Java 8新特性之一Stream的官方描述:
Classes in the new
java.util.streampackage provide a Stream API to support functional-style operations on streams of elements.The Stream API is integrated into the Collections API, which enables bulk operations on collections, such as sequential or parallel map-reduce transformations.
Stream是一组用来处理数组、集合的API。
Java 8为什么引入函数式编程呢?简单说为了简洁,效率。
- 函数式编程写出的代码简洁且意图明确,基本告别繁琐的for循环
- 多核友好,函数式编程编写并行执行程序简单,调用一下parallel()方法就好
那么,使用Stream API怎么个简洁法呢?我们先来看一下Stream API给我们提供了哪些方法,然后实际操作一下,看看使用上有是不是真的很爽。
Stream API主要方法介绍
- long
count()
Returns the count of elements in this stream.
返回stream中的元素个数
- Stream
distinct()
Returns a stream consisting of the distinct elements (according to Object.equals(Object)) of this stream.
返回由该流的不同元素(根据 Object.equals(Object) )组成的流。(也就是去重后组成的新的stream)
- Stream
filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate)
Returns a stream consisting of the elements of this stream that match the given predicate.
返回由与此给定谓词匹配的此流的元素组成的流。
- Optional
findAny()
Returns an Optional describing some element of the stream, or an empty Optional if the stream is empty.
返回描述流的一些元素的Optional如果流为空,则返回一个空的Optional 。
- Optional
findFirst()
Returns an Optional describing the first element of this stream, or an empty Optional if the stream is empty.
返回描述此流的第一个元素的可选项,如果流为空,则返回空的可选项。
- void
forEach(Consumer<? super T> action)
Performs an action for each element of this stream.
对该流的每个元素执行操作。
- static Stream
generate(Supplier s)
Returns an infinite sequential unordered stream where each element is generated by the provided Supplier.
返回无限顺序无序流,其中每个元素由参数Supplier生成 。 (
生成的是一个无限多元素的流,所以需要其他方法来限制一下)
- static Stream
iterate(T seed, UnaryOperator f)
Returns an infinite sequential ordered Stream produced by iterative application of a function f to an initial element seed, producing a Stream consisting of seed, f(seed), f(f(seed)), etc.
返回有序无限连续 Stream由函数的迭代应用产生 f至初始元素 seed ,产生 Stream包括 seed , f(seed) , f(f(seed)) ,等
- Stream
limit(long maxSize)
Returns a stream consisting of the elements of this stream, truncated to be no longer than maxSize in length.
返回由此流的元素组成的流,截短长度不能超过 maxSize 。
- IntStream
mapToInt(ToIntFunction<? super T> mapper)
Returns an IntStream consisting of the results of applying the given function to the elements of this stream.
返回一个 IntStream ,其中包含将给定函数应用于此流的元素的结果。 (类似的还有
map,mapToDouble,mapToLong)
- Optional
max(Comparator<? super T> comparator)
Returns the maximum element of this stream according to the provided Comparator.
根据提供的 Comparator返回此流的最大元素。 (类似的还有
min)
- static Stream
of(T t)
Returns a sequential Stream containing a single element.
返回包含单个元素的顺序 Stream 。(类似的还有
of(T... values))
- Stream
skip(long n)
Returns a stream consisting of the remaining elements of this stream after discarding the first n elements of the stream.
在丢弃流的第一个 n元素后,返回由该流的 n元素组成的流。
- Stream
peek(Consumer<? super T> action)
Returns a stream consisting of the elements of this stream, additionally performing the provided action on each element as elements are consumed from the resulting stream.
返回由该流的元素组成的流,另外在从生成的流中消耗元素时对每个元素执行提供的操作。
- Stream
sorted()
Returns a stream consisting of the elements of this stream, sorted according to natural order.
返回由此流的元素组成的流,根据自然顺序排序。
- Stream
sorted(Comparator<? super T> comparator)
Returns a stream consisting of the elements of this stream, sorted according to the provided Comparator.
返回由该流的元素组成的流,根据提供的 Comparator进行排序。
- Object[]
toArray()
Returns an array containing the elements of this stream.
返回一个包含此流的元素的数组。
玩一玩Stream API
关于Stream API,一般情况下是结合
Lambda表达式来使用的。我们来看一下具体怎么操作。
Stream的创建
- 通过数组创建一个Stream
Arrays.stream(array)
/**
* 通过数组创建Stream
*/
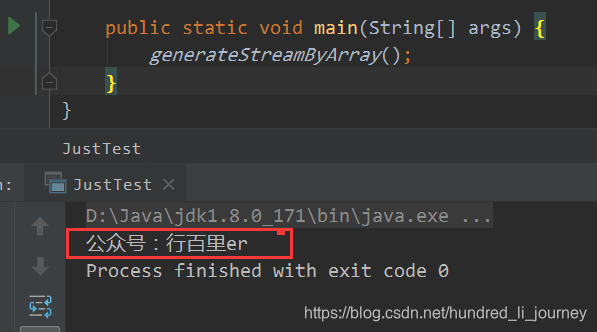
static void generateStreamByArray(){
String[] str = {"公众号:", "行", "百", "里", "er"};
Stream<String> arrStream = Arrays.stream(str);
arrStream.forEach(System.out::print);
}
可以通过stream.forEach(System.out::print)这种Lambda表达式的方式打印Stream中的每个元素,运行结果:
- 通过集合创建一个Stream
list.stream()
static void generateStreamByList(){
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("公众号:", "行", "百", "里", "er");
list.stream().forEach(System.out::print);
//list.forEach(System.out::print);
}
- 通过generate方法创建Stream
Stream.generate(Supplier<T> s)
generate方法的参数是一个Supplier接口,这个接口的描述是:

