9]的流量,这样的上下界不方便处理,可以统一都减去1变成[0,8]的范围,最后答案再加回1.这样就没有下界需要处理了。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int maxn =20005;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
struct Edge
{
int v,cap,nxt;
};
int first[maxn],tot;
Edge edge[200*maxn];
int n,m;
int S,T;
void addedge(int u, int v, int cap)
{
edge[tot]=Edge{v,cap,first[u]};
first[u]=tot++;
edge[tot]=Edge{u,0, first[v]};
first[v]=tot++;
}
struct Val{
int fir,sec;
int emp;
};
Val mp[200][200];
int r[200][200],c[200][200],bel[200][200];
int row[10000],col[10000];
Val turn(char s[8])
{
Val ret;
if(s[0]=='X' || s[0]=='.') ret.fir=-1;
else{
int tmp=0;
for(int i=0; i<3; i++){
tmp=tmp*10+s[i]-'0';
}
ret.fir=tmp;
}
if(s[4]=='X'||s[4]=='.') ret.sec=-1;
else{
int tmp=0;
for(int i=0; i<3; i++){
tmp=tmp*10+s[i+4]-'0';
}
ret.sec=tmp;
}
ret.emp= (s[0]=='.'&&s[4]=='.');
return ret;
}
void init()
{
tot=0;
memset(first, -1, sizeof(first));
char s[8];
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
for(int j=1; j<=m; j++){
scanf("%s", s);
mp[i][j]=turn(s);
}
}
S=0,T=n*m+1;
int rowc=1,colc=1;
int cnt=1;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
for(int j=1; j<=m; j++){
Val cur=mp[i][j];
if(cur.emp){
continue;
}
if(cur.sec!=-1){
int ed=j+1;
while(ed<=m && mp[i][ed].emp) r[i][ed]=rowc,ed++;
row[rowc]=cnt++;
addedge(0, row[rowc++], cur.sec-(ed-j-1));
}
if(cur.fir!=-1){
int ed=i+1;
while(ed<=n && mp[ed][j].emp) c[ed][j]=colc,ed++;
col[colc]=cnt++;
addedge(col[colc++], T, cur.fir-(ed-i-1));
}
}
}
memset(bel, -1, sizeof(bel));
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
for(int j=1; j<=m; j++)
if(mp[i][j].emp){
addedge(row[r[i][j]], col[c[i][j]], 8);
bel[i][j]=tot-2;
}
}
}
int d[maxn];
int que[maxn*100], head,tail;
void bfs(int s)
{
memset(d, inf, sizeof(d));
d[s]=0;
head=0;tail=-1;
que[++tail]=s;
while(tail+1!=head){
int u=que[head++];
for(int i=first[u]; i!=-1; i=edge[i].nxt){
int v=edge[i].v, c=edge[i].cap;
if(d[v]!=inf || !c) continue;
d[v]=d[u]+1;
que[++tail]=v;
}
}
}
int cur[maxn];
int dfs(int u, int T, int f)
{
if(u==T) return f;
for(int &i=cur[u]; i!=-1; i=edge[i].nxt){
int v=edge[i].v, c=edge[i].cap, r=i^1;
if(d[v]!=d[u]+1 || !c) continue;
int tmp=dfs(v, T, min(c,f));
if(tmp){
edge[i].cap-=tmp;
edge[r].cap+=tmp;
return tmp;
}
}
return 0;
}
int dinic(int S, int T)
{
int ret=0;
while(true){
bfs(S);
if(d[T]==inf) break;
for(int i=0; i<=T; i++) cur[i]=first[i];
int f=inf;
while( (f=dfs(S,T,f))>0) ret+=f;
}
return ret;
}
int ans[maxn][maxn];
int main()
{
int cas=1;
while(cin>>n>>m){
init();
int t=dinic(S, T);
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
for(int j=1; j<=m; j++){
int p=n+m+j+(i-1)*m;
if(bel[i][j]==-1){
ans[i][j]=0;
continue;
}
ans[i][j]=9-edge[bel[i][j]].cap;
}
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
for(int j=1; j<=m; j++){
if(!ans[i][j])
putchar('_');
else printf("%d", ans[i][j]);
putchar(j==m?'\n':' ');
}
}
}
return 0;
}






















 127
127

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








