组件的生命周期
一个 React Native 组件从它被 React Native 框架加载,到最终被 React Native 框架卸载,会经历一个完整的生命周期。
在这个生命周期中,我们可以定义一些生命周期函数,用来处理在特定条件下 React Native 组件将要执行的操作,比如在某个时间点读取数据等。
在iOS中UIViewController提供了(void)viewWillAppear:(BOOL)animated, - (void)viewDidLoad,(void)viewWillDisappear:(BOOL)animated等生命周期方法
在Android中Activity则提供了 onCreate(),onStart(),onResume(),onPause(),onStop(),onDestroy()等生命周期方法,这些生命周期方法展示了一个界面从创建到销毁的一生
那么在React 中组件(Component)也是有自己的生命周期方法的
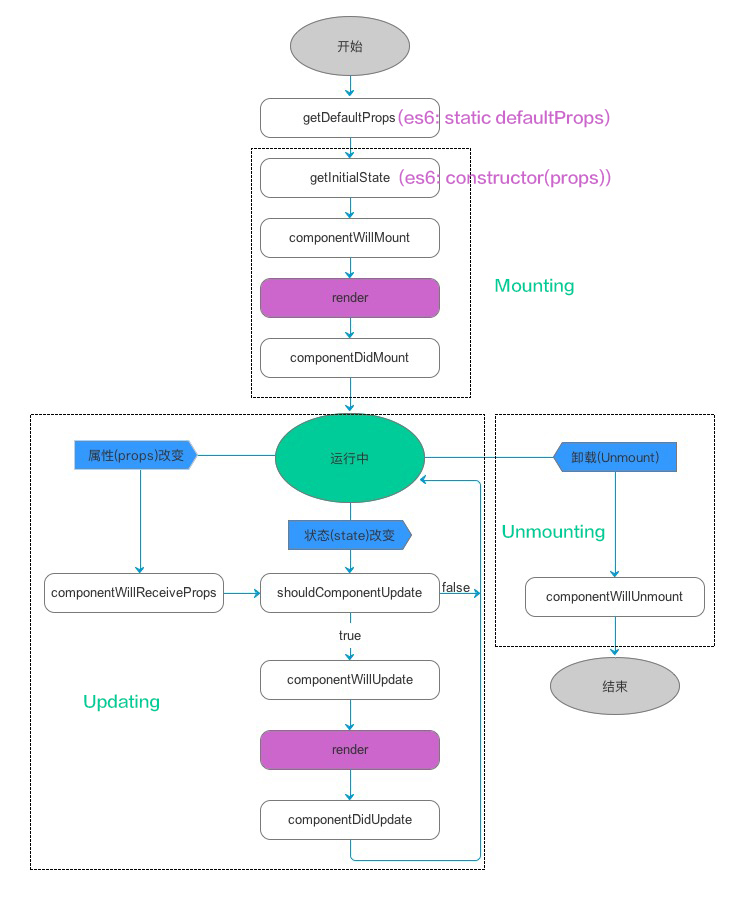
组件的生命周期分成三个状态:
- Mounting:已插入真实 DOM
- Updating:正在被重新渲染
- Unmounting:已移出真实 DOM
你会发现这些React 中组件(Component)的生命周期方法从写法上和iOS中
UIViewController的生命周期方法很像,React 为每个状态都提供了两种处理函数,will 函数在进入状态之前调用,did 函数在进入状态之后调用。
组件的生命周期的三个状态
Mounting(装载)
Mounting(装载)分为创建阶段和实例化阶段
创建阶段
- getDefaultProps():该阶段主要发生在创建组件类的时候,在这个阶段中会初始化组件的属性类型和默认属性。通常会将固定的内容放在这个过程中进行初始化和赋值。
- 在 ES6 中统一使用 static 成员来实现
static defaultProps = {
autoPlay: false,
maxLoop: 10,
};实例化阶段
该阶段主要发生在实例化组件类的时候,也就是该组件类被调用的时候触发。这个阶段会触发一系列的流程,按执行顺序如下:
getInitialState(): 在组件挂载之前调用一次。这里主要对组件的一些状态进行初始化。其实就是constructorcomponentWillMount():服务器端和客户端都只调用一次,准备加载组件,这里可以做一些业务初始化操作或者设置组件状态- render():生成页面需要的DOM结构,并且返回该结构
componentDidMount():在组件加载成功并初始化渲染执行之后立刻调用一次,仅客户端有效(服务器端不会调用),一般会将网络请求等加载数据的操作放在这里进行,保证不会出现 UI 上的错误
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Text } from 'react-native';
export default class LifecycleComponent extends Component {
// 组件初始化的时候进行调用,其实就是调用getInitialState()方法
constructor(props){
super(props)
console.log('constructor.....')
}
// 初始化渲染执行之前立刻调用
componentWillMount() {
console.log('componentWillMount.....')
}
// 初始化渲染执行之后立刻调用一次,render之后才调用
componentDidMount() {
console.log('componentDidMount......')