说明Supplier是一个函数式接口,只有一个方法get(),因此我们可以用Lambda表达式来搞:
//Stream.generate
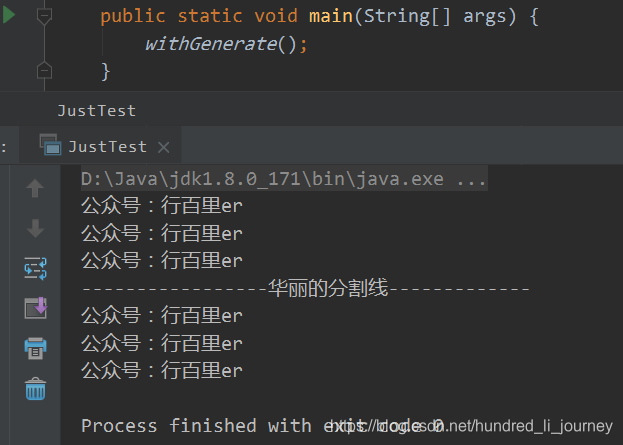
static void withGenerate() {
Supplier<String> s = () -> "公众号:行百里er";
//用limit方法限制生成的个数
Stream.generate(s).limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-----------------华丽的分割线-------------");
Stream<String> stream = Stream.generate(() -> "公众号:行百里er");
//用limit方法限制生成的个数
stream.limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);
}
- 通过iterate方法创建Stream
Stream.iterate(seed, UnaryOperator<T>)
通过调用Stream的iterate方法也能生成一个stream,该方法有2个参数,第一个参数是种子,专门为第二个参数UnaryOperator提供初始值,那么UnaryOperator是个什么鬼呢?来看描述:

