Spring的AOP逐层深入——采用注解完成AOP(七)
这篇我们使用注解方式来实现一个AOP,我们先看一下项目的目录。
我们采用的是JDK代理,所以首先将接口和实现类代码附上:
package com.tgb.spring;
public interface UserManager {
public void addUser(String userName,String password);
public void delUser(int userId);
public String findUserById(int userId);
public void modifyUser(int userId,String userName,String password);
} package com.tgb.spring;
public class UserManagerImpl implements UserManager {
@Override
public void addUser(String userName, String password) {
System.out.println("----UserManagerImpl.add()----");
}
@Override
public void delUser(int userId) {
System.out.println("----UserManagerImpl.delUser()----");
}
@Override
public String findUserById(int userId) {
System.out.println("----UserManagerImpl.findUserById()----");
if(userId <= 0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("该用户不存在");
}
return "jiuqiyuliang";
}
@Override
public void modifyUser(int userId, String userName, String password) {
System.out.println("----UserManagerImpl.modifyUser()----");
}
} 上面代码跟我们平时写的一样,关键看我们的切面类,同理,切面类可以换成安全性检测以及日志管理等等:
package com.tgb.spring;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
@Aspect
public class AspectJAdvice {
/**
* Pointcut
* 定义Pointcut,Pointcut的名称为aspectjMethod(),此方法没有返回值和参数
* 该方法就是一个标识,不进行调用
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* find*(..))")
private void aspectjMethod(){};
/**
* Before
* 在核心业务执行前执行,不能阻止核心业务的调用。
* @param joinPoint
*/
@Before("aspectjMethod()")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("-----doBefore.invoke-----");
System.out.println(" 此处意在执行核心业务逻辑前,做一些安全性的判断等等");
System.out.println(" 可通过joinPoint来获取所需要的内容");
System.out.println("-----End of doBefore()------");
}
/**
* Around
* 手动控制调用核心业务逻辑,以及调用前和调用后的处理,
*
* 注意:当核心业务抛异常后,立即退出,转向AfterAdvice
* 执行完AfterAdvice,再转到ThrowingAdvice
* @param pjp
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Around(value = "aspectjMethod()")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("-----doAround.invoke-----");
System.out.println(" 此处可以做类似于Before的事情");
//调用核心逻辑
Object retVal = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println(" 此处可以做类似于After的事情");
System.out.println("-----End of doAround()------");
return retVal;
}
/**
* After
* 核心业务逻辑退出后(包括正常执行结束和异常退出),执行此Advice
* @param joinPoint
*/
@After(value = "aspectjMethod()")
public void doAfter(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("-----doAfter.invoke-----");
System.out.println(" 此处意在执行核心业务逻辑之后,做一些日志记录操作等等");
System.out.println(" 可通过joinPoint来获取所需要的内容");
System.out.println("-----End of doAfter()------");
}
/**
* AfterReturning
* 核心业务逻辑调用正常退出后,不管是否有返回值,正常退出后,均执行此Advice
* @param joinPoint
*/
@AfterReturning(value = "aspectjMethod()", returning = "retVal")
public void doReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint, String retVal) {
System.out.println("-----doReturn().invoke-----");
System.out.println("Return Value: " + retVal);
System.out.println(" 此处可以对返回值做进一步处理");
System.out.println(" 可通过joinPoint来获取所需要的内容");
System.out.println("-----End of doReturn()------");
}
/**
* 核心业务逻辑调用异常退出后,执行此Advice,处理错误信息
*
* 注意:执行顺序在Around Advice之后
* @param joinPoint
* @param ex
*/
@AfterThrowing(value = "aspectjMethod()", throwing = "ex")
public void doThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception ex) {
System.out.println("-----doThrowing().invoke-----");
System.out.println(" 错误信息:"+ex.getMessage());
System.out.println(" 此处意在执行核心业务逻辑出错时,捕获异常,并可做一些日志记录操作等等");
System.out.println(" 可通过joinPoint来获取所需要的内容");
System.out.println("-----End of doThrowing()------");
}
} 我们配置完切面类之后,还需要将Spring的IOC和AOP结合:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.1.xsd">
<!-- 启用Spring对基于@AspectJ aspects的配置支持 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
<bean id="userManager" class="com.tgb.spring.UserManagerImpl"></bean>
<bean id="aspectJAdvice" class="com.tgb.spring.AspectJAdvice"></bean>
</beans> 所有都完成之后,最重要的一步就是编写客户端,进行测试,看是否和我们预想的结果一致。
package com.tgb.spring;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BeanFactory factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserManager userManager = (UserManager) factory.getBean("userManager");
//可以查找张三
userManager.findUserById(1);
System.out.println("=====我==是==分==割==线=====");
try {
// 查不到数据,会抛异常,异常会被AfterThrowingAdvice捕获
userManager.findUserById(0);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
}
}
} 运行结果如图:

正常运行,无异常抛出(一)
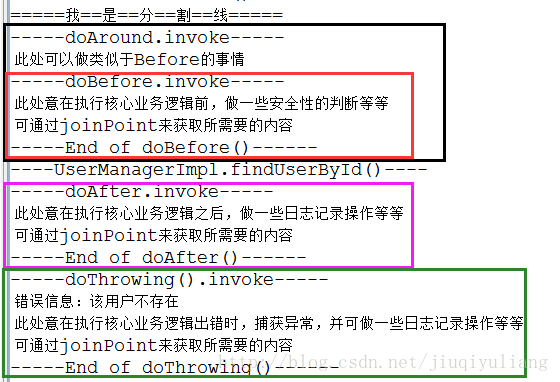
不正常运行,有异常抛出(二)
上面两张图的目的为了给大家描述Advice五种类型的运行顺序,让大家对他们有一个更加清晰的认识。
使用注解方式可以很好的帮助我们理解AOP的原理,如果对AOP的原理不是特别清晰,可以看一下上篇博文的图。下面我们采用xml方式再实现一遍AOP。

























 363
363

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