}
render() {
console.log('render......')
return <Text>你好我在学习RN</Text>
}
}
Updating (更新)
该阶段主要发生在用户操作之后或者父组件有更新的时候,此时会根据用户的操作行为进行相应的页面结构的调整。这个阶段也会触发一系列的流程,按执行顺序如下:
- componentWillReceiveProps(object nextProps) 在组件接收到新的 props 的时候调用。在初始化渲染的时候,该方法不会调用。用此函数可以作为 react 在 prop 传入之后, render() 渲染之前更新 state 。老的 props 可以通过 this.props 获取到。在该函数中调用 this.setState() 将不会引起第二次渲染。
- shouldComponentUpdate(object nextProps, object nextState): 在接收到新的 props 或者 state,将要渲染之前调用。该方法在初始化渲染的时候不会调用,在使用 forceUpdate 方法的时候也不会。如果确定新的 props 和 state 不会导致组件更新,则此处应该 返回 false(也就是说该方法用来拦截新的 props 或 state,然后根据事先设定好的判断逻辑,做出最后要不要更新组件的决定)
- componentWillUpdate(object nextProps, object nextState):在接收到新的 props 或者 state 之前立刻调用。在初始化渲染的时候该方法不会被调用。使用该方法做一些更新之前的准备工作。你不能在该方法中使用 this.setState()。如果需要更新 state 来响应某个 prop 的改变,请使用
componentWillReceiveProps(当上面的方法拦截返回 true 的时候,就可以在该方法中做一些更新之前的操作) - render:根据一系列的 diff 算法,生成需要更新的虚拟 DOM 数据。(注意:在 render 中最好只做数据和模板的组合,不应进行 state 等逻辑的修改,这样组件结构会更加清晰)
- componentDidUpdate(object prevProps, object prevState): 在组件的更新已经同步到 DOM 中之后立刻被调用。该方法不会在初始化渲染的时候调用。使用该方法可以在组件更新之后操作 DOM 元素。
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Text } from 'react-native';
export default class LifecycleComponent extends Component {
constructor(props){
super(props)
this.state = {
count: 0
}
}
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps, nextContext) {
console.log('componentWillReceiveProps...............')
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState, nextContext) {
console.log('shouldComponentUpdate...............')
return true
}
componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState, nextContext) {
console.log('componentWillUpdate...............')
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
console.log('componentDidUpdate...............')
}
render() {
console.log('render...............')
return <Text onPress={() => {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count+1
})
}}>你好我在学习RN,学习次数:{this.state.count}</Text>
}
}

Unmounting(移除)
该阶段主要在组件消亡的时候触发。
- componentWillUnmount:在组件从 DOM 中移除的时候立刻被调用。在该方法中执行任何必要的清理,比如无效的定时器,或者清除在 componentDidMount 中创建的 DOM 元素
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Text } from 'react-native';
export default class LifecycleComponent extends Component {
constructor(props){
super(props)
this.state = {
count: 0
}
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('componentWillUnmount........')
}
render() {
console.log('render...............')
return <Text onPress={() => {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count+1
})
}}>你好我在学习RN,学习次数:{this.state.count}</Text>
}
}
在App.js中通过点击将上面这个组件引入或者移除的时候就会触发componentWillUnmount方法
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Text, View } from 'react-native';
import LifecycleComponent from './LifecycleComponent';
export default class HelloWorldApp extends Component {
constructor(props){
super(props)
this.state = ({
remove: false
})
}
render() {
var view = this.state.remove ? null : <LifecycleComponent />
var text = this.state.remove ? '让他显示' : '干掉他'
return (
<View style={{ flex: 1, justifyContent: "center", alignItems: "center" }}>
<Text onPress={() => {
this.setState({
remove: !this.remove
})
}}> {text} </Text>
{view}
</View>
);
}
}
生命周期函数详细介绍
constructor
函数原型:constructor(props)
基本介绍:
- 它是组件的构造函数。它的第一个语句必须是 super(props)。
- 构造函数将在组件被加载前最先调用,并且仅调用一次。
常见用途:构造函数最大的作用,就是在这里定义状态机变量
componentWillMount
函数原型:componentWillMount()
基本介绍:
- 在组件的生命周期中,这个函数只会被执行一次。
- 这个函数无参数并且不需要任何返回值。
- 它在初始渲染(render 函数被 React Native 框架调用执行)前被执行,当它执行完后, render 函数会马上被 React Native 框架调用执行。注意:如果在这个函数里调用 setstate 函数改变了某些状态机变量的值, React Native 框架不会执行渲染操作,而是等待这个函数执行完成后再执行初始渲染。