它的源码:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface UnaryOperator<T> extends Function<T, T> {
/**
* Returns a unary operator that always returns its input argument.
*
* @param <T> the type of the input and output of the operator
* @return a unary operator that always returns its input argument
*/
static <T> UnaryOperator<T> identity() {
return t -> t;
}
}
说明UnaryOperator也是函数式的,表示对单个操作数执行的操作,该操作产生与其操作数类型相同的结果。这是专门针对操作数和对操作结果类型相同这一类的。
比如我要产生一个stream,给定种子元素为2,产生3个元素,每个元素是是前一个元素的2倍,可以这样来:
//Stream.iterate(seed, UnaryOperator)
static void withIterate() {
UnaryOperator<Integer> u = i -> i * 2;
Stream.iterate(2, u).limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("---------华丽的分割线-----------");
//等价于下面这种写法
Stream.iterate(2, i -> i * 2).limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);
}
- 其他方式创建Stream
字符串的chars()方法也能生成stream,不过是IntStream:
static void others() {
IntStream chars = "公众号:行百里er".chars();
//打印的是int类型
chars.forEach(System.out::println);
}
运行结果:

要想按照字符输出,做一下强制转换就行了:
static void others() {
IntStream chars = "公众号:行百里er".chars();
//打印的是int类型
//chars.forEach(System.out::println);
//可以将int转成char输出
chars.forEach((c) -> System.out.print((char) c));
}

还有这种操作?
输出一个集合中所有的偶数
一句话搞定:
Arrays.asList(11, 2, 3, 4, 5, 19, 8, 18, 23).stream().filter((x) -> x % 2 == 0).forEach(System.out::println);
filter方法的参数Predicate<T>也是函数式接口,代表一个谓词(boolean-valued函数)的一个参数。
计算一个集合中所有偶数的和
int sum = Arrays.asList(11, 2, 3, 4, 5, 19, 8, 18, 23).stream().filter((x) -> x % 2 == 0).mapToInt(x -> x).sum();
这里要注意的是,filter出偶数之后要转成IntStream,才有sum()方法,用mapToInt(ToIntFunction<? super T> mapper)转即可。
参数ToIntFunction:表示产生值为int的结果的函数。这是专门为int- production转换提供的方法。
输出集合中的最大值、最小值
用max,min方法:
List<Integer> intList = Arrays.asList(11, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
//输出最大值
Optional<Integer> maxOptional = intList.stream().max(Comparator.comparingInt(x -> x));
Integer max = maxOptional.get();
System.out.println("max:" + max);
//输出最小值
System.out.println(intList.stream().min(Comparator.comparingInt(x -> x)).get());
不用max,min也能实现,我们可以先排好序:
//输出最小值,先排好序,sorted不传参默认升序排序,找到第一个就是最小的了
System.out.println(intList.stream().sorted().findFirst().get());
//按照降序排序,再找第一个就是最大的了
System.out.println(intList.stream().sorted((x, y) -> y - x).findFirst().get());
集合去重
使用distinct方法或转成Set:
//去重
Stream<Integer> distinctStream = Arrays.asList(1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 5, 3).stream().distinct();
distinctStream.forEach(System.out::println);
//去重方法二:转成Set
Set<Integer> collect = Arrays.asList(1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 5, 3).stream().collect(Collectors.toSet());
collect.forEach(System.out::println);
输出一个区域内的数字
比如,构造一个集合,里面存放1 ~ 50数字,要求输出21 ~ 30这10个数。
可以使用iterate方法构造stream,用limit限制为50个,然后调用skip方法跳过前20个,这时会返回一个从21 ~ 50的stream,我们只需在limit一下就可以满足只有20 ~ 30的stream了:
//输出21~30
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.iterate(1, x -> x + 1).limit(50).skip(20).limit(10);
stream.forEach(System.out::println);
小结
- Stream 不是集合元素,它不是数据结构并不保存数据,它是有关算法和计算的,它更像一个高级版本的 Iterator。
原始版本的 Iterator,只能显式地一个一个遍历元素并对其执行某些操作;
高级版本的 Stream,只要给出需要对其包含的元素执行什么操作,比如 “过滤掉长度大于 10 的字符串”、“获取每个字符串的首字母”等,Stream 会隐式地在内部进行遍历,做出相应的数据转换。
- Stream不支持索引访问
- Stream很容易生成数组或集合
- Stream支持过滤,查找,转换,汇总,聚合等操作
想变强就要坚持!





















 863
863











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








