android中常见布局:
- RelativeLayout相对布局
- AbsoluteLayout绝对布局
- LinearLayout线性布局
- TableLayout表格布局
- FrameLayout帧布局
注意:布局尽可能不要嵌套太深,嵌套越深越慢
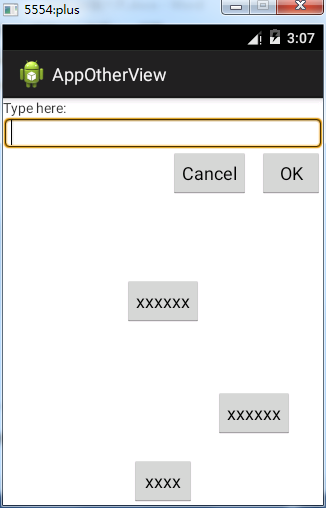
1. RelativeLayout相对布局
RelativeLayout按照各子元素之间的位置关系完成布局。注意在指定位置关系时,引用的ID必须在引用之前,先被定义,否则将出现异常。
RelativeLayout是Android五大布局结构中最灵活的一种布局结构,比较适合一些复杂界面的布局。推荐开发时使用相对布局。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/label"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Type here:"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/entry"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:drawable/editbox_background"
android:layout_below="@id/label"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/ok"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/entry"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dip"
android:text="OK" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/ok"
android:layout_alignTop="@id/ok"
android:text="Cancel" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/b1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:text="xxxx" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_above="@id/b1"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/b1"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dp"
android:text="xxxxxx" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="xxxxxx" />
</RelativeLayout>
运行效果:
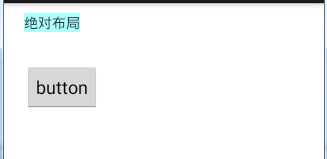
2. AbsoluteLayout绝对布局
android:layout_x和android:layout_y属性用于描述该子元素的坐标位置。
在此布局中的子元素可以相互重叠。在实际开发中,通常不采用此布局格式,因为它的界面代码过于刚性,以至于有可能不能很好的适配各种终端。该类已经过期,不推荐使用了。
<AbsoluteLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="20dp"
android:layout_y="10dp"
android:background="#AAFFFF"
android:text="绝对布局" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn"
android:layout_x="20dp"
android:layout_y="60dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="button" />
</AbsoluteLayout>
运行效果:
3. LinearLayout线性布局
这种布局比较常用,有水平线性布局(一个元素占一列)和垂直线性布局(一个元素占一行)。
LinearLayout按照垂直或者水平的顺序依次排列子元素,每一个子元素都位于前一个元素之后。LinearLayout中的子元素属性android:layout_weight生效,它用于描述该子元素在剩余空间中占有的大小比例。加入一行只有一个文本框,那么它的默认值就为0,如果一行中有两个等长的文本框,那么他们的android:layout_weight值可以是同为1。如果一行中有两个不等长的文本框,那么他们的android:layout_weight值分别为1和2,那么第一个文本框将占据剩余空间的三分之二,第二个文本框将占据剩余空间中的三分之一。android:layout_weight遵循数值越小,重要度越高的原则。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_result"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#E8F2FE"
android:editable="false"
android:enabled="false"
android:gravity="right|top"
android:lines="6"
android:text=""
android:textColor="#0000ff" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:padding="0dp" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_ce"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="CE" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_back"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_weight="3"
android:text="BACK" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
运行效果:

4. TableLayout表格布局
适用于N行N列的布局格式。一个TableLayout由许多TableRow组成,一个TableRow代表一行。
TableRow是LinearLayout的子类,TablelLayout并不需要明确地声明包含多少行、多少列,有几个TableRow就有几行,TableRow中有几个组件就有几列, TableRow也是容器,因此可以向TableRow里面添加其他组件,每添加一个组件该表格就增加一列。在表格布局中,列的宽度由该列中最宽的单元格决定,整个表格布局的宽度取决于父容器的宽度(默认是占满父容器本身)。
常用属性:
android:stretchColumns=“0,2” 拉伸第0列和第2列
android:shrinkColumns=“1” 收缩第1列
android:layout_column=“1” 组件位于第1列
android:layout_span=“2” 组件占据2列
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:stretchColumns="0,1">
<!-- 允许被拉伸第0列、第1列,默认从第0列开始 -->
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_column="1"
android:text="Open..."
android:padding="3dp" />
<TextView
android:text="Ctrl-O"
android:gravity="right"
android:padding="3dp" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_column="1"
android:text="Save As..."
android:padding="3dp" />
<TextView
android:text="Ctrl-Shift-S"
android:gravity="right"
android:padding="3dp" />
</TableRow>
<View
android:layout_height="2dp"
android:background="#FF909090" />
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:text="X"
android:padding="3dp" />
<TextView
android:text="Import..."
android:padding="3dp" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:text="xxxxx"
android:padding="3dp"
android:layout_span="2"
android:gravity="right"
android:background="#FFFF00"/>
<TextView
android:layout_column="2"
android:text="Quit"
android:gravity="right"
android:padding="3dp" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
运行效果:
5. FrameLayout帧布局
帧布局是从屏幕的左上角(0,0)坐标开始布局,多个组件层叠排列,第一个添加的组件放到最底层,最后添加到框架中的视图显示在最上面。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="#00BFFF"
android:text="aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:background="#FFC0CB"
android:text="bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#FFFF00"
android:text="ccccc"/>
</FrameLayout>
运行效果:
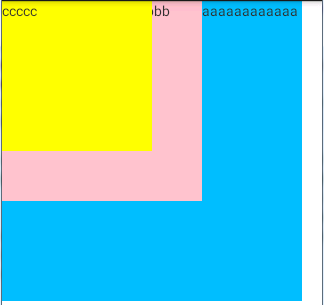
说明:从图中可以看出最上层的控件会遮盖它下面的控件。























 323
323











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