- 如果子组件也有 componentWillMount 函数,它会在父组件的 componentWillMount 函数之后被调用。
常见用途:如果我们需要从本地存储中读取数据用于显示,那么在这个函数里进行读取是一个很好的时机。
render
函数原型:render()
基本介绍:
- render 是一个组件必须有的方法,用于界面渲染。
- 这个函数无参数,返回 JSX 或者其他组件来构成 DOM。注意:只能返回一个顶级元素。
componentDidMount
函数原型:componentDidMount()
基本介绍
- 在组件的生命周期中,这个函数只会被执行一次。
- 这个函数无参数并且不需要任何返回值。
- 它在初始渲染执行完成后会马上被调用。在组件生命周期的这个时间点之后,开发者可以通过子组件的引用来访问、操作任何子组件。
- 如果子组件也有 componentDidMount 函数,它会在父组件的 componentDidMount 函数之前被调用。
常见用途:如果 React Native 应用需要在程序启动并显示初始界面后从网络侧获取数据,那么把从网络侧获取数据的代码放在这个函数里是一个不错的选择。
componentWillReceiveProps
函数原型:componentWillReceiveProps()
基本介绍
- 组件的初始渲染执行完成后,当组件接收到新的 props 时,这个函数将被调用。
- 这个函数不需要返回值。接收一个 object 参数, object 里是新的 props。
- 如果新的 props 会导致界面重新渲染,这个函数将在渲染前被执行。在这个函数中,老的 props 可以通过 this.props 访问,新的 props 在传入的 object 中。
- 如果在这个函数中通过调用 this.setState 函数改变某些状态机变量的值, React Native 框架不会执行对这些状态机变量改变的渲染,而是等 componentWillReceiveProps 函数执行完成后一起渲染。
- 当 React Native 初次被渲染时,componentWillReceiveProps 函数并不会被触发,这种机制是故意设计的
shouldComponentUpdate
函数原型:boolean shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState)
基本介绍:
- 组件的初始渲染执行完成后,当组件接收到新的 state 或者 props 时这个函数将被调用。
- 该函数接收两个 object 参数,其中第一个是新的 props,第二个是新的 state。
- 该函数需要返回一个布尔值,告诉 React Native 框架针对这次改变,是否需要重新渲染本组件。默认返回 true。如果此函数返回 false,React Native 将不会重新渲染本组件,相应的,该组件的 componentWillUpdate 和 componentDidUpdate 函数也不会被调用。
常见用途:
- 这个函数常常用来阻止不必要的重新渲染,提高 React Native 应用程序性能。
- 比如我们可以在该函数中比较新老版本的 state 和 props,判断是否需要进行重新渲染。下面是一个简单的使用样例:
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
if(this.state.inputedNum.length < 3) return false;
return true;
}
componentWillUpdate
函数原型:componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState)
基本介绍:
- 组件的初始渲染执行完成后, React Native 框架在重新渲染该组件前会调用这个函数。
- 该函数不需要返回值,接收两个 object 参数,其中第一个是新的 props,第二个是新的 state。
- 我们可以在这个函数中为即将发生的重新渲染做一些准备工作,但不能在这个函数中通过 this.setState 再次改变状态机变量的值。如果需要改变,则在 componentWillReceiveProps 函数中进行改变。
componentDidUpdate
函数原型:componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState)
基本介绍:
- 组件的初始渲染执行完成后,React Native 框架在重新渲染该组件完成后会调用这个函数。
- 该函数不需要返回值,接收两个 object 参数,其中第一个是渲染前的 props,第二个是渲染前的 state。
componentWillUnmount
函数原型:componentWillUnmount()
基本介绍:
- 在组件被卸载前,这个函数将被执行。
- 这个函数没有参数,也没不需要返回值。
常见用途:
如果组件申请了某些资源或者订阅了某些消息,那么需要在这个函数中释放资源,取消订阅。
总体代码示例
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import {
AppRegistry,
StyleSheet,
TextInput,
View,
Text,
Clipboard
} from 'react-native';
export default class Main extends Component {
//构造函数
constructor(props) {
super(props);
console.log("constructor");
//初始化状态值
this.state = {message: "欢迎访问 hangge.com"}
}
//准备加载组件
componentWillMount() {
console.log("componentWillMount");
}
//渲染界面
render() {
console.log("render");
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text style={styles.info}>
{this.state.message}
</Text>
</View>
);
}
//组件加载成功并渲染出来
componentDidMount() {
console.log("componentDidMount");
}
//组件接收到新的 props 时触发
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) {
console.log("componentWillReceiveProps");
}
//决定是否需要更新组件
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
console.log("shouldComponentUpdate");
}
//组件重新渲染前会调用
componentWillUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
console.log("componentWillUpdate");
}
//组件重新渲染后会调用
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
console.log("componentDidUpdate");
}
//组件被卸载前会调用
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log("componentWillUnmount");
}
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container:{
flex:1,
marginTop:40,
alignItems:'center',
},
info:{
fontSize:20,
},
});
AppRegistry.registerComponent('HelloWorld', () => Main);






















 308
308











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








